Abstract
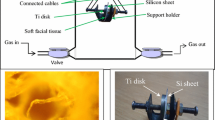
A newly developed ionization gauge using carbon nanotube (CNT) field emission effect has been designed and manufactured. The fabricated ionization gauge is of a triode type, consisting of a cathode (carbon nanotube field emitter arrays), a grid and a collector. The principle involved here is that for a constant number of electrons available for ionization emitted from carbon nanotube arrays by the grid potential, a constant fraction of gas will be ionized and the number of ions collected in the collector will be proportional to the number of gas molecules in the chamber traversed by the electrons. Due to the excellent field emission characteristics of CNT, it is possible to make a cost effective cold cathode ionization gauge. A screen-printing method has been used to make the CNT cathode. The glass grid with Cr deposited by E-beam has been put on the cathode with a gap of 200 μm between the two electrodes. Using the voltage applied to the grid, the electrons emitted from the carbon nanotube ionize gas molecules in the chamber and the ionized molecules are gathered in the collector. At this time, the collector voltage is maintained at a lower level than that of the grid voltage to obtain a large ionization ratio. The current detected in the collector is proportional to the pressure in the chamber. The ionization characteristics are dependent on the gas and the voltage applied to the grid and collector. In this paper we have shown the various metrological characteristics of the simple pressure sensor utilizing carbon nanotube.
Similar content being viewed by others

References
Choi, W. B., Chung, D. S., Kang, J. H., Kim, H. Y., Jin, Y. W., Han, I. T., Lee, Y. H., Jung, J. E., Lee, N. S., Park, G. S. and Kim, J. M., 1999, “Fully Sealed, High-brightness Carbon-nanotube Field-emission Display,”Applied Physics Letter, Vol. 75, No. 20, pp. 3129–3131.
Guilorn, M. A., Melechko, A. V., Merkulov, V. I., Hensley, D. K., Simpson, M. L. and Lowndes, D. H., 2002, “Self-aligned Gated Field Emission Devices using Single Carbon Nanofiber Cathodes,”Applied Physics Letter, Vol. 81, No. 19, pp. 3660–3662.
Harland G. Tompkins, “Vacuum Gauging and Control,” AVS monograph series, Chap. 4.
Modi, A., Koratkar, N., Lass, E., Wei, B. and Ajayan, P. M., 2003, “Miniaturized Gas Ionization Sensors using Carbon Nanotubes,”Letters to Nature, Vol. 424, pp. 171–174.
Pirio, G., Legagneux, P., Pribat, D., Teo, K. B. K., Chhowalla, M., Amaratunga, G. A. J. and Milne, W. I., 2002, “Fabrication and Electrical Characteristics of Carbon Nanotube Field Emission Microcathodes with an Integrated Gate Electrode,”Nanotechnology, Vol. 13, pp. 1–4.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Choi, IM., Woo, SY. & Kim, BS. Ionization gauge by carbon nanotube field emission. J Mech Sci Technol 19, 2127–2132 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02916508
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02916508