Summary
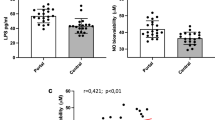
The purpose of the present study was to assess the correlation that likely exists among increased portal pressure (Pp), portal blood flow quantity (Qp) and ETA and ETB receptor mRNA expression in human cirrhosis.In situ hybridization and reverse-transcription polymerase chain reactions (RT-PCR) were performed to determine the expression of ETA and ETB receptor mRNA in liver tissues from traumatic subjects (n=10) and cirrhotic patients (n=15) in whom hepatic hemodynamic values were measured. The expression of the two transcripts was significantly higher in liver samples of cirrhotic patients than in those obtained from traumatic subjects. It has shown that ETA receptor mRNA predominantly located in hepatic stellate cells (HSCs) and vascular smooth muscle cells of intrahepatic arteries and portal veins, ETB receptor mRNA in HSCs, sinusoidal endothelial cells and Kuppfer cells. There was a highly significant direct relationship between ETA and ETB receptor mRNA and Pp and Qp in cirrhotic patients. It suggests that liver paracrine endothelin system may be overactivated in human cirrhosis accompanied with increased expression of ETA and ETB receptor mRNA which may play an important role in the pathogenesis and maintenance of splanchnic hyperdynamics.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sakurai T, Yanagisawa M, Masaki T. Molecular characterization of endothelin receptors. Trends Pharmacol Sci, 1992, 13: 103
Ohlstein E H, Elliott J D, Feuerstein G Zet al. Endothelin receptors: receptor classification, novel receptor antagonists and potential therapeutic targets. Med Res Rev, 1996, 16: 365
Bernardi M, Gulberg V, Colantoni Aet al. Plasma endothelin-1 and-3 in cirrhosis: relationship with systemic hemodynamics, renal function and neurohumoral systems. J Hepatol, 1996, 24: 161
Veglio M, Pinna C, Melchio Ret al. Plasma endothelin levels in cirrhotic subjects. J Hepatol, 1992, 15: 85
Cardillo C, Kilcoyne C M, Waclawiw Met al. Role of endothelin in the increased vascular tone of patients with essential hypertension. Hypertension, 1999, 33: 753
Hosoda K, Nakao K, Arai Het al. Cloning and expression of human endothelin-1 receptor cDNA. FEBS Lett, 1991, 289: 23
Ogawa Y, Nakao K, Arai Het al. Molecular cloning of a non-isopeptide selective human endothelin receptor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 1991, 178: 248
Pinzani M, Milani S, De Franco Ret al. Endothelin-1 is overexpressed in human cirrhotic liver and exerts multiple effects on actived hepatic stellate cells. Gastroenterology, 1996, 110: 534
Gandhi C R, Sproat L A, Subbotin V M. Increased hepatic endothelin-1 levels and endothelin receptor density in cirrhotic rats. Life Sci, 1995, 58: 55
Sakamoto M, Ueno T, Kin Met al. Ito cell contraction in response to endothelin-1 and substance P. Hepatology, 1993, 18: 978
Rockey D C, Weisiger R A. Endothelin induced contractility of stellate cells from normal and cirrhotic rat liver: implications for regulation of portal pressure and resistance. Hepatology, 1996, 24: 233
Housset C, Rockey D C, Bissell D M Endothelin receptors in rat liver: Lipocytes as a contractile target for endothelin 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 1993, 90: 9266
Pinzani M, Filli P, Ruocco Cet al. Fat-storing cells as liver specific pericytes: Spatial dynamics of agonist-stimulated intracellular calcium transients. J Clin Invest, 1992, 90: 642
Jouneaux C, Mallat A, Serradeit Le Gal Cet al. Coupling of endothelin B receptors to the calcium pump and phospholipase C via Gs and Gq in rat liver. J Biol Chem, 1994, 269: 1845
Friedman S Let al. The cellular basis of hepatic fibrosis. New Engl J Med, 1993, 328: 1828
Rockey D C, Chung J J Endothelin antagonism in experimental hepatic fibrosis: implications for endothelin in the pathogenesis of wound healing. J Clin Invest, 1996, 96(6): 1381
Sogni P, Moreau R, Gomola Aet al. Beneficial hemodynamic effects of bosentan, a mixed ETA and ETB receptor antagonist, in portal hypertensive rats. Hepatology, 1998, 28: 655
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
DENG Xiaorong, male, born in 1967, M. D., Ph.D
This project was supported by a grant from national Natural Scienc Foundation of China (No. 39470685).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xiaorong, D., Zhen, Y. Increased expression of endothelin receptors in human cirrhosis —Relationship with splanchnic hemodynamics. Current Medical Science 22, 37–41 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02904784
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02904784