Abstract
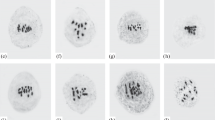
Progenies were raised from seeds ofLens esculenta L., cultivar JLS-3 treated with 0.03%, 0.09%, 0.16% and 0.26% (by volume) aqueous solutions of EMS, MES and MMS. Meiotic ohromosomes were studied from anthersmears. Ring and chain configurations of chromosomes were found more abundant with higher doses of mutagens particularly those of EMS. Chromosome bridges and multinucleolate nuclei were also frequently seen.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- EMS:
-
ethyl methanesulphonate
- MES:
-
methyl ethanesulphonate
- MMS:
-
methyl methanesulphonate
References
McClintock, W. B.: The relation of particular chromosomal element to the development of nucleoli inZea mays. - Zellforsoh. Anat.21: 294–328, 1934.
Razarietblva, E. K., Belbskii, Y. D., Zhdanov, A.: The genetical nature of mutation induced by N-nitroso-N-methyl urea in sunflower, variegated leaf forms. - Genetika6: 102–107, 1970.
Siddiq, E. A.: Cytogenetical effects of physical and chemical mutagens in rice. - Ind. J. Genet.33: 162–173, 1973.
Todabova, G. Y.: X-ray influence on chromosome aberration inHelianthus annuus. - Genet. Plant Breed.2: 269–276, 1969.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chaghtai, S.A., Hasan, Z. Effect of EMS, MES and MMS on the chromosomal behaviour ofLens esculenta during microsporogenesis. Biol Plant 21, 280–283 (1979). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02902210
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02902210