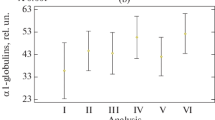
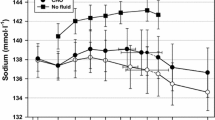
Abstract
The objective of this investigation was to evaluate the effect of a daily intake of fluid and salt supplementation (FSS) on blood plasma trace elements concentrations in physically healthy volunteers after exposure to 364 d of hypokinesia (decreased number of steps per day). The studies were performed after exposure to 364 d of Hypokinesia (HK) on 30 long-distance runners of volunteers who had a VO2 max 67 mL/kg/min and were ranging in the age of 19–24 yrs. Prior to their exposure to HK all volunteers were on an average of 10,000 steps/d. For the simulation of the hypokinetic effect the volunteers were kept under an average of 3000 steps/d. All volunteers were divided into three equal groups. The first group of volunteers subjected to HK and received daily FSS (water 26 mL/kg body wt and sodium chloride 0.16 g/kg body wt.), the second groups of volunteers submitted only to HK, and the third group of volunteers underwent a normal ambulatory life and served as control. The content of manganese, calcium, magnesium, iron, lead, copper, tin, nickel, zinc and cobalamine were determined in blood plasma of volunteers. By the end of the hypokinetic period the blood plasma concentration of microelements increased significantly in the hypokinetic subjects (second group), whereas in the hyperhydrated subjects (first group) decreased. It was concluded that prolonged restriction of motor activity induced significant increases in blood trace elements concentrations whereas daily hyperhydration had a normalizing effect on their concentration in blood plasma. This indicates that daily hyperhydration may be used to normalize blood plasma concentrations of microelements in physically healthy volunteers subjected to prolonged restriction of motor activity.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yu. M. Bala and V. M. Lifshits, inTrace Elements in the Practice of Internal Medicine, Meditsina, Voronezh, Russia, 1973, p. 240.
L. P. Bushmeleva, inBiological Role of Trace Elements and Electrolytes, and Their Significance in Medicine, Meditsina, Tomsk, Russia, 1977, p. 255.
R. P. Volosyanko, T. I. Bida and L. I. Syrovaya, inBiological Role and Clinical Use of Trace Elements in Medicine, Meditsina, Riga, Latvia, 1975, p. 218.
M. G. Kolomiytseva, and R. D. Gabovich, inMicrolements in Medicine, Moscow, Russia, 1970, p. 230.
Y. G. Zorbas, Y. F. Federenko, and K. A. Naexu, Bone mineralization and blood trace elements after hypokinesia and physical exercise with fluid and salt supplementation.Model. Simul. Control 32(7): 47–69 (1992).
Y. G. Zorbas, Y. F. Federenko, and K. A. Naexu, Effect of daily hyperhydrated of fluid-electrolyte, excretion in healthy subjects during prolonged restriction of motor activity.Model Simul. Control 32(4): 22–35 (1992).
Y. G. Zorbas, I. O. Matveyev, and R. K. Tantareli, Rehydration effect in increasing men's tolerance to maximum physical loads after hypokinesia and chronic rehydration.Int. J. Rehab. Res. 12(6), 156–161 (1989).
J. Durin and M. Rahaman. The assessment of the amount of fat in the human body from measurements of skinfold thickness.Br. J. Nutr. 21, 681–689 (1967).
Y. G. Zorbas, Y. F. Federenko, and M. N. Togawa, Renal excretion of water in men under hypokinesia and physical exercise with fluid and salt supplementation.Acta Astronautica 21(8), 599–605 (1990).
Y. G. Zorbas, V. R. Bobylev, and A. N. Marketi, Physical exercise in preserving men's body mass under hypokinesia.Int. J. Rehab. Res. 12(3), 326–330 (1989).
I. V. Fedorov, inMetabolism Under Hypokinetic Conditions, Izdatel'stvo Nauka, Moscow, Russia, 1982, p. 254.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zorbas, Y.G., Federenko, Y.F. & Naexu, K.A. Plasma trace elements concentrations in trained subjects after exposure to hypokinesia and daily hyperhydration. Biol Trace Elem Res 40, 71–82 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02916822
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02916822