Abstract
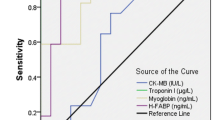
Early identification of patients with acute myocardial infarction is of prime importance due to the associated very high mortality. Only 22% of the patients presenting at emergency cardiology care with chest pain have coronary disease. A number of biochemical tests like CKMB and Troponin-T/I have been introduced for early detection of the coronary syndrome (ACS). Ischemia modified albumin (IMA) has been recently introduced as a marker of myocardial ischemia. We estimated serum IMA in four sequential samples from 25 patients admitted to ICCU. Twenty five healthy volunteers formed the control group from which the normal range was derived. IMA was significantly raised in ischemia patients than in controls as well as compared to the patients who did not have cardiac ischemia. IMA demonstrated good discrimination between the ischemic and the non-ischemic patients with an Odds Ratio of 16.9 (6.29–46.87) than CKMB which showed an Odds Ratio of 2.07 (1.18–6.08). Sensitivity and specificity of IMA for the detection of ACS was 78.0% and 82.7% compared to 58.0% and 60.0%, respectively for the CK-MB assay. The area under the ROC curve of IMA for ischemic v/s non-ischemic patients was 0.834. IMA appears to be developing into a new and very potent marker, of cardiac ischemia.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Graff, L.G., Dallara, J. and Ross, M.A. (1997). Impact on the care of the emergency department chest pain patient from the chest pain evaluation registry (CHEPER) study. Am. J. Cardiol. 80, 563–569.
Kontos, M.C. and Jesse, R.L. (2000) Evaluation of the emergency department chest pain patient. Am. J. Cardiol. 85, 32B-39B.
Gomez, M.A., Anderson, J.L., Karagounis, L.A., Muhlestein, J.B. and Mooers, F.B. (1996). An emergency medicine based protocol for rapidly ruling out myocardial ischemia reduces hospital time and expense. Results of randomized study (ROMO). J. Am Coll. Caridol. 28. 25–33.
Bar-Or, D., Lau, E., Rao, N., Bampos, N., Winkler, J.V. and Curtis, C.G. (1999). Reduction in the cobalt binding capacity of human albumin with myocardial ischemia. Ann. Emerg. Med. 34, 566.
Bar-Or, D., Lau, E., Rao, N., Bampos, N. and Winkler, J.V. (2000). A novel assay for cobalt albumin binding and its potential as a marker for myocardial ischemia—a preliminary report. J. Emerg. Med. 19, 311–315.
Bar-Or, D., Winkler, J.V., VanBenthuysen, K., Harris, L., Lau, E. and Hetzel, F.W. (2001). Reduced albumin cobalt binding with transient myocardial ischemia after elective percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty: A preliminary comparison to creatine Kinase-MB, myoglobin and Troponin I. Am. Heart. J. 141, 985–991.
Auxter, Sue (2003). Cardiac ischemia testing: a new era in chest pain evaluation. Clin Lab. News 29, 1–3.
Committee on enzymes of the Scandinavian Society for Clinical Chemistry and Clinical Physiology (1979). Recommended method for the determination of creatinine kinase. Scand. J. Clin. Lab. Invest. 39, 1–5
Neumeier, D., Prellwitz, W. and Wurzburg, U. (1976) Determination of creatine kinase isoenzyme MB activity in serum using immunological inhibition of creatine kinase M subunit activity—Activity kinetics and diagnostic significance in Myocardial infarction. Clin. Chim. Acta. 73, 445–451.
IFCC method for LDH (1994). Estimation of lactate dehydrogenase activity. J. Clin. Chem. Biochem. 30, 639–642.
Fagan, G.J., Hollie, Wayment, Deborah, L. Morris and Peter, Crosby (2002). The albumin cobalt binding test: analytical performance of a new automated chemistry assay for the detection of ischemia modified albumin (IMA). J. Clin. Leg. Assay 25, 178–187.
Laussac, J.P. and Sarkar, B. (1984). Characterization of the copper (II) and nickel (II) —transport site of human serum albumin. Studies of copper (II) and nickel (II) binding to peptide 1–24 of human serum albumin by 13C and 1H NMR spectroscopy. Biochemistry 23, 2832–2838.
Sinha, M.K., Roy, D., Gaze, D.C., Collinson, P.C. and Kaski, J.C. (2004). Role of “Ischemia modified Albumin”, a new biochemical marker of Myocardial ischemia, in the early diagnosis of acute coronary syndrome [in Process Citation]. Emerg. Med. J. 21, 29–34.
Christenson, R.H., Duh, S.H., Sanhal, W.R., Wu, A.H.B., Holtman, V., Painter, P., Branham, E., Apple, F.S., Murakami, M.A. and Morris, D. (2001). Characteristics of an albumin cobalt binding test for the assessment of acute coronary syndrome patients: a multicenter study. Clin. Chem. 47, 464–470.
Bhagwan, N.v., Ernest, M. Lai, Rios, P.A., Yang, J., Ortega-Lopez, A.M. and Shinoda, H. (2003). Evaluation of human serum albumin cobalt binding assay for the assessment of myocardial ischemia and myocardial infarction. Clin. Chem. 49, 581–585.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chawla, R., Goyal, N., Calton, R. et al. Ischemia modified albumin: A novel marker for acute coronary syndrome. Indian J Clin Biochem 21, 77–82 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02913070
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02913070