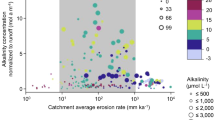
Abstract
How has the Earth maintained a habitable environment while its closest neighbors, Venus and Mars, are currently too hot or too cold? This fortunate state has been attributed to a negative feedback hypothesis that has stood unchallenged for years. In this model, any increase in atmospheric CO2 production is balanced by increased CO2 uptake by silicate weathering under greenhouse conditions. A decrease in atmospheric CO2, then, is balanced by decreased silicate weathering rates under the colder climate. A global experiment utilizing published geochemical data from large rivers at different latitudes helps us test the climate dependence of weathering, central to this hypothesis. When rivers draining granitic shields and basaltic provinces are compared, there is no systematic latitudinal variation (temperature dependence) in the rates of chemical weathering. At global scale the physical mechanisms superimpose a threshold effect on the underlying climate-dependence of silicate weathering. On tropical cratons, the buildup of lateritic regolith suppresses weathering. In the arctic/ subarctic, frost action efficiently removes the regolith and generates physical exposure of silicate rocks to the weathering agents (water, CO2), thereby accelerating reaction. Available field observations do not support the currently standard Clausius-Clapeyron-Arrhenius model.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Åberg, G. and Wickman, F.E., 1987, Variations of87Sr/86Sr in water from streams discharging into the Bothnian Bay, Baltic Sea, Nordic Hydrology, 18, 33–42.
Ambrosi, J.P. and Nahon, D., 1986, Petrological and geochemical differentiation of lateritic iron profile. Chemical Geology, 57, 371–393.
Anderson, S.P., Drever, J.I. and Humphrey, N.F., 1997, Chemical weathering in glacial environments. Geology, 25, 399–402.
Andersson, P.S., Wasserburg, G.J., Ingri, J. and Stordal, M.C., 1994, Strontium, dissolved and particulate loads in fresh and brackish waters: the Baltic Sea and Mississippi Delta, Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 124, 195–210.
Berner, R.A., 1978, Equilibrium, kinetics and the precipitation of magnesian calcite from seawater. American Journal of Science, 278, 1435–1455.
Berner, R.A. and Kothavala, Z., 2001, GEOCARB III: A revised model of atmospheric CO2 over Phanerozoic time. American Journal of Science, 301, 182–204.
Berner, R.A., Lasaga, A.C. and Garrels, R.M., 1983, The carbonatesilicate geochemical cycle and its effect on atmospheric carbon dioxide over the past 100 million years. American Journal of Science, 283, 641–683.
Blum, J.D. and Erel, Y., 1995, A silicate weathering mechanism linking increases in marine87Sr/86Sr with global glaciation, Nature, 373, 415–418.
Bluth, G.J.S. and Kump, L.R., 1994, Lithologic and climatologic controls of river chemistry. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 58, 2341–2359.
Bourman, R.P., 1993, Models of ferricrete genesis: evidence from southeastern Australia. Zeitschrift Geomorphologie, 37, 77–101.
Brown, E.T., Bourlès, D.L., Colin, F., Sanfo, Z., Raisbeck, G.M. and Yiou, F., 1994, The development of iron crust lateritic systems in Burkina Faso, West Africa examined with in-situ produced cosmogenic nuclides. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 124, 19–33.
Dessert, C., Dupré, B., François, L.M., Schott, J., Gaillardet, J., Chakrapani, G. and Bajpai, S., 2001, Erosion of Deccan Traps determined by river geochemistry: impact on the global climate and the87Sr/86Sr ratio of seawater. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 188, 459–474.
Edmond, J.M. and Huh, Y., 1997, Chemical weathering yields from basement and orogenic terrains in hot and cold climates. In: Ruddiman, W.F. (ed.), Tectonic Uplift and Climate Change. Plenum Press, New York, p. 329–351.
Edmond, J.M., Palmer, M.R., Measures, C.I., Grant, B. and Stallard, R.F., 1995, The fluvial geochemistry and denudation rate of the Guayana Shield in Venezuela, Colombia and Brazil. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 59, 3301–3325.
Huh, Y. and Edmond, J.M., 1999, The fluvial geochemistry of the rivers of Eastern Siberia: III. Tributaries of the Lena and Anabar draining the basement terrain of the Siberian Craton and the Trans-Baikal Highlands. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 63, 967–987.
Huh, Y., Panteleyev, G., Babich, D., Zaitsev, A. and Edmond, J.M., 1998a, The fluvial geochemistry of the rivers of Eastern Siberia: II. Tributaries of the Lena, Omoloy, Yana, Indigirka, Kolyma, and Anadyr draining the collisional/accretionary zone of the Verkhoyansk and Cherskiy ranges. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 62, 2053–2075.
Huh, Y., Tsoi, M.-Y., Zaitsev, A. and Edmond, J.M., 1998b, The fluvial geochemistry of the rivers of Eastern Siberia: I. Tributaries of the Lena River draining the sedimentary platform of the Siberian Craton, Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 62, 1657–1676.
Kalvoda, J., 1992, Geomorphological Record of the Quaternary Orogeny in the Himalaya and the Karakoram, Elsevier, Amsterdam, 315 p.
LaSalle, P., De Kimpe, C.R. and Laverdiere, M.R., 1985, Sub-till saprolites in southeastem Quebec and adjacent New England: Erosional, stratigraphic, and climatic significance. Geological Society of America Special Paper, 197, 13–20.
Louvat, P., 1997, Etude géochimique de l'érosion fluviale d'îles volcaniques à l'aide des éléments majeurs et traces. Ph.D. thesis, Université Paris 7, Paris, 322 p. (in French)
Louvat, P. and Allègre, C.J., 1998, Riverine erosion rates on Sao Miguel volcanic island, Azores archipelago. Chemical Geology, 148, 177–200.
Louvat, P. and Allègre, C.J., 1997, Present denudation rates on the island of Réunion determined by river geochemistry: Basalt weathering and mass budget between chemical and mechanical erosions. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 61, 3645–3669.
Mackenzie, F.T., 2003, Our Changing Planet. Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, New Jersey, 580 p.
Martin, C., 1987, Les mesures de l'érosion chimique et interprétation des résultats dans les petits bassins versants de roches cristallines: exemples pris dans le massif des Maures (Var, France). In: Processus et mesure de l'érosion. CNRS, p. 329–348. (in French)
McDowell, W.H. and Asbury, C.E., 1994, Export of carbon, nitrogen, and major ions from three tropical montane watersheds. Limnology and Oceanography, 39, 111–125.
Meybeck, M., 1986, Composition chimique des ruisseaux non pollués de France, Sciences Géologique (Bulletin), 39, 3–77, (in French).
Millot, R., Gaillardet, J., Dupré, B. and Allègre, C.J., 2002, The global control of silicate weathering rates and the coupling with physical erosion: new insights from rivers of the Canadian Shield. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 196, 83–98.
Négrel, P., Allègre, C.J., Dupré, B. and Lewin, E., 1993, Erosion sources determined by inversion of major and trace element ratios and strontium isotopic ratios in river water: The Congo Basin case. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 120, 59–76.
Ollier, C.D., 1991, Aspects of silcrete formation in Australia. Zeischrift Geomorphologie, 35, 151–163.
Palmer, M.R. and Edmond, J.M., 1989, The strontium isotope budget of the modern ocean. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 92, 11–26.
Palmer, M.R. and Edmond, J.M., 1992, Controls over the strontium isotope composition of river water. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 56, 2099–2111.
Pewe, T.L., 1975, Quaternary Geology of Alaska, U. S. Geological Survey Professional Paper, 835, 145 p.
Raymo, M.E. and Ruddiman, W.F., 1992, Tectonic forcing of late Cenozoic climate. Nature, 359, 117–122.
Sharp, M., Tranter, M., Brown, G.H. and Skidmore, M., 1995, Rates of chemical denudation and CO2 drawdown in a glacier-covered alpine catchment, Geology, 23, 61–64.
Stallard, R.F. and Edmond, J.M., 1983, Geochemistry of the Amazon 2. The influence of geology and weathering environment on the dissolved load. Journal of Geophysical Research, 88, 9671–9688.
Thomas, M.F., 1994, Ages and geomorphic relationships of saprolite mantles. In: Robinson, D.A. and Williams, R.B.G. (eds.), Rock Weathering and Landform Evolution. John Wiley & Sons Ltd., New York, p. 287–301.
Topp, S.E., Salbu, B., Roaldset, E. and Jorgensen, P., 1984, Vertical distribution of trace elements in lateritic soil. Chemical Geology, 47, 159–174.
Twidale, C.R., 1990, The origin and implications of some erosional landforms. Journal of Geology, 98, 343–364.
Vegas-Vilarrubia, T., Maass, M., Rull, V., Elias, V., Ramon, A., Ovalle, C., Lopez, D., Schneider, G., Depetris, P.J. and Douglas, I., 1994, Small catchment studies in the tropical zone. In: Moldan, B. and Cerny, J. (eds.), Biogeochemistry of Small Catchment: A Tool for Environmental Research. Wiley, U. K., p. 343–360.
Viers, J., Dupré, B., Braun, J.-J., Deberdt, S., Angeletti, B., Ngoupayou, J.N. and Michard, A., 2000, Major and trace element abundances, and strontium isotopes in the Nyong basin rivers (Cameroon): constraints on chemical weathering processes and elements transport mechanisms in humid tropical environments. Chemical Geology, 169, 211–241.
Vigier, N., Bourdon, B., Turner, S. and Allègre, C.J., 2001, Erosion timescales derived from U-decay series measurements in rivers. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 193, 549–563.
Vinogradov, V.I. and Leytes, A.M., 1987, Rb-Sr dating of the stages of granitization of the South Aldan Shield. In: Shukolyukov, Y.A., (ed.), Isotope Dating of Metamorphic and Metasomatic Processes, Nauka, Moscow, p. 103–115.
Wadleigh, M.A., Veizer, J. and Brooks, C., 1985, Strontium and its isotopes in Canadian rivers: Fluxes and global implications. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 49, 1727–1736.
Walder, J. and Hallet, B., 1985, A theoretical model of the fracture of rock during freezing. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 96, 336–346.
Walker, J.C.G., Hays, P.B. and Kasting, J.F., 1981, A negative feedback mechanism for the long-term stabilization of Earth's surface temperature. Journal of Geophysical Research, 86, 9776–9782.
Wallmann, K., 2001, Controls on the Cretaceous and Cenozoic evolution of seawater composition, atmospheric CO2 and climate. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 65, 3005–3025.
Webster, P.J., 1994, The role of hydrological processes in oceanatmosphere interactions. Reviews of Geophysics, 32, 427–476.
Wedepohl, K.H., 1995, The composition of the continental crust. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 59, 1217–1232.
White, A.F. and Blum, A.E., 1995, Effect of climate on chemical weathering in watersheds. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 59, 1729–1747.
White, A.F. and Brantley, S.L., 1995, Chemical Weathering Rates of Silicate Minerals. Reviews in Mineralogy, Volume 31, Mineralogical Society of America, Washington, D.C., 583 p.
White, A.F., Bullen, T.D., Vivit, D.V., Schulz, M.S. and Clow, D.W., 1999, The role of disseminated calcite in the chemical weathering of granitoid rocks, Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 63, 1939–1953.
Wickman, F.E. and Åberg, G., 1987, Variations in the87Sr/86Sr ratio in lake waters from Central Sweden, Nordic Hydrology, 18, 21–32.
Yang, C., Telmer, K. and Veizer, J., 1996, Chemical dynamics of the St. Lawrence riverine system: δDH2O, δ18OH2O, δ13CDIC, δ34SSulfate, and dissolved87Sr/86Sr. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 60, 851–866.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huh, Y. Chemical weathering and climate — a global experiment: A review. Geosci J 7, 277–288 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02910294
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02910294