Summary
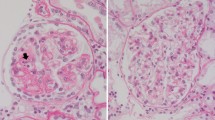
Progress has been made in understanding glomerulonephritis but the answers to many key questions still elude us. It appears that glomerular damage arises from immune events which result from an interaction between a susceptible individual and some environmental agents, usually an infection. In the developed world the role of the genetic constitution is predominant, whilst in the Third world the overwhelming exposure to pathogens may be crucial. Immune complex formation undoubtedly plays a major role in the initiation of glomerular injury, but deposition of soluble preformed complexes within the glomerulus now seems to be only one mechanism,in situ combination of fixed antigen and free antibody, and insoluble (precipitating) complexes both playing a part as well. New understanding of modes of damage to the glomerulus strongly implicates monocytes as injurious agents in both experimental and human nephritis, and platelets may also play a role in amplifying injury. One of the main questions is why only some forms of glomerulonephritis in only some patients progress to renal failure. Whilst continuing exposure to the antigen initiating the nephritis may be important, secondary mechanisms involving autologous antigens may be important. Further, non-immunologic mechanisms which arise from hyperperfusion of glomerular capillaries appear capable of damaging the glomerulus, and both this mechanism and proteinuria itself appear capable of inducing glomerulosclerosis. The role these non-immunologic mechanisms play may be the reason for our failure, in general, to influence the course of glomerulonephritis by manoeuvres designed to inhibit immunologic injury.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdou N. I., Sagawa A., Pascal E., Hevert J., Sadeghee S.: Suppressor T cell abnormality in systemic lupus erythematosus — Clin. Immunol. Immunopath.6, 192, 1976.
Adler S., Salant D. J., Dittmer J. E., Madaio M. P., Couser W. G.: Mediation of proteinuria in membranous nephropathy (MN) induced by a planted subepithelial antigen (AG). In: Abstracts, American Society of Nephrology, Washington, November 1981; p. 68A.
Adler S., Wang H., Cohen A., Border W.: Electropharmacologic modulation ofin situ complex formation in experimental membranous nephropathy. In: Abstracts, American Society of Nephrology, Washington, November 1981; p. 68A.
Adu D., Dobson J., Williams D. G.: DNA-anti-DNA circulating complexes in the nephritis of systemic lupus erythematosus — Clin. exp. Immunol.43, 605, 1981.
Agnello V.: Complement deficiency states — Medicine (Baltimore)57, 1, 1978.
Amend W. J. C., Vincenti F., Feduska M. J., Salvatierra O., Johnston J., Tilney N., Garavoy M., Burwell E. L.: Recurrent systemic lupus erythematosus involving renal allografts — Ann. intern. Med.94, 444, 1981.
Atkins R. C., Holdsworth S. R., Glasgow E. F., Mathews F. G.: The macrophage in human rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis — Lanceti, 830, 1976.
Baldwin D. S.: Nephrology forum. Chronic glomerulonephritis: non-immunologic mechanisms of progressive glomerular damage — Kidney int.21, 109, 1982.
Barnett E. V., Knutson D. W., Abrass C. K., Chia D. S., Young L. S., Liebling M. R.: Circulating immune complexes: their immunochemistry, detection and importance — Ann. intern. Med.91, 430, 1979.
Barsotti G., Guiducci A., Ciardella F., Giovannetti S.: Effects on renal function of a low nitrogen diet supplemented with essential amino acids and keto-analogues and of haemodialysis and free protein supply in patients with chronic renal failure — Nephron27, 113, 1981.
Bartolotti S. R., Peters D. K.: Delayed removal of renal-bound antigen in decomplemented animals with acute serum sickness — Clin. exp. Immunol.32, 199, 1978.
Barton C. H., Vaziri N. D., Spear G. S.: Nephrotic syndrome associated with adenocarcinoma of the breast — Amer. J. Med.68, 308, 1980.
Batsford S. R., Rohrbach R., Vogt A.: The role of change in subepithelial glomerular immune deposit formation. In: Abstracts, American Society of Nephrology, Washington, November 1981; p. 69A.
Batsford S. R., Takmiya H., Vogt A.: A model ofin situ immune complex glomerulonephritis in the rat employing cationised ferritin — Clin. Nephrol.14, 211, 1980.
Bhan A. K., Collins A. B., Schneeberger E. E., McCluskey R. T.: A cell-mediated reaction against glomerular-bound immune complexes — J. exp. Med.150, 1410, 1979.
Bhan A. K., Schneeberger E. E., Collins A. B., McCluskey R. T.: Evidence for a pathogenic role of a cell-mediated immune mechanism in experimental glomerulonephritis — J. exp. Med.148, 246, 1978.
Border W. A.: Immune complex detection in glomerular diseases — Nephron24, 105, 1979.
Border W. A., Ward H. J., Kamil E. S., Cohen A. H.: Induction of membranous nephropathy in rabbits by administration of an exogenous cationic antigen: demonstration of a pathogenic role for electrical change — J. clin. Invest.69, 451, 1982.
Boulton-Jones M., Sissons J. G. P., Naish P. F., Evans D. J., Peters D. K.: Self-induced glomerulonephritis — Brit. med. J.iii, 387, 1974.
Boyns A. R., Hardwicke J.: The relationship between circulating soluble antigen-antibody complexes and the production of chronic glomerulonephritis in the rabbit — Immunology14, 367, 1968.
Bradfield J. W. B., Cattell V.: The mesangial cell in glomerulonephritis. I. Mechanism of hypercellularity in experimental immune complex glomerulonephritis — Lab. Invest.36, 481, 1977.
Cameron J. S.: Clinicopathological correlations — problems and limitations — Clin. Nephrol.4, 1, 1975.
Cameron J. S.: Platelets and glomerulonephritis — Nephron18, 253, 1977.
Cameron J. S.: The natural history of glomerulonephritis. In:Black D. A. K., Jones N. F. (Eds): Renal disease. Oxford Sci. Publ., Oxford, 1979; p. 329.
Cameron J. S.: The natural history of glomerulonephritis. In:Kincaid-Smith P., D’Apice A. J. F., Atkins R. C. (Eds): Progress in glomerulonephritis. John Wiley and Sons, New York, 1979; p. 1.
Cameron J. S.: Clinicopathological correlations in glomerular disease. In: Kidney disease, present status. IAP Monographs no. 20, Williams and Wilkins, Baltimore, 1979; p. 76.
Cameron J. S.: Pathogenesis and treatment of membranous nephropathy — Kidney int.15, 88, 1979.
Cameron J. S.: Glomerulonephritis. In:Marsh F. P. (Ed.): A textbook of modern nephrology. Heinemann, London, 1982. (In press).
Cameron J. S.: The treatment of immunologically mediated renal disease. In:Zabriskie J., Fillit H. M. (Eds): Immunology of the kidney. John Wiley and Sons, New York, 1982. (In press).
Cameron J. S., Clark W. F.: A role for insoluble complexes in glomerulonephritis? — Clin. Nephrol., 1982. (In press).
Cattell V., Jameson S. W.: The origin of glomerular crescents in experimental nephrotoxic serum nephritis in man — Lab. Invest.39, 584, 1978.
Chatenoud L., Bach M.-A.: Abnormalities of T cell subsets in glomerulonephritis and systemic lupus erythematosus — Kidney int.20, 267, 1981.
Clark W. F., Friesen M., Linton A. L., Lindsay R. M.: The platelet as mediator of tissue damage in immune complex glomerulonephritis — Clin. Nephrol.6, 287, 1976.
Clark W. F., Turnbull D. I., Driedger A. A., Lindsay R. M., Linton A. L.: Intrarenal insoluble immune complex formation — J. clin. Lab. Immunol.4, 21, 1980.
Cochrane C. G.: Mechanisms involved in the deposition of immune complexes in tissues — J. exp. Med.134, 75s, 1971.
Cochrane C. G., Dixon F. J.: Antigen-antibody complex induced disease. In:Miescher P. A., Muller-Eberhard H. E. (Eds): Clinical immunopathology. Grune and Stratton, New York, 1976; p. 137.
Cochrane C. G., Hawkins D. J.: Studies on circulating immune complexes. III. Factors governing the ability of circulating complexes to localise in blood vessels — J. exp. Med.127, 137, 1968.
Cochrane C. G., Koffler D.: Immune complex disease in experimental animals and in man — Advanc. Immunol.16, 185, 1973.
Cohen A. H., Mampaso F., Zamboni L.: Glomerular podocyte degeneration in human renal disease. An ultrastructural study — Lab. Invest.37, 30, 1977.
Cotran R. S.: The role of monocytes and macrophages in glomerulonephritis. In: Proc. 8th Congr. Int. Soc. Nephrol., Athens, June 1981. (Introduction). Karger, Basel, 1981; p. 853.
Couser W. G.: What are circulating immune complexes doing in glomerulonephritis? — New Engl. J. Med.304, 1230, 1981.
Couser W. G., Salant D.:In situ complex formation and glomerular injury — Kidney int.17, 1, 1980.
Danno K., Fukuyama K., Epstein W. L.: Renal deposition of antinuclear antibody in athymic mice infected withSchistosoma mansoni — Lab. Invest.40, 358, 1979.
Dausset J., Contu L.: The MHC and immune response in man. In:Fougereau M., Dausset J. (Eds): Immunology 80. Pergamon Press, New York, 1980; p. 503.
Davies D. J., Brewer D. B., Hardwicke J.: Urinary proteins and glomerular morphometry in protein overload proteinuria — Lab. Invest.38, 232, 1978.
Davison A., Kerr D. N. S., Cameron J. S.: Natural history of untreated idiopathic glomerulonephritis in adults. In: Abstracts, 8th Congr. Int. Soc. Nephrol., Athens, June 1981, no. CN-196; p. 291.
Deen W. M., Maddox D. A., Robertson C. R., Brenner B. M.: Dynamics of glomerular ultrafiltration in the rat. VII. Response to reduced renal mass — Amer. J. Physiol.227, 556, 1974.
Deuel T. F., Senior R. M., Chang D., Griffin G. L., Henrikson R. S., Kaiser E. T.: Platelet factor 4 is chemotactic for neutrophils and monocytes — Proc. nat. Acad. Sci. (Wash.)78, 4584, 1981.
Dixon F. J.: The pathogenesis of glomerulonephritis — Amer. J. Med.44, 493, 1968.
Dixon F. J., Feldman J. D., Vasquez J. J.: Experimental glomerulonephritis. The pathogenesis of a laboratory model resembling the spectrum of human glomerulonephritis — J. exp. Med.113, 899, 1961.
Dubois C. H., Foidart J. B., Hautier M. B., Dechenne C. A., Lemaire M. J., Mahieu P. R.: Proliferative glomerulonephritis in rats: evidence that mononuclear phagocytes infiltrating the glomerulus stimulate the proliferation of endothelial and mesangial cells — Europ. J. clin. Invest.11, 91, 1981.
Ehrich W. E., Forman C. W., Seifer J.: Diffuse glomerular nephritis and lipid nephrosis. Correlation of clinical, morphological and experimental observations — Arch. Path.54, 463, 1952.
El-Nahas A. M., Paraskevakou H., Evans D. J., Rees A. J.: Protection from renal failure after subtotal nephrectomy in rats by dietary protein restriction — Clin. Sci.62, 33P, 1981. (Abstract).
Farquhar M. G., Vernier R. L., Good R. A.: Electron microscope study of glomerulus in nephrosis, glomerulonephritis and lupus erythematosus — J. exp. Med.106, 649, 1951.
Fillastre J. P.: Drug-induced glomerulonephritis — Dialysis Transplant.10, 716, 1981.
Fischer E., Camus D., Santoro F., Capron A.:Schistosoma mansoni: autoantibodies and polyclonal B cell activation in infected mice — Clin. exp. Immunol.46, 89, 1981.
Fleuren G., Grond J., Hoedemaker P. J.:In situ formation of subepithelial glomerular immune complexes in passive serum sickness — Kidney int.17, 631, 1980.
Ford P. M., Kosatka I.: A mechanism of enhancement of immune complex deposition followingin situ complex formation in the mouse glomerulus — Immunology43, 433, 1981.
Gabbiani G., Badonnel M. C., Vassalli P.: Experimental focal glomerular lesions elicited by insoluble immune complexes. Ultrastructural and immunofluorescent studies — Lab. Invest.32, 33, 1975.
George C. R. P., Clark W. F., Cameron J. S.: The role of platelets in glomerulonephritis — Advanc. Nephrol.4, 19, 1975.
Germuth F. G. Jr.: A comparative histologic and immunologic study in rabbits of induced hypersensitivity of the serum sickness type — J. exp. Med.97, 257, 1953.
Germuth F. G. Jr.,Rodriguez E. L.: Immunopathology of the renal glomerulus. Immune complex deposit and anti-basement membrane disease — Little, Brown and Co., Boston, 1973.
Germuth F. G. Jr.,Rodriguez E., Lorelle C. A., Trump E. I., Milano L. L., Wise O.: Passive immune complex glomerulonephritis in mice: models for various lesions found in human disease. I. High avidity complexes and mesangiopathic glomerulonephritis — Lab. Invest.41, 360, 1979.
Germuth F. G. Jr.,Rodriguez E., Lorelle C. A., Trump E. I., Milano L. L., Wise O.: Passive immune complex glomerulonephritis in mice: models for various lesions found in human disease. II. Low avidity complexes and diffuse proliferative glomerulonephritis with subendothelial deposits — Lab. Invest.41, 366, 1979.
Germuth F. G. Jr.,Senterfit L. B., Dreesman G. R.: Immune complex disease. V. The nature of the circulating complexes associated with glomerular alterations in the BSA rabbit system — Johns Hopk. med. J.131, 344, 1972.
Germuth F. G. Jr.,Senterfit L. B.,Pollak A. D.: Immune complex disease. I. Experimental acute and chronic glomerulonephritis — Johns Hopk. med. J.120, 225, 1967.
Germuth F. G. Jr.,Taylor J. J., Siddiqui S. Y., Rodriguez E.: Immune complex disease. VI. Some determinants of the varieties of glomerular lesions in the chronic bovine serum albumin — rabbit system — Lab. Invest.37, 162, 1977.
Glasser R. J., Velosa J. A., Michael A. F.: Experimental model of focal sclerosis. I. Relationship to protein exaction in aminonucleoside nephrosis — Lab. Invest.36, 519, 1977.
Glassock R. J.: A clinical and immunopathologic dissection of rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis — Nephron22, 253, 1978.
Glassock R. J., Cohen A. H.: Secondary glomerular disease. In:Brenner B. M., Rector R. C. (Eds): The kidney. W. B. Saunders, Philadelphia, 1981; 2nd ed., p. 1493.
Glassock R. J., Cohen A. H., Bennett C. M., Martinez-Maldonado M.: Primary glomerular diseases. In:Brenner B. M., Rector R. C. (Eds): The kidney. 2nd ed. W. B. Saunders, PHiladelphia, 1981; p. 1351.
Gocke D. J., Hsu K., Morgan C., Bombardieri S., Lockshin M., Christian C. L.: Association between polyarteritis and Australia antigen — Lancetii, 1149, 1970.
Golbus S., Wilson C. B.: Experimental glomerulonephritis induced byin situ formation of immune complexes in glomerular capillary wall — Kidney int.16, 148, 1979.
Goodman M. G.: Cellular aspects of polyclonal activation of B lymphocytes — Immunology Today, November 1980; p. 92.
Grishman E., Churg J.: Focal glomerular sclerosis in nephrotic patients: an electron microscopic study of glomerular podocytes — Kidney int.7, 111, 1975.
Hammer D. K., Dixon F. J.: Experimental glomerulonephritis. II. Immunologic events in the pathogenesis of nephrotoxic serum nephritis in the rat — J. exp. Med.117, 1019, 1963.
Heidland A., Jult J., Rockel A., Heidbreder E.: Evaluation of essential amino acids and keto acids in uraemic patients on a low protein diet — Amer. J. clin. Nutr.31, 1784, 1978.
Heptinstall R. H.: Pathology of the kidney — 1st ed., Little, Brown and Co., Boston, 1966; 2nd ed., 1974.
Holdsworth S. R., Neale T. J., Wilson C. B.: The participation of macrophages and monocytes in experimental immune complex glomerulonephritis — Clin. Immunol. Immunopath.15, 510, 1980.
Holdsworth S. R., Neale T. J., Wilson C. B.: Abrogation of macrophage-dependent injury in experimental glomerular injury in the rabbit. Use of an anti-macrophage serum — J. clin. Invest.68, 686, 1981.
Hostetter T. H., Olson J. L., Rennke H. G., Venkatachalam M. A., Brenner B. M.: Hyperfiltration in remnant nephrons: a potentially adverse response to renal ablation — Amer. J. Physiol.241, F85, 1981.
Hunsicker L. G., Shearer T. P., Plattner S. B., Weisenburger D.: The role of monocytes in serum sickness nephritis — J. exp. Med.150, 413, 1979.
Ibels L. S., Alfrey A. C., Hant L., Huffer W. E.: Preservation of function in experimental renal disease by dietary restriction of phosphate — New Engl. J. Med.298, 122, 1978.
Iversen B. M.: The effect of hypertension on experimental glomerulonephritis — Thesis, Bergen University, 1981.
Iversen P., Brun C.: Aspiration biopsy of the kidney — Amer. J. Med.11, 324, 1951.
Izui S., Lambert P. H., Fournié G. J., Türler H., Miescher P. A.: Features of systemic lupus erythematosus in mice injected with bacterial lipopolysaccharides. Identification of circulating DNA and renal localisation of DNA-anti-DNA complexes — J. exp. Med.145, 1115, 1977.
Izui S., Lambert P. H., Miescher P. A.:In vitro demonstration of a particular affinity of glomerular basement membrane and collagen for DNA. A possible basis for local formation of DNA-anti-DNA complexes in systemic lupus erythematosus — J. exp. Med.144, 428, 1976.
Jones D. B.: Inflammation and repair of the glomerulus — Amer. J. Path.27, 991, 1951.
Karlinsky M. L., Haut L., Buddington B., Schrier N. A., Alfrey A. C.: Preservation of renal function in experimental glomerulonephritis — Kidney int.17, 293, 1980.
Kibukamusoke J. W.: Nephrotic syndrome of quartan malaria — Edward Arnold, Bristol, 1973.
Kim Y., Michael A. F.: Chronic bacteremia and nephritis — Ann. Rev. Med.29, 319, 1978.
Kincaid-Smith P.: Modification of the vascular lesions of rejection in cadaveric renal allografts by dipyridamole and anticoagulants — Lancetii, 920, 1969.
Kincaid-Smith P.: The kidney — Blackwell Sci. Publ., Oxford, 1975; p. 193.
Kincaid-Smith P., D’Apice A. J. F., Atkins R. C. (Eds): Progress in glomerulonephritis — John Wiley and Sons, New York, 1979.
Kincaid-Smith P., Mathew T. H., Becker E. L.: Glomerulonephritis. Morphology, natural history and treatment — John Wiley and Sons, New York, 1973.
Klouda P. T., Manos J., Acheson E. J., Dyer P. A., Goldby F. S., Harris R., Lawler W., Mallick N. P., Williams G.: Strong association between idiopathic membranous nephropathy and HLA-DRW3 — Lancetii, 770, 1979.
Kluthe R., Oechslin D., Quirin H., Jesdinsky H. J.: Six years experience with a special low-protein diet. In:Kluthe R., Berlyne G., Burton B. (Eds): Uraemia; pathogenesis, diagnosis and treatment. Thieme-Verlag, Stuttgart, 1971; p. 250.
Lambert P. H., Bricteux N., Salmon J., Miescher P. A.: Dynamics of immune complex nephritis during antibody excess — Int. Arch. appl. Immunol.45, 185, 1973.
Lange K., Ahmed U., Kleinberger H., Treser G.: A hitherto unknown streptococcal antigen and its probable relation to post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis — Clin. Nephrol.5, 207, 1976.
Lawley T. J.: Immune complex and reticuloendothelial function in human disease — J. invest. Derm.74, 339, 1980.
Lawrence G. M., Brewer D. B.: Effect of strain and sex on the induction of hyperalbuminaemic proteinuria in the rat — Clin. Sci.61, 751, 1981.
Lee S., Kjellstrand C. M.: Renal disease in infectious mononucleosis — Clin. Nephrol.9, 236, 1978.
Levinsky R. J., Malleson P. N., Barratt R. M., Soothill J. F.: Circulating immune complexes in steroid responsive nephrotic syndrome — New Engl. J. Med.298, 128, 1978.
Levy M., Kleinknecht C.: Membranous glomerulonephritis and hepatitis B infection — Nephron26, 259, 1980.
Losito A., Buccarelli E., Masi-Benedetti F., Lato M.: Membranous glomerulonephritis in congenital syphilis — Clin. Nephrol.12, 32, 1979.
Mannik M.: Physicochemical and functional relationships of immune complexes — J. invest. Derm.74, 333, 1980.
Marchesi D., Parbtani A., Frampton G., Livio M., Remuzzi G., Cameron J. S.: Thrombotic tendency in systemic lupus erythematosus — Lanceti, 719, 1981. (Letter).
Masugi M.: Über die experimentelle Glomerulonephritis durch das spezifische Antireninserum. Ein Beitrag zur Pathogenese der diffusen Glomerulonephritis — Beitr. path. Anat.92, 429, 1934.
Mauer S. M., Sutherland D. E. R., Howard R. J., Fish A. J., Najarian J. S., Michael A. F.: The glomerular mesangium. III. Acute immune mesangial injury. A new model of glomerulonephritis — J. exp. Med.137, 553, 1973.
McDevitt H. O., Bodmer W. F., Chinitz A.: HL-A, immune response gene and disease — Lanceti, 1269, 1974.
McIntosh R. W., Garcia R., Rubio L., Rabideau D., Allen J. E., Carr R. I., Rodriguez-Iturbe B.: Evidence for an autologous immune complex pathogenesis mechanism in acute post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis — Kidney int.14, 501, 1978.
Mellors R. C., Arias-Stella J., Siegel M., Pressman D.: Analytical pathology. II. Histopathologic demonstration of glomerular-localizing antibodies in experimental glomerulonephritis — Amer. J. Path.31, 687, 1955.
Michael A. F., Drummond K. N., Good R. A., Vernier R. L.: Acute post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis: immune deposit disease — J. clin. Invest.45, 237, 1966.
Mitch W. E., Walser M., Buffington C. A., Lemann J.: A simple method for estimating progression of chronic renal failure — Lancetii, 1326, 1976.
Moller G., Strom H., Al-Balaghi S.: Role of polyclonal activation in specific immune responses — Scand. J. Immunol.12, 177, 1980.
Morimoto C., Reinherz E. L., Schlossman S. F., Schur P. H., Mills J. A., Steinberg A. D.: Alterations in immunoregulatory T cell subsets in active systemic lupus erythematosus — J. clin. Invest.66, 1171, 1980.
Morita T., Suzuki Y., Churg J.: Structure and development of the glomerular crescent — Amer. J. Path.72, 349, 1973.
Muehrcke R. C., Kark R. M., Pirani C. L.: Technique of percutaneous renal biopsy in the prone position — J. Urol. (Baltimore)74, 267, 1955.
Naish P., Penn G. B., Evans D. J., Peters D. K.: The effects of defibrination of nephrotoxic nephritis in the rabbit — Clin. Sci.42, 643, 1972.
Nakashima Y., Hirose S., Hamashima Y.: Proliferation of cultured rabbit renal glomerular cells stimulated by platelet factor — Acta path. jap.30, 1, 1980.
Nathan C. F., Murray H. W., Cohn Z. A.: The macrophage as an effector cell — New Engl. J. Med.303, 622, 1980.
Neild G. H., Gärtner H.-V., Bohle A.: Penicillamine-induced membranous glomerulonephritis — Scand. J. Rheum.28 (Suppl.), 79, 1979.
Nussenzweig V.: Interaction between complement and immune complexes: role of complement in containing immune complex damage. In:Fougereau M., Dausset J. (Eds): Immunology 80. Pergamon Press, New York, 1980; p. 1044.
Olson J. L., Hostetter T. H., Rennke H. G., Brenner B. M., Venkatachalam M. A.: Altered charge and size selective properties of the glomerular wall: a response to reduced renal mass — Kidney int.16, 857, 1979. (Abstract).
O’Regan S., Smith M., Drummond K. N.: Antigens in human immune complex nephritis — Clin. Nephrol.6, 417, 1976.
Parbtani A., Cameron J. S.: Platelet involvement in glomerulonephritis. In:Remuzzi G., Mecca G., De Gaetano G. (Eds): Hemostasis, prostaglandins and renal disease. Raven Press, New York, 1980; p. 45.
Peters D. K., Lachmann P. J.: Immunity deficiency in pathogenesis of glomerulonephritis — Lanceti, 58, 1974.
Petty R. E., Steward M. W., Soothill J. F.: The heterogeneity of antibody affinity in inbred mice and its possible immunopathologic significance — Clin. exp. Immunol.12, 231, 1972.
Pinto J., Lacerda G., Cameron J. S., Turner D. R., Bewick M., Ogg C. S.: Recurrence of focal segmental glomerulosclerosis in renal allografts — Transplantation32, 83, 1981.
Poels L. G., Van Niekerk C. C., Jerusalem C.: Glomerulopathy in mice infected withPlasmodium berghei. Induction of an autoimmune process — Israel J. med. Sci.14, 651, 1978.
Proceedings of a Symposium on immune complexes and disease — J. exp. Med.134 (Suppl.), 1s, 1971.
Purtell J. N., Pesce A. J., Clyne D. H., Miller W., Pollak V.: Isoelectric point of albumin: effect on renal handling of albumin — Kidney int.16, 366, 1979.
Ramzy M. H., Cameron J. S., Turner D. R., Neild G. H., Ogg C. S., Hicks J.: The long-term outcome of idiopathic membranous nephropathy — Clin. Nephrol.16, 13, 1981.
Rees A. J., Peters D. K., Compston D. A. S., Batchelor J. R.: Strong association between HLA-DRW2 antibody-mediated Goodpasture’s syndrome — Lanceti, 966, 1978.
Rees A. J., Peters D. K., Welsh K., Batchelor J. R.: Genetic factors influence the severity of antibody-mediated Goodpasture’s syndrome. In: Abstracts, 8th Congr. Int. Soc. Nephrol., Athens, June 1981, no. CN-243; p. 303.
Remuzzi G., Mecca G., De Gaetano G. (Eds): Hemostasis, prostaglandins and renal disease — Raven Press, New York, 1980.
Remuzzi G., Mecca G., Marchesi D., Livio M., De Gaetano G., Donati M. B., Silver M. J.: Platelet hyperaggregability and the nephrotic syndrome — Thrombos. Res.16, 345, 1979.
Roberts J. L., Lewis E. J.: Identification of anti-native DNA antibodies in cryoglobulinemic states — Amer. J. Med.65, 437, 1978.
Rodriguez-Iturbe B., Carr R. I., Garcia R., Rabideau D., McIntosh R. M.: Circulating immune complexes and serum immunoglobulins in acute post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis — Clin. Nephrol.13, 1, 1980.
Rodriguez-Iturbe B., Castillo L., Valbuena R., Cuenca L.: Acute post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis. Recent developments — Paediatrician8, 307, 1979.
Rodriguez-Iturbe B., Rabideau D., Garcia R., Rubio L., McIntosh R. M.: Characterization of the glomerular antibody in acute post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis — Ann. intern. Med.92, 478, 1980.
Rosenthal A. S.: Regulation of the immune response: role of the macrophage — New Engl. J. Med.303, 1153, 1980.
Ross R., Vogel A.: The platelet-derived growth factor. (Review) — Cell14, 203, 1978.
Rudofsky U. H.: Murine lupus nephritis is accelerated by anti-glomerular basement membrane antibodies — Clin. exp. Immunol.44, 18, 1981.
Rutherford W. E., Blondin J., Miller J. P., Greenwalt A. S., Vaura J. D.: Chronic progressive renal disease: rate of change of serum creatinine — Kidney int.11, 62, 1977.
Salant D. J., Belok S., Madaio M. P., Couser W. G.: A new role for complement in experimental membranous nephropathy in rats — J. clin. Invest.66, 1339, 1980.
Schifferli J. A., Morris S. M., Dash A., Peters D. K.: Complement-mediated solubilisation in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus, nephritis or vasculitis — Clin. exp. Immunol.46, 557, 1981.
Schreiner G. F., Cotran R. S., Pardo V., Unanue E. R.: A mononuclear cell component in experimental glomerulonephritis — J. exp. Med.147, 369, 1978.
Schreiner G. F., Cotran R. S., Unanue E. R.: Glomerular cell types and immune function. In: Proc. 8th Congr. Int. Soc. Nephrol., Athens, June 1981. Karger, Basel, 1981; p. 858.
Schreiner G. F., Cotran R. S., Unanue E. R.: Characterisation of resident glomerular cells in the rat expressing Ia determinants and manifesting genetically restricted interactions with lymphocytes — J. clin. Invest.68, 920, 1981.
Seligson G., Lange K., Cronin W.: Evidence for thein situ origin of post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis. In: Abstracts, American Society of Nephrology, Washington, November 1981; p. 86A.
Shaw S., Kavathas P., Pollack M. S., Charmot D., Mawas C.: Family studies define a new histocompatibility locus, SB, between HLA-DR and GLO — Nature (Lond.)293, 745, 1981.
Shigematsu H.: Glomerular events during the initial phase of rat Masugi nephritis — Virchows Arch. Abt. B5, 187, 1970.
Shigematsu H., Niwa Y., Takizawa J., Akikusa B.: Arthus type nephritis. I. Characterisation of glomerular lesions induced by insoluble and poorly soluble immune complexes — Lab. Invest.40, 492, 1979.
Shigematsu H., Shishido H., Kuhara K., Tsuchida H., Suzuki H., Hirose K., Tojo S.: Participation of monocytes in transient glomerular hypercellularity in post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis — Virchows Arch. Abt. B12, 367, 1973.
Shimamura T., Morrison A. B.: A progressive glomerulosclerosis occurring in partial five-sixths nephrectomy — Amer. J. Path.79, 95, 1975.
Sitprija V., Pipatanagul V., Boonpucknavig V., Boonpucknavig S.: Glomerulitis in typhoid fever — Ann. intern. Med.81, 210, 1974.
Steinman C. R.: Circulating DNA in systemic lupus erythematosus. Association with central nervous system vasculitis — Amer. J. Med.67, 429, 1979.
Stejskal J., Pirani C. L., Okade M., Mandelanakis N., Pollak V. E.: Discontinuities (gaps) of the glomerular capillary wall and basement membrane in renal diseases — Lab. Invest.28, 149, 1973.
Svejgaard A., Morling N., Platz P., Ryder C. P., Thomson M.: HLA disease. In:Fougereau M., Dausset J. (Eds): Immunology 80. Pergamon Press, New York, 1980; p. 530.
Swaak A. J., Aarden L. A., Statius Van Eps L. W., Feltkamp T. E.: Anti-dsDNA and complement profiles as prognostic guides in systemic lupus erythematosus — Arthr. and Rheum.22, 226, 1979.
Takahashi M., Takahashi S., Brade V., Nussenzweig V.: Requirements for the solubilisation of immune aggregates by complement. The role of the classical pathway — J. clin. Invest.62, 349, 1978.
Tarantino A., De Vecchi A., Montagnino G., Imbasciati E., Mihatsch M. J., Zollinger H. O., Di Belgiojoso G. B., Busnach G., Ponticelli C.: Renal disease in essential mixed cryoglobulinaemia. Long-term follow-up of 44 cases — Quart. J. Med.46, 1, 1981.
Theophilopoulos A. N., Dixon F. J.: The biology and detection of immune complexes — Advanc. Immunol.28, 117, 1979.
Thomson N. M., Holdsworth S. R., Glasgow E. F., Atkins R. C.: The macrophage in the development of experimental crescentic glomerulonephritis — Amer. J. Path.94, 223, 1979.
Thomson N. M., Holdsworth S. R., Glasgow E. F., Peters D. K., Atkins R. C.: Mechanisms of injury in experimental glomerulonephritis. In:Kincaid-Smith P., D’Apice A. J. F., Atkins R. C. (Eds): Progress in glomerulonephritis. John Wiley and Sons, New York, 1979; p. 51.
Tikkanen I., Tornroth T., Miettinen A., Fyhrqvist F.: Heymann nephritis — DOCA — NaCl hypertension in the rat. Role of nephritis, DOCA, NaCl and vascular lesions in the development of hypertension — Nephron28, 90, 1981.
Trevillian P., Cameron J. S.: The interaction of antiglomerular basement membrane antibody deposition with immune elimination of bovine serum albumin in the rabbit — Clin. exp. Immunol.35, 338, 1979.
Van Damme B. J. C., Fleuren G. J., Bakker W. W., Vernier R. L., Hoedemaker P. H. J.: Experimental glomerulonephritis in the rat induced by antibodies directed against tubular antigens — Lab. Invest.38, 502, 1978.
Van Es L. A., Block A. P. R., Schoenfeld L., Glassock R. J.: Chronic nephritis induced antibodies reacting with glomerular-bound immune complexes — Kidney int.11, 106, 1977.
Vassalli P., McCluskey R. T.: The pathogenic role of the coagulation process in rabbit Masugi nephritis — Amer. J. Path.45, 653, 1964.
Vermylen J., Defreyn G., Carreras L. O., Machin S. J., Schaeren J. V., Verstraete M.: Thromboxane synthetase inhibition as anti-thrombotic strategy — Lanceti, 1073, 1981.
Walser M.: Ketoacids in the treatment of uraemia — Clin. Nephrol.3, 180, 1975.
Wardle E. N.: The role of platelets in glomerulonephritis and transplantation — J. roy. Coll. Phycns Lond.7, 5, 1972.
Whittle B. J. R., Moncada S., Whiting F., Vane T. R.: Carbacyclin — a potent stable prostacyclin analogue for the inhibition of platelet aggregation — Prostaglandins19, 605, 1980.
Williams R. C.: A second look at rheumatoid factor and other ‘autoantibodies’ — Amer. J. Med.67, 179, 1979.
Wilson C. B.: Nephritogenic antibody mechanisms involving antigens within the glomerulus — Immunol. Rev.55, 257, 1981.
Wilson C. B., Dixon F. J.: The quantitation of acute and chronic serum sickness in the rabbit — J. exp. Med.134, 7s, 1971.
Wilson C. B., Dixon F. J.: The renal response to immunological injury. In:Brenner B. M., Rector F. C. (Eds): The kidney. 2nd ed., W. B. Saunders, Philadelphia, 1981; p. 1237.
Winfield J. B., Faiterman I., Koffler D.: Avidity of anti-DNA antibodies in serum and IgG glomerular eluates from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Association of high avidity antibody with glomerulonephritis — J. clin. Invest.59, 90, 1977.
Wolstenholme G. E. W., Cameron M. P. (Eds): Renal biopsy. Clinical and pathological significance — Ciba Foundation Symposium, London, 1961.
Zimmerman T. S.: The coagulation mechanism and the inflammatory response. In:Miescher P. A., Muller-Eberhard H. E. (Eds): Clinical immunopathology. Grune and Stratton, New York, 1976; p. 95.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Lecture given in Bergamo (Italy) on February 27, 1982, at the Symposium on ‘Pathogenesis of Glomerulonephritis’ devoted to the 300th anniversary of Morgagni’s birth.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cameron, J.S. The pathogenesis of glomerulonephritis. La Ricerca Clin. Lab. 12, 539–564 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02909340
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02909340