Abstract
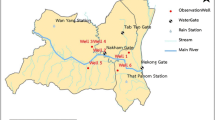
This study investigates the application of time series analysis for evaluating groundwater discharge rates into a subway system in Seoul, Korea. A time series of daily precipitation and groundwater discharge rates observed at three subway stations— Gireum, Garibong and Sadang station—in 2001 were used for the time series modeling. Correlation analyses show that groundwater discharge rates are auto-correlated and correlated with precipitation. Based on these correlation analyses, the transfer function noise (TFN) models including the Box-Jenkins (BJ) autoregressive moving average (ARMA) model were applied to evaluate the groundwater discharge rates into a subway tunnel when precipitation data is given. As a result, the TFN model is acceptable at all three stations. Though the analyses are limited to regularly observed time series data and a linear groundwater system, this study provides a practical application of time series models for groundwater discharge management in the subway system. In particular, for the Seoul subway system where the rapid deterioration of water resources occurs, the estimation of groundwater discharge rates is very important for an efficient management of the water resources in the urban environment.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bierkens, M.F.P., Knotters, M. and van Geer, F.C., 1999, Calibration of transfer function-noise models to sparsely or irregularly observed time series. Water Resources Research, 35, 1741–1750.
Box, G.E.P., Jenkins, G.M. and Reinsel, G.C., 1994, Time series analysis: Forecasting and control. Prentice Hall, New Jersey, 598 p.
Forth, R.A. and Thorley, C.B.B., 1997, Construction dewatering in Hong Kong. Groundwater in the Urban Environment, 1, 231–236.
Houston, J.F.T., 1983, Groundwater system simulation by time series techniques. Ground Water, 21, 301–310.
Kim, Y.-Y. and Lee, K.-K., 2002, Construction and interpretation of a hydrogeological database for the Seoul goundwater system. Geosciences Journal, 6, 319–330.
Kim, Y.-Y. and Lee, K.-K., 2003, Disturbance of groundwater table by subway construction in the Seoul area, Korea, Geosciences Journal, 6, 319–330.
Knotters, M. and De Gooijer, J.G., 1999, TARSO modeling of water table depths. Water Resources Research, 35, 695–705.
Kool, J.B. and van Genuchten, M.Th. 1992, HYDRUS: One-dimensional variably saturated flow and transport model, including hysteresis and root water uptake (version 3.4). IGWMC, Golden, CO.
Korea Institute of Construction Technology (KICT), 2001, Research on applications and treatments of discharged groundwater, 204 p.
Lee, J.Y. and Lee, K.K., 2000, Use of hydrologic time series data for identification recharge mechanism in a fractured bedrock aquifer system. Journal of Hydrology, 229, 190–201.
Ministry of construction and transportation, 2000, Groundwater observation annual report. 857 p.
Peng, M.H., Liu, J.K. and Shih, T.Y., 2000, Groundwater level forecasting with time series analysis. In proceedings of ACRS 2000: GIS development. http://www.gisdevelopment.net/aars/acrs/2000/ts2/water0005a.shtml.
Salas, J.D. and Obeysekera, J.T.B., 1982, ARMA model identification of hydrological time series. Water Resources Research, 29, 2011–2026.
Tankersley, C.D., Graham, W.D. and Hatfield, K., 1993, Comparison of univariate and transfer function noise models of groundwater fluctuations. Water Resources Research, 29, 2011–2026.
Yi, M.J., 2001, Transfer function-noise modeling of irregularly observed groundwater heads with precipitation date, Korea. M.S. thesis, Seoul National University, Seoul, 58 p.
Van Geer, F.C. and Zuur, A.F., 1997, An extension of Box-Jenkins transfer/noise models for spatial interpolation of groundwater head series. Journal of Hydrology, 192, 65–80.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, SJ., Hyun, Y. & Lee, KK. Time series modeling for evaluation of groundwater discharge rates into an urban subway system. Geosci J 9, 15–22 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02910550
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02910550