Abstract
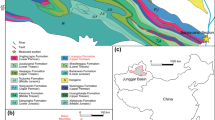
The Cretaceous (Neocomian to Aptian—Albian) Yongdong Basin is a NE-SW trending strike-slip basin (8–10×50 km2), filled with alluvial, fluvial, and lacustrine deposits. The southeastern margin of the basin includes ca. 700-m-thick siliciclastic sequence, consisting of conglomerate, (gravelly) sandstone, and reddish or dark gray mudstone. A detailed facies analysis reveals that the sequence can be represented by 13 sedimentary facies which can be organized into 3 facies associations (FA) representing three distinctive depositional environments. The FA I (stream-dominated alluvial fan) comprises decimeter- to 1-m-thick, granule-to-cobble conglomerates, horizontally stratified gravelly sandstone, and reddish mudstone, deposited by hyperconcentrated flows, stream flows, and overbank suspension fallout. The FA II (fan-delta slope) consists of decimeter- to 2-m-thick, pebble-to-boulder conglomerates with wedge or lobate geometry and decimeter- to 2.5-m-thick, (crudely) stratified (laminated), graded or massive (gravelly) sandstones. They were deposited by debris flows and turbidity currents, respectively. The FA III (prodelta/basin plain) comprises a few cm to 1.2-m-thick, horizontally stratified (laminated), massive or graded (gravelly) sandstones with wedge or sheetform geometry, and decimeter- to 1.5-m-thick mudstone and sandstone-mudstone couplet. They were deposited by high- or low-concentration turbidity currents and settling from suspended sediments in buoyant plumes. The FA I is distributed along the basin margin and passes into the FA II toward the basin center, where FA III is in gradational contact with FA II, forming a radial distributional pattern from the basin margin. These facies associations form a mass-flow-dominated, lacustrine fan-delta system (Ibawisan fan-delta system) with a vertically-/laterally-stacked, fining-upward megasequence. The Ibawisan system probably resulted from continuous faulting along the basin margin and was associated with high rate of sediment supply, and thus formed thick, coarse-grained basin margin deposits abruptly wedging out toward the basin axis. The development of Ibawisan fan-delta system is related to locally different tectonic setting within the basin, and the recognition of lacustrine fan-delta system along the southeastern basin margin is important to understand the tectonic evolution and sequential development of the Yongdong Basin through time.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen, J.R.L., 1984, Parallel lamination developed from upper-stage plane beds: a model based on the larger coherent structures of the turbulent boundary layer. Sedimentary Geology, 29, 31–66.
Allen, J.R.L. and Leeder, M.R., 1980, Criteria for the instability of upper-stage plane beds. Sedimentology, 27, 209–217.
Allen, P.A., 1981, Sediments and processes on a small streamflow dominated Devonian alluvial fan, Shetland Islands. Sedimentary Geology, 29, 31–66.
Bagnold, R.A., 1954, Experiments on a gravity-free dispersion of large, solid spheres in a Newtonian fluid under shear. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London, 225A, 49–63.
Ballance, P.F., 1984, Sheet-flow-dominated gravel fans of the non-marine Middle Cenozoic Simmler Formation, Central California. Sedimentary Geology, 38, 337–359.
Bouma, A.H., 1962. Sedimentology of Some Flysch Deposits. Elsevier, Amsterdam, 166 p.
Bowman, D., 1990, Climatically triggered Gilbert-type lacustrine fan deltas, the Dead Sea area, Israel. In: Corella, A. and Prior, D.B. (eds.), Coarse-Grained Deltas. International Association of Sedimentologists, Special Publication, 10, 273–280.
Choi, S.J., Kim, Y.B. and Kim, B.C., 1995, Stratigraphy and Paleontology of the Cretaceous Sedimentary Strata in the Yongdong Basin. Report KR-95(C)-1, Korea Institute of Geology, Mining and Materials, Taejon, 118 p.
Choi, Y.S., 1995, Structural Evolution of the Cretaceous Eumsung Basin, Korea. Ph.D. thesis, Sebul National University, Seoul, 158 p.
Chun, H.Y., Um, S.H., Choi, S-J., Kim, Y.B., Kim, B.C. and Choi, Y.S., 1993, Fossil Floral and Faunal Assemblage and Paleoenvironmental Modelling Study on the Cretaceous Sedimentary Basins Scattered in/near the Ogcheon Belt (I). Report KR-93(T)-11, Korea Institute of Geology, Mining and Materials, Taejon, 122 p.
Chun, S.S. and Chough, S.K., 1992a, Tectonic history of Cretaceous sedimentary basins in the western Korean Peninsula and Yellow Sea. In: Chough, S.K. (ed.), Sedimentary Basins in the Korean Peninsula and Adjacent Seas. Korean Sedimentology Research Group, Special Publication, p. 60–76.
Chun, S.S. and Chough, S.K., 1992b, Depositional sequences from high-concentration turbidity currents, Cretaceous Uhangri Formation (SW Korea). Sedimentary Geology, 77, 225–233.
Cole, R.B. and Stanley, R.G., 1995, Middle Tertiary extension recorded by lacustrine fan-delta deposits, Plush Ranch Basin, western transverse ranges, California. Journal of Sedimentary Research, B65, 455–468.
Collinson, J.D., 1986, Alluvial sediments. In: Reading, H.G. (ed.), Sedimentary Enironments and Facies (2nd edn.). Blackwell Scientific Publications, Oxford, p. 20–62.
Costa, J.E., 1988, Rheologic, geomorphic, and sedimentologic differentiation of water floods, hyperconcentrated flows, and debris flows. In: Baker, V.R., Kochel, R.C., and Patton, P.C. (eds.), Flood Geomorphology. John Wiley, New York, p. 113–122.
Dorsey, R.J., Umhoefer, P.J., and Renne, P.R., 1995, Rapid subsidence and stacked Gilbert-type fan deltas, Pliocene Loreto Basin, Baja California Sur, Mexico. In: Chough, S.K. and Orton, G.J. (eds.), Fan deltas: Depositional Styles and Controls. Sedimentary Geology, 98, 181–204.
Esteban, M. and Klappa, C.F., 1983, Subaerial exposure environment. In: Scholle, P.A., Bebout, D.G. and Moore, C.H. (eds.), Carbonate Depositional Environments. American Association of Petroleum Geologists, Memoir, 33, 1–54.
Ethridge, F.G. and Wescott, W.A. 1984. Tectonic setting, recognition and hydrocarbon reservoir potential of fan-delta deposits. In: Koster, E.H. and Steel, R.J. (eds.), Sedimentology of Gravels and Conglomerates. Canadian Society of Petroleum Geologists, Memoir, 10, 217–235.
Evans, J.E., 1991, Facies relationships, alluvial architecture, and paleohydrology of a Paleogene, humid-tropical alluvial-fan system: Chumstick Formation, Washington State, U.S.A. Journal of Sedimentary Petrology, 61, 732–755.
Ghibaudo, G., 1992, Subaqueous sediment gravity flow deposits: practical criteria for their field description and classification. Sedimentology, 39, 423–454.
Hampton, M.A., 1972, The role of subaqueous debris flow in generating turbidity currents. Journal of Sedimentary Petrology, 4, 775–793.
Hein, F.J. and Walker, R.G., 1977, Bar evolution and development of stratification in the gravelly, braided Kicking Horse River, British Columbia. Canadian Journal of Earth Sciences, 14, 562–570.
Holmes, A., 1965. Principles of Physical Geology (2nd edn.). Roland Press Company, New York, 1288 p.
Hong, S.H., Lee, B.J. and Kim, W.Y., 1980, Explanatory Text of the Geological Map of Muju Sheet (1∶50,000). Korea Institute of Energy and Resources, Seoul, 55 p.
Howell, D.G. and Link, M.H., 1979, Eocene conglomerate sedimentology and basin analysis, San Diegoand southern California borderland. Journal of Sedimentary Petrology, 49, 517–540.
Kazanci, N., 1990, Fan-delta sequences in the Pleistocene and Holocene Burdur Basin, Turkey: the role of basin-margin configuration in sediment entrapment and differential facies development. In: Colella, A. and Prior, D.B. (eds.), Coarse-Grained Deltas. International Association of Sedimentologists, Special Publication, 10, 185–198.
Kim, B.C., 1996, Sequential Development of Depositional Systems in a Strike-Slip Basin: Southern Part of the Cretaceous Yongdong Basin, Korea. Ph.D. thesis, Yonsei University, Seoul, 336 p.
Kim, D.H. and Lee, B.J., 1986, Geological Report of the Ch'onsan Sheet (1∶50,000). Korea Institute of Energy and Resources, Seoul, 43 p.
Kim, D.H., Chang, T.W., Kim, W.Y. and Hwang, J.H., 1978, Explanatory text of the Geological Map of Ogcheon Sheet (1∶50,000). Korea Institute of Energy and Resources, Seoul, 40 p.
Kim, H.M., 1974a. Paleocurrent analysis of the Yongdong Group, southern Korea. Journal of the Geological Society of Korea, 10, 1–24.
Kim, H.M., 1974b. Sedimentation of the Yongdong Group, southern Korea. Journal of the Geological Society of Korea, 10, 225–244.
Kim, K.B. and Hwang, J.H., 1986, Geological Report of the Yongdong Sheet (1∶50,000). Korea Institute of Energy and Resources, Seoul, 44 p.
Larsen, V. and Steel, R.J., 1978, The sedimentary history of a debris flow dominated, Devonian alluvial fan—a study of textural inversion. Sedimentology, 25, 37–59.
Lee, D.W., 1990, Sedimentation and Tectonic Evolution of the Cretaceous Yongdong Basin, Korea. Ph.D. thesis, Korea University, Seoul, 273 p.
Lee, D.W. and Paik, K.H., 1989, Sedimentological characteristics along Yongdong fault zone in Cretaceous Yongdong Basin, Korea. Journal of the Geological Society of Korea, 25, 259–272.
Lee, D.W. and Paik, K.H., 1990, Evolution of strike-slip fault-controlled Cretaceous Yongdong Basin, South Korea: signs of strike-slip tectonics during infilling. Journal of the Geological Society of Korea, 26, 257–276.
Lowe, D.R., 1979, Sediment gravity flows: their classification and some problems of application to natural flows and deposits. In: Doyle, L.J. and Pilky, O.H. (eds.), Geology of Continental Slopes. Society of Economic Paleontologists and Mineralogists, Special Publication, 27, 279–297.
Lowe, D.R., 1982, Sediment gravity flows II: depositional models with special reference to the deposits of high-density turbidity currents. Journal of Sedimentary Petrology, 52, 279–297.
Lowe, D.R., 1988, Suspended-load fallout rate as an independent variable in the analysis of current structures. Sedimentology, 35, 765–776.
Maizels, J., 1993. Lithofacies variations within sandur deposits: the role of runoff regime, flow dynamics and sediment supply characteristics. Sedimentay Geology, 85, 299–325.
Mastalerz, K., 1995, Deposits of high-density turbidity currents on fan-delta slopes: an example from the upper Visean Szczawno Formation, Intrasudetic Basin, Poland. In: Chough, S.K. and Orton, G.J. (eds.), Fan Deltas: Depositional Styles and Controls. Sedimentary Geology, 98, 121–146.
McCallum, J.E. and Robertson, A.H.F., 1995, Sedimentology of two fan-delta systems in the Pliocene—Pleistocene of the Mesaoria Basin, Cyprus. In: Chough, S.K. and Orton, G.J. (eds.), Fan Deltas: Depositional Styles and Controls. Sedimentary Geology, 98, 215–244.
Miall, A.D., 1978, Lithofacies types and vertical profile models in braided river deposits: a summary. In: Miall, A.D. (ed.), Fluvial Sedimentology. Canadian Society of Petroleum Geologists, Memoir, 5, 597–604.
Middleton, G.V. and Hampton, M.A., 1976, Subaqueous sediment transport and deposition by sediment gravity flows. In: Stanley, D.J. and Swift, D.J.P. (eds.), Marine Sediment Transport and Environmental Management. John Wiley, New York, p. 197–218.
Nemec, W., 1990, Aspects of sediment movement on steep delta slopes. In: Collela, A. and Prior, D.B. (eds.), Coarse-Grained Deltas. International Association of Sedimentologists, Special Publication, 10, 29–73.
Nemec, W. and Steel, R.J., 1984, Alluvial and coastal conglomerates: their significant features and some comments on gravelly mass-flow deposits. In: Koster, E.H. and Steel, R.J. (eds.), Sedimentology of Gravels and Conglomerates. Canadian Society of Petroleum Geologists, Memoir, 10, 1–32.
Nemec, W. and Steel, R.J., 1988. What is a fan delta and how do we recognize it? In: Nemec, W. and Steel, R.J. (eds.), Fan Deltas: Sedimentology and Tectonic Settings. Blackie, Glasgow and London, p. 2–13.
Nemec, W., Porebski, S.J. and Steel, R.J., 1980, Texture and structure of resedimented conglomerates—examples from Ksiaz Formation (Famennian—Tournaisian), southwestern Polland. Sedimentology, 27, 519–538.
Nemec, W., Steel, R.J., Porebski, S.J. and Spinnavgr, A., 1984, Domba conglomerate, Devonian, Norway: process and lateral variability in a mass flow-dominated, lacustrine fan-delta. In: Koster, E.H. and Steel, R.J. (eds.), Sedimentology of Gravels and Conglomerates. Canadian Society of Petroleum Geologists, Memoir, 10, 295–320.
Nilsen, T.H. and McLaughlin, R.J., 1985, Comparison of tectonic framework and depositional patterns of the Hornelen strike-slip basin of Norway and Ridge and Little Sulphur Creek strike-slip basins of California. Society of Econmic Paleontologists and Mineralogists, Special Publication, 37, 79–103.
Pierson, T.C. and Scott, K.M., 1985, Downstream dilution of a lahar. Transition from debris flow to hyperconcentrated streamflow. Water Resources Research, 21, 1511–1524.
Postma, G., 1984, Mass-flow conglomerates in a submarine canyon: Abrioja fan-delta, Pliocene, southeast Spain. In: Koster, E.H., and Steel, R.J. (eds.), Sedimentology of Gravels and Conglomerates. Canadian Society of Petroleum Geologists, Memoir, 10, 237–258.
Postma, G., 1986, Classification for sediment gravity-flow deposit based on flow conditions during sedimentation. Geology, 14, 291–294.
Postma, G. and Roep, T.B., 1985, Resedimented conglomerates in the bottomsets of Gilbert-type gravel deltas. Journal of Sedimentary Petrology, 55, 874–885.
Postma, G. and Cruickshank, C., 1988, Sedimentology of a late Weichselian to Holocene terraced fan delta, Varangerfjord, northern Norway. In: Nemec, W. and Steel, R.J. (eds.), Fan Deltas: Sedimentology and Tectonic Settings. Blackie, Glasgow and London, p. 144–157.
Prior, D.B. and Bornhold, B.D., 1988. Submarine morphology and processes of fjord fan deltas and related high-gradient systems: modern examples from British Columbia, In: Nemec, W. and Steel, R.J. (eds.), Fan Deltas: Sedimentology and tectonic Settings. Blackie, Glasgow and London, p. 125–143.
Prior, D.B., Wiseman, Wm.J., Jr. and Bryant, W.R., 1981a. Submarine chutes on the slopes of fjord delta. Nature, 290, 326–328.
Prior, D.B., Wiseman, Wm.J., Jr. and Gilbert, R., 1981b, Submarine slope processes on a fan delta, Howe Sound, British Columbia. Geo-Marine Letters, 1, 85–90.
Reedman, A.J. and Um, S.H., 1975, Geology of Korea, Geological and Mineralogical Institute of Korea, Seoul, 139 p.
rust, B.R. 1978, Depositional models for braided alluvium. In: Miall, A.D. (ed.), Fluvial Sedimentology. Canadian Society of Petroleum Geologists, Memoir, 5, 605–625.
Rust, B.R. and Koster, E.H. 1984, Coarse alluvial deposits. In: Walker, R.G. (ed.), Facies Models. Geoscience Canada Reprint Series, 1, 53–69.
Shimamura, S., 1925, Geologic Map of Chosen, Yongdong and Cheongsan Sheet (1∶50,000). Geological Survey of Chosen.
Shultz, A.W., 1984, Subaerial debris-flow deposition in the Upper Paleozoic Culter Formation, western Colorado. Journal of Sedimentary Petrology, 54, 759–772.
Smith, G.A., 1986, Coarse-grained nonmarine volcaniclastic sediment: terminology and depositional process. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 97, 1–10.
Smith, N.D., 1974, Sedimentology and bar formationin the upper Kicking Horse River, a braided outwash stream. Journal of Geology, 81, 205–223.
Sneh, A., 1979, Late Pleistocene fan-deltas along the Dead Sea Rift. Journal of Sedimentary Petrology, 49, 541–552.
Sohn, Y.K. and Chough, S.K., 1989, Depositional processes of Suwolbong tuff ring, Cheju Island (Korea). Sedimentology, 36, 837–855.
Son, C.M., Cheong, C.H., Lee, S.M. and Um, S.H., 1969, A study on the sedimentary environments and geological structure of Korea. Research Report of Ministry of Science and Technology (Korea). p. 25–26.
Steel, R.J., 1977, Devonian basins of western Norway—sedimentary response to tectonism and to varying tectonic context. Tectonophysics, 36, 207–224.
Steel, R.J. and Gloppen, T.G., 1980, Late Caledonian (Devonian) basin formation, western Norway: signs of strike-slip tectonics during infilling. In: Ballance, P.F. and Reading, H.G. (eds.), Sedimentation in Oblique-Slip Mobile Zones. International Association of Sedimentologists, Special Publication, 4, 79–103.
Todd, S.P., 1989, Stream-driven, high-density gravelly traction carpets: possible deposits in the Trabeg Conglomerate Formation, SW Ireland and theoretical considerations of their origin. Sedimentology, 36, 513–530.
Walker, R.G., 1975, Conglomerate: sedimentary structures and facies models. In: Harms, J.C., Southard, J.B., Spearing, D.R., and Walker, R.G. (eds.), Depositional Environments as Interpreted from Primary Sedimentary Structures and Stratification Sequences. Society of Econmic Paleontologists and Mineralogists, Short Course, 2, 133–161.
Walker, R.G., 1985, Mudstones and thin-bedded turbidites associated with the upper Cretaceous Wheeler Gorge conglomerates, California: a possible channel-levee complex. Journal of Sedimentary Petrology, 55, 279–290.
Wells, S.G. and Harvey, A.M., 1987, Sedimentologic and geomorphic variations in storm-generated alluvial fans, Howgill Fells, northwest England. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 98, 182–198.
Won, C.G. and Kim, K.T., 1969, Explanatory Text of the Geological Map of Sangju Sheet (1∶50,000). Geological Survey of Korea, Seoul, 64 p.
Yun, S.K. and Park, B.K., 1968, Explanatory Text of the Geological Map of Seolcheon Sheet (1∶50,000). Geological Survey of Korea, Seoul, 55 p.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, BC., Yu, KM., Chun, HY. et al. The southeastern margin of the Cretaceous Yongdong Basin, Korea: a lacustrine fan-delta system. Geosci J 1, 61–74 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02910478
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02910478