Abstract
Aim To compare the efficacy and functional durability of the American Medical Systems 800 (AMS 800) artificial urinary sphincter (AUS) device for patients with neurogenic and non-neurogenic incontinence.
Methods From 1985 to 2000, 38 patients underwent implantation of an AMS 800 AUS at our institution. Thirty of these patients had complete records and follow-up data available. The mean follow-up for these two groups of patients was six years. Seventeen devices (57%) were implanted for non-neurogenic indications including incontinence after prostatectomy or hysterectomy. Thirteen devices (43%) were implanted for neurogenic conditions including spina bifida, spinal cord injury or severe pelvic trauma. The primary end point measured was continence. Secondary end points included mechanical and non-mechanical device failure, re-operation and complication rates between the two groups.
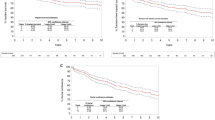
Results In the neurogenic group, only two patients (15%) have their original device in situ without revisions. Only three patients (23%) in this group are entirely dry. In contrast, seven patients (41%) in the non-neurogenic group are completely dry with their original device in situ. A further four (23%) are entirely dry after device revision or replacement surgery. The rates of mechanical failure were not statistically different between the two groups. The rate of non-mechanical failure (NMF) was statistically greater in the neurogenic group in comparison to that in the non-neurogenic group (p<0.05).
Conclusions Insertion of an AMS 800 artificial sphincter remains a durable means of regaining urinary continence. Patients who are incontinent as a result of an underlying neurological deficit should be counselled that they might have a higher risk of non-mechanical device failure, requirement for re-operation and that their overall long-term continence rates may be poor.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Walsh PC, Retik AB, Stamey TA et al. Campbell’s Urology, 6th ed. Philadelphia: WB Saunders Co, 1992.
Scott FB, Bradley WE, Timm GW. Treatment of urinary incontinence by implantable prosthetic sphincter.Urology 1973; 1 (3): 2–259.
Elliott DS, Barrett DM. Mayo Clinic long-term analysis of the functional durability of the AMS 800 artificial urinary sphincter: a review of 323 cases.J Uro J 1998; 159: 1206–8.
Kowalczyk JJ, Spicer DL, Mulcahy JJ. Erosion rate of the double cuff AMS800 artificial urinary sphincter: long-term follow up.J Urol 1996; 156: 1300–01.
Bradley C Leibovich. Use of the artificial urinary sphincter in men and women.World J Urol 1997 15: 216–319.
Marks JL, Light JK. Management of urinary incontinence after prostatectomy.J Urol 1989; 142: 1459.
Fishman JJ, Shabshigh R, Scott FB. Experience with the artificial urinary sphincter model AS800 in 148 patients.J Urol 1989; 141: 307.
Malloy TR, Wein AJ. Surgical success with AMS 800 GU sphincter for male incontinence.Urology 1989; 33: 274.
Montague DK. The artificial urinary sphincter: experience with 166 consecutive patients.J Urol 1992; 147: 380–2.
Simeoni L et al. Artificial urinary sphincter implantation for neurogenic bladder: a multi-institutional children.Br J Urol 1996; 78: 287–93.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Murphy, S., Rea, D., O’Mahony, J. et al. A comparison of the functional durability of the AMS 800 artificial urinary sphincter between cases with and without an underlying neurogenic aetiology. Ir J Med Sci 172, 136–138 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02914499
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02914499