Abstract
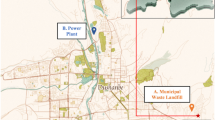
Monoterpenes in ambient air were determined in various sites in Guangzhou, and it was revealed that monoterpene concentrations in some special sites, like landfills, were even higher than those in locations with much more vegetation. On the average, monoterpene contents in samples from streets and highways were 1.9 μg/m3; from gardens, plantations and wooded lands, 2.2 μ/m3; from farmlands, 1.5 μ/m3; but from landfills, 4.1 μ/m3. So other sources like landfills, apart from living plants, might also contribute to the biogenic non-methane hydrocarbons (NMHCs) in the atmospheric environment. On the other hand, the composition pattern of monoterpenes in air samples from landfills were obviously different compared with those from living plants, this might result from the different synthesis pathways of monoterpenes, the oxygen-depleted environment and the microbiogenic process might affect the synthesis in landfills.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fred, F., Jack, C., Day, F.et al., Emissions of volatile organic compounds from vegetation and the implications for atmospheric chemistry,Global Biogeochem. Cycle, 1992, 6(4): 389.
Hewitt, C. N., Rachel, A. S., A qulitative assessment of the emission of non-methane hydrocarbon compounds from the biosphere to the atmosphere in the U.K.: present knowledge and uncertainties,Atmos. Environ., 1992, 26A(17): 3069.
Tingey, D. T., Manning, M., Grothaus, L. C.et al., The influence of light and temperature on monoterpene emision rates from slash pine.Pl. Physiol., 1980, 65: 797.
Zhao Meiping, Shao Ming, Bai Yuhuaet al., Study on characteristics of several typical trees in China,Chinese J. of Environ. Chem. (in Chinese), 1996, 15(1): 69.
Croteau, R., Biosynthesis and catabolism of monoterpenes,Chem. Rev., 1987, 87: 924.
Fu Jiamo, Sheng Guoying, Wang Xingminget al., Preliminary study of air pollution in Guangzhou, Hong Kong and Macao, in ACSSymposium 671:Biomarkers in Environmental Geochemistry, 1997, 164.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, X., Sheng, G., Fu, J. et al. Characteristics and possible origins of atmospheric monoterpenes from nonliving plants in Guangzhou. Chin.Sci.Bull. 44, 747–750 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02909718
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02909718