Abstract
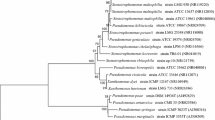
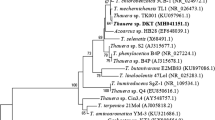
A strain of bacteria able to detoxicate the herbicide diuron in pure culture was isolated from sites contaminated with different urea herbicides. Diuron was used as a sole source of carbon and energy by this isolate which is a Gram-negative, aerobic, rod-shaped bacterium with a single polar flagellum, and grows at 40°C. The strain has been identified asPseudomonas sp.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alva A.K., Singh M.: Sorption of bromacil, diuron, norflurazon, and simazin at various horizons in two soils.Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol.45, 365–374 (1990).
Behki R., Topp E., Dick W., Germon P.: Metabolism of the herbicide atrazine byRhodococcus strains.Appl. Environ. Microbiol.59, 1955–1959 (1993).
Čerňáková M.: Biological degradation of isoproturon, chlortoluron and fenitrothion.Folia Microbiol.40, 201–206 (1995).
Čerňáková M., Ondrovičová M.: Short-run tests for determining harmful effects of PCB-containing engine oils on cells.Folia Microbiol.43, 417–420 (1998).
Čerňáková M., Zemanovićová A.: Microbial activity of soil contaminated with chlorinated phenol derivativesFolia Microbiol.43, 411–416 (1998).
Ditzelmüller G., Loidi M., Streichsbier F.: Isolation and characterization of a 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid-degrading soil bacterium.Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol.31, 93–96 (1989).
El-Dib M.A., Aly O.A.: Persistence of some phenylamide pesticides in aquatic environment hydrolysis.Water Res.10, 1047–1050 (1976).
Engelhard G., Wallnofer P.R., Plapp K.: Identification ofN,O-dimethylhydroxylamine as a microbial degradation product of herbicide linuron.Appl. Microbiol.23, 664–668 (1972).
Fu M.H., Alexander M.: Biodegradation of styrene in samples of natural environments.Environ. Sci. Technol.26, 1540–1544 (1992).
Geissbühler H.: The substituted urea, pp. 79–111 inDegradation of Herbicides (P.C. Kearny, D.D. Kaufman, Eds). Marcel Dekker, New York 1971.
Gerhardt P.R., Murray E.G., Costilow N.R., Nester W.E., Wood A.W., Krieg R.N., Phillips B.G.:Manual of Method for General Bacteriology. American Society for Microbiology, Washington (DC) 1981.
Haugland R.A., Schlemm D.J., Lyons IIIR.P., Sfera P.R., Chakrabarty A.M.: Degradation of the chlorinated phenoxyacetate herbicide 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid by pure and mixed bacterial cultures.Appl. Environ. Microbiol.56, 1357–1362 (1990).
Hassal K.A.:The Biochemistry and Uses of Pesticides, 2nd ed., pp. 440–447. VCH Verlagsgessellschaft, Weinheim 1990.
Kaate H.R., Roberts D.J., Stevens T.O., Crawford L.R., Crawford L.D.: Bioremediation of soils contaminated with herbi-cide 2-sec-butyl-4,6-dinitrophenol (dinoseb).Appl. Environ. Microbiol.58, 1683–1689 (1992).
Kathleen H.B., Adeney A.J.: Residues of diuron and phytotoxic degradation products in aquatic situations. 1. Analytical methods for soil and water.Pestic. Sci.9, 342–353 (1978).
Kerr R.P., Capone D.G.: The effect of salinity on the microbial mineralization of two polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in estuarine sediments.Marine Environ. Res.26, 181–198 (1988).
King R.J., Short K.A., Seider R.J.: Assay for detection and enumeration of genetically engineered microorganisms which is based on the activity of a deregulated 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetate monooxygenase.Appl. Environ. Microbiol.57, 1790–1792 (1991).
Kozak J., Weber J.B.: Adsorption of five phenylurea herbicides by selected soils of Czechoslovakia.Weed Sci.31, 368–372 (1983).
Lang E., Viedt H.: Degradation by and toxicity to bacteria of chlorinated phenols and benzenes, and hexachlorocyclohexane isomers.Microbiol. Ecol.28, 53–65 (1994).
Looa A.M.: Indicator medium for microorganisms degrading chlorinated pesticides.Microbiology21, 104–107 (1975).
McBride E.K., Kenny W.J., Stalker M.D.: Metabolism of the herbicide bromoxynil byKlebsiella pneumoniae subsp.ozœnae.Appl. Environ. Microbiol.52, 325–330 (1986).
Müller D., Gabriel J.: Bacterial degradation of the herbicide bromoxynil byAgrobacterium radiobacter in biofilm.Folia Microbiol.44, 377–379 (1999).
Oh K., Tuovines O.H.: Bacterial degradation of phenoxy herbicide mixtures 2,4-D and MCPP.Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol.47, 1–8 (1991).
Pieper D.H., Reinke W., Engesser K.H., Knacmuss H.J.: Metabolism of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid, 4-chloro-2-methyl-phenoxyacetic acid byAlcaligenes eutrophus JMP 134.Arch. Microbiol.150, 95–102 (1988).
Rickard R.W., Camper N.D.: Degradation of fluometuron byRhizoctonia solani.Pestic. Biochem. Physiol.9, 183–189 (1978).
Roberts J.S., Walker A., Waddington J.M., Welch J.S.: Isolation of a bacterial culture capable of degrading linuron, pp. 51–58 inPesticides in Soils and Water. Current Perspectives (A. Walker, Ed.); BCPC Monograph 47. British Crop Protection Council, Surrey 1991.
Rojas-Avelizapa N.G., Rodríguez-Vázquez R., Martínez-Cruz J., Esparza-García F., Montes de Oca-García A., Ríos-Leal E., Fernández-Villagómez G.: Isolation and characterization of bacteria degrading polychlorinated biphenyls from transformer oil.Folia Microbiol.44, 317–321 (1999).
Shiaris M.P.: Seasonal biotransformation of naphthalene, phenanthrene and benzo(a)pyrene in surficial estuarine sediments.Appl. Environ. Microbiol.55, 1391–1399 (1989).
Skryabin G.K., Golovleva L.A.:Application of Microorganisms in the Organic Synthesis. (In Russian) Nauka, Moscow 1976.
Smith-Greneir L.L., Adkins A.: Degradation of diclofop-methyl by pure cultures of bacteria isolated from Manitoban soils.Can. J. Microbiol.42, 227–233 (1996).
Stanier R.Y., Palleroni J.N., Douderoff M.: The aerobic pseudomonads: a taxonomic study.J. Gen. Microbiol.43, 159–271 (1966).
Tett V.A., Willetts J.A., Lappin-Scott M.H.: Enantioselective degradation of the herbicide mecoprop [2-(methyl-4-chlorophenoxy)propionic acid] by mixed and pure cultures.FEMS Microbiol. Ecol.14, 191–200 (1994).
Ward D.M., Brock T.D.: Hydrocarbon biodegradation in hypersaline environments.Appl. Environ. Microbiol.35, 353–359 (1978).
Ware G.W.:Theory and Application, p. 321. W.H. Freeman & Co., San Francisco 1983.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
El-Deeb, B.A., Soltan, S.M., Ali, A.M. et al. Detoxication of the herbicide diuron byPseudomonas sp.. Folia Microbiol 45, 211–216 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02908946
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02908946