Abstract
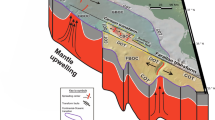
Single and multichannel reflection profiles from the Ulleung Basin and the eastern Korean continental margin reveal that the acoustic basement is cut by two major N-S trending fault systems: (1) the Hupo and Yangsan faults in the continental shelf and the southeastern Korean Peninsula and (2) the Ulleung fault along the western margin of the Ulleung Basin. The right-stepping Hupo-Yangsan fault system experienced coeval dextral strike-slip deformation in the Early Miocene with a lateral displacement of about 35 km. This fault movement resulted in pull-apart opening of the Pohang-Youngduk Basin. The Ulleung Fault is expressed as a steep (> 30°) and relatively smooth basement escarpment along the present base of slope. In the southwestern margin of the Ulleung Basin, the fault merges with the Tsushima Fault. This fault is interpreted as part of the western boundary fault system resulting from an extensile shear deformation during the back-are opening of the East Sea (Sea of Japan) during Early Miocen time. The fault kinematics of these fault systems supports the hypothesis that the East Sea formed as a result of pull-apart opening accompanied by a southward drift of the SW Japanese Arc. During the major opening of the Ulleung Basin, the SW Japanese Arc apparently migrated 250–300 km southward, detached from the east Asian continent. This latter block movement induced major dextral shear deformation along the Ulleung Fault which, in turn, triggered secondary shear deformation in the juxtaposed Hupo-Yangsan fault system within the rigid continental crust.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Badley, 1985. Practical Seismic Interpretation. D. Reidel Publishing Company, IHRDC, Boston, 266 p.
Barg, E, 1986. Cenozoic Geohistory of the Southwestern Margin of the Ulleung Basin, East Sea. M. S. thesis, Seoul National University, Scoul, 174 p.
Bishop, D.G., 1968, The geometric relationships of structural features associated with major strike-slip faults in New Zealand. New Zealand Journal of Geology and Geophysics, 11, 405–417.
Bong, P.Y., 1985, Palynology of the Neogene Strata in the Pohang Sedimentary Basin. Ph.D. thesis, Seoul National University, Seoul, 239 p.
Celaya, H. and McCabe, R., 1987, Kinematic model for the opening of the Sea of Japan and the bending of the Japanese islands. Geology, 15, 553–574.
Chae, B.G. and Chang, T.W., 1994, Movement history of Yangsan Fault and its related fractures at Chongha—Yongdok area, Korea. Journal of the Geological Society of Korea, 30, 379–394. (in Korean)
Chang, K.H., Woo, B.G., Lee, J.H., Park, S.O. and Yao, A., 1990, Cretaceous and Early Cenozoic stratigraphy and history of eastern Kyongsang Basin, S. Korea. Journal of the Geological Society of Korea, 26, 471–487.
Chapman, M.C. and Solomon, S.C., 1976, North American plate boundary in northeast Asia. Journal of Geophysical Research, 81, 921–930.
Chough, S.K. and Barg, E., 1987, Tectonic history of Ulleung basin margin, East Sea (Sea of Japan). Geology, 15, 45–48.
Chough, S.K. and Lee, K.E., 1992, Multi-stage volcanism in the Uleung Back-arc Basin, East Sea (Sea of Japan). The Island Arc, 1, 32–39.
Christie-Blick, N. and Biddle, K.T., 1985, Deformation and basin formation along strike-slip faults. In: Biddle, K.T., and Christie-Blick, N. (eds.), Strike-Slip Deformation, Basin Formation and Sedimentation. Society of Economic Paleontologists and Mineralogists, Special Publication, 37, 1–34.
Faure, M. and Lalevée, F., 1987, Bent structural trends of Japan: flexural-slip folding related to the Neogene opening of the Sea of Japan. Geology, 15, 49–52.
Harding, T.P., 1974, Petroleum traps associated with wrench faults. American Association of Petroleum Geologists Bulletin, 58, 1290–1304.
Harding, T.P., 1985. Seismic characteristics and identification of negative flower structures, positive flower structures, and positive structural inversion. American Association of Petroleum Geologists Bulletin, 69, 582–600.
Harding, T.P., 1990, Identification of wrench faults using subsurface structural data: criteria and pitfalls. American Association of Petroleum Geologists Bulletin, 74, 1590–1609.
Hirata, N., Tokuyama, H. and Chung, T.W., 1989, An anomalously thick layering of the crust of the Yamato Basin, southeastern Sea of Japan: the final stage of back-arc spreading. Tectonophysics, 165, 304–314.
Honza, E., Yuasa, M. and Ishibashi, K., 1978, Cored material. In: Honza, E. (ed.), Geological Investigations in the Northern Margin of the Okinawa Trough and the Western Margin of the Japan Sea. Cruise Report 10, Geological Survey of Japan, Tokyo, p. 39–42.
Huntec Ltd., 1967, Report on the offshore geophysical survey in the Pohang area, Republic of Korea. UN ECAFE/CCOP Technical Bulletin, 1, 1–12.
Hwang, I.G., 1993, Fan-Delta Systems in the Pohang Basin (Miocene), SE Korea. Ph.D. thesis, Seoul National Univer-sity, Seoul, 923 p.
Ingle, J.C., Jr., 1992, Subsidence of the Japan Sea: stratigraphic evidence from ODP sites and onshore sections. Proceedings of the Ocean Drilling Program, Scientific Results 127/128 (part 2), p. 1197–1218.
Isezaki, N., 1986. A magnetic anomaly map of the Japan Sea. Journal of Geomagnetism and Geoelectricity, 38, 403–410.
Jolivet, L. and Tamaki, K., 1992, Neogene kinematics in the Japan Sea region and volcanic activity of the Northeast Japan Arc. Proceedings of the Ocean Drilling Program, Scientific Results 127/128 (part 2), p. 1311–1331.
Jolivet, L., Shibuya, H. and Fournier, M., 1995. Paleomagnetic rotations and the Japan Sea opening. Active Margins and Marginal Basins of the Western Pacific, American Geophysical Union, p. 355-369.
Kaneoka, I., Takigami, Y., Takaoka, M., Yamashita, S. and Tamaki, K., 1992,40Ar-39Ar analysis of volcanic rocks recovered from the Japan Sea floor: constraints on the age of formation of the Japan Sea. Proceedings of the Ocean Drilling Program, Scientific Results 127/128 (part 2), p. 819–836.
Kang, P.J., 1979, Geological analysis of Landsat imagery of South Korea. Journal of the Geological Society of Korea, 15, 109–191.
Kim, B.K., 1965, The stratigraphic and paleontologic studies on the Tertiary (Miocene) of the Pohang area, Korea. Journal of Seoul National University, Science Technical Series, 15, 32–121.
Kim, C.S., 1981, Submarine Geology of Continental Margin of the East Sea, Korea. Ph.D. thesis, Seoul National University, Seoul, 81 p. (in Korean)
Kim, W.H., 1990, Significance of Early to Middle Miocene planktonic foraminiferal biostratigraphy of the E-core in the pohang basin, Korea. Journal of the Paleontological Society of Korea, 6, 144–164.
Kim, Y.H. and Lee, K., 1988. A geoelectric study on the structure of the Yangsan Fault in the south of Kyeongju, Journal of the Geological Society of Korea, 24, 47–61.
Kim, Y.H., Lee, K. and Seong, I.K., 1990, A geoelectric study on the structure of the Yangsan fault, north of Kyeongju. Journal of the Geological Society of Korea, 26, 393–403.
Kimura, G and Tamaki, K., 1986, Collision, rotation, and back-arc spreading in the region of the Okhotsk and Japan Seas. Tectonics, 5, 389–401.
Kono, M., 1986, Magnetic anomalies in the Sea of Japan: a speculation on the tectonic history. Journal of Geomagnetism and Geoelectricity, 38, 411–426
KORDI (Korea Ocean Research and Development Institute), 1992, A Geophysical Study on the Ulleung Basin, the East Sea (Sea of Japan). Research Report BSPE 00242-433-5, Korea Ocean Research and Development Institute, Ansan, 280 p.
Lallemand, S. and Jolivet, L., 1985, Japan Sea: a pull-apart basin. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 76, 375–389.
Lee, J.S., 1989, Pérologie et Relations Structurales des Volcanites Crétacé Cénozoïques de la Corée du Sud, Implications Géody Namiques sur la Marge Est-Eurasiatique. Ph.D. thesis, Université d'Orléans, Orléans, France, 349 p.
Lee, H.Y., 1994, Neogene Foraminifera Biostratigraphy of the Southern Margin of the Ulleung Basin, East Sea, Korea. Ph. D. thesis, Seoul National University, Seoul, 377 p.
Lee, H.J., Chun, S.S., yoon, S.H. and Kim, S.R., 1993, Slope stability and geotechnical properties of sediment of the southern margin of Ulleung Basin, East Sea (Sea of Japan). Marine Geology, 110, 31–45.
Ludwig, W.J., Murauchi, S. and Houtz, R.E., 1975, Sediments and structure of the Japan Sea. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 86, 651–664.
Nester, D., Mitchum, B., Meckel, L., Vosbein, M., Harris, D., Brinkman, F., Stanley, E., Loren, D., Kulha, J. and Gibson, L., 1989, Exploration and Production Evaluation Block VI-1, Ulleung Basin. Exploration Report, Exploitech Inc., Houston.
Otofuji, Y. and Matsuda, T. 1983, Paleomagnetic evidence for the clockwise rotation of southwest Japan. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 62, 349–359.
Otofuji, Y., Matsuda, T. and Nohda, S., 1985, Paleomagnetic evidence for the Miocene counter-clockwise rotation of Northeast Japan—rifting process of the Japan Arc. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 75, 265–277.
Park, C.H., Kim, H.J., Yang, C.S., Suk, B.C. and Isezaki, N., 1996, Crustal structure of the Ulleung Basin, the East Sea (Japan Sea), from gravity and ocean bottom seismometer data. Journal of the Geological Society of Korea, 32, 276–290.
Park, K.S., 1992, Geologic structure and seismic stratigraphy of the southern part of Ulleung basin. In: Chough, S.K.(ed.), Sedimentary Basins in the Korean Peninsula and Adjacent Seas. Korean Sedimentology Research Group, Special Publication, p. 40–59.
Pitman, W.C. and Andrews, J.A., 1985, Subsidence and thermal history of small pull-apart basins. In: Biddle, K.T. and Christie-Blick, N. (eds.), Strike-Slip Deformation, Basin Formation, and Sedimentation. Society of Economic Paleontologists and Mineralogists, Special Publication, 37, 45–49.
Sato, T., Baba, K., Ohguchi, T. and Takayama, T., 1991, Discovery of early Miocene calcareous nannofossils from Japan Sea side, northern Honshu, Japan, with reference to paleoenvironment in the Daijima and Nishikurosawa ages. Japan Association of Petroleum Technologists Bulletin, 56, 263–279.
Schlüter, H.V. and Chun, W.C., 1974, Seismic survey of the east coast of Korea. UN ECAFE/CCOP Technical Bulletin, 8, 1–16.
Shibata, K., Uchiumi, S. and Nakagawa, T. 1979, K−Ar age results—1. Bulletin of Geological Survey of Japan, 30, 675–686.
Shipboard Scientific Party, 1990, Introduction, Background, and Principal Results of Leg 128 of the Ocean Drilling Program, Japan Sea. Proceedings of the Ocean Drilling Programt, Initial Reports 128, p. 5–38.
Sillitoe, R.H., 1977, Metallogeny of an Andean type continental margin in South Korea: implications for opening of the Japan Sea. In: Talwani, M. and Pitman, W.C., III (eds.), Island Arcs, Deep Sea Trenches and Back Arc Basins. American Geophysical Union, Maurice Ewing Series, 1, 303–310.
Son, H.W., 1984, A study on the Subsurface in the Pohang Area by Gravity Survey. M.S. thesis, Yonsei University, Seoul, 78 p.
Sylvester, A.G., 1988, Strike-slip faults. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 100, 1666–1703.
Tamaki, K., 1988, Geological structure of the Japan Sea and its tectonic implications. Bulletin of the Geological Survey of Japan, 39, 269–365.
Tamaki, K. and Honza, E., 1985, Incipient subduction and obduction along the eastern margin of the Japan Sea. Tectonophysics, 119, 381–406.
Tamaki, K., Suyehiro, K., Allan, J., Ingle, J.C., Jr. and Pisciotto, K.A., 1992, Tectonic Synthesis and Implications of Japan Sea ODP drilling. Proceedings of Ocean Drilling Program, Scientific Results 127/128 (part 2), p. 1333–1348.
Woo, K.S. and Park, K.H., 1993. Sr isotope ages of well preserved mollusks from the Chunbuk Formation (Pohang Basin) and the Shinhyun Formation (Yangnam Basin), Korea, Journal of the Geological Society of Korea,29, 353–359.
Yoon, S.H., 1994, The Eastern Continental Margin of Korea: Seismic Stratigraphy, Geologic Structure and Tectonic Evolution. Ph.D. thesis, Seoul National University, Seoul, 235 p.
Yoon, S.H. and Chough, S.K., 1995, Regional strike slip in the eastern continental margin of Korea and its tectonic implications for the evolution of Ulleung Basin, East Sea (Sea of Japan). Geological Society of America Bulletin, 107, 83–97.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yoon, S.H., Park, S.J. & Chough, S.K. Western boundary fault systems of Ulleung Back-arc Basin: further evidence of pull-apart opening. Geosci J 1, 75–88 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02910479
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02910479