Abstract
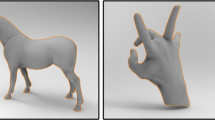
In this study, a complete 3D surface reconstruction method is proposed based on the concept that the vertices of surface model can be completely matched to the unstructured point cloud. In order to generate the initial mesh model from the point cloud, the mesh subdivision of bounding box and shrink-wrapping algorithm are introduced. The control mesh model for well representing the topology of point cloud is derived from the initial mesh model by using the mesh simplification technique based on the original QEM algorithm, and the parametric surface model for approximately representing the geometry of point cloud is derived by applying the local subdivision surface fitting scheme on the control mesh model. And, to reconstruct the complete matching surface model, the insertion of isolated points on the parametric surface model and the mesh optimization are carried out. Especially, the fast 3D surface reconstruction is realized by introducing the voxel-based nearest-point search algorithm, and the simulation results reveal the availability of the proposed surface reconstruction method.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bernardini, F., Mittelman, J., Rushmeier, H., Silva, C. and Taubin, G., 1999, “The Ball-Pivoting Algorithm for Surface Reconstruction,”IEEE Transaction on Visualization and Computer Graphics, Vol. 5, No. 4, pp. 349–359.
Boissonnant, J. D., 1984, “Geometric Structures for Three-Dimensional Shape Reconstruction,”A CM Transactions on Graphics, Vol. 3, No. 4, pp. 266–289.
Cho, J. H. and Song, Samuel M. H., 2003, “Three-Dimensional Shape Reconstruction from Images by Shape-from-Silhouette Technique and Iterative Triangulation,”KSME International Journal, Vol. 17, No. 11, pp. 1665–1673.
Gopi, M., Krisnan, S. and Silva, C., 2000, “Surface Reconstruction Based on Lower Dimensional Localized Delaunay Triangulation,”Computer Graphics Forum, Vol. 19, No. 3, pp. 467–478.
Hoppe, H., DeRose., T., Duchamp, T., McDonald, J. and Stuetzle, W., 1992, “Surface Reconstruction from Unorganized Points,”Proceedings of SIG-GRAPH, pp. 71–78.
Jeong, W. K. and Kim, C. H., 2002, “Direct Reconstruction of Displaced Subdivision Surface from Unorganized Points,”Graphical Models, Vol. 64, No. 2, pp. 78–93.
Lee, A., Moreton, H. and Hoppe, H., 2000, “Displaced Subdivision Surfaces,”Proceedings of SIGGRAPH, pp. 85–94.
Leif, P. K., Jens, V., Ulf, L. and Seidel, H. P., 1999, “A Shrink Wrapping Approach to Remeshing Polygonal Surface,”Computer Graphics Forum, Vol. 18, No. 3, pp. 119–130.
Michael, G. and Paul, S. H., 1997, “Surface Simplification Using Quadric Error Metrics,”Proceedings of SIGGRAPH, pp. 209–216.
Mülayim, A. Y., Ulas, Y. and Atalay, V., 2003, “Silhouette-based 3D Model Reconstruction from Multiple Images,”IEEE Trans. on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics — Part B, Vol. 33, No. 4, pp. 582–591.
Suzuki., H., Takeuchi., S. and Kanai., T., 1999, “Subdivision Surface Fitting to a Range of Points,”Proceedings of SIGGRAPH, pp. 158–167.
Taubin, G., 1995, “A Signal Processing Approach to Fair Surface Design,”Proceedings of SIGGRAPH, pp. 351–358.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, SI., Li, R. Complete 3D surface reconstruction from unstructured point cloud. J Mech Sci Technol 20, 2034–2042 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02916320
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02916320