Abstract
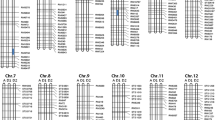
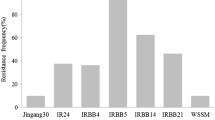
Ricexa5 gene provides recessive, race-specific resistance to bacterial blight disease caused by the pathogenXanthomonas oryzae pv.oryzae and has great value for research and breeding. In an effort to clonexa5, an F2 population of 4892 individuals was developed from thexa5 near isogenic lines, IR24 and IRBB5. A fine mapping procedure was conducted and tightly linked RFLP markers were used to screen a BAC library of IRBB56, a resistant rice line containing thexa5 gene. A 213 kb contig covering thexa5 locus was constructed. According to the sequences from the International Rice Genome Sequening Project (IRGSP), the Chinese Superhybrid Rice Genome Project (SRGP) and some sub-clones of the contig, twelve SSLP and CAPS markers were developed for fine mapping. Thexa5 gene was mapped to a 0.3 cM interval between markers K5 and T4, which spanned an interval of approximately 24 kb, co-segregating with marker T2. Sequence analysis of the 24 kb region revealed that an ABC transporter and a basal transcription factor (TFIIa) were potential candidates for thexa5 resistance gene product. The molecular mechanism by which thexa5 gene provides recessive, race-specific resistance to bacterial blight will be elucidated by the functional tests of the 24 kb DNA and the candidate genes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Flor, H. H., Host-parasite interaction in flax rust—its genetics and other implications, Phytopathology, 1955, 45: 680–685.
Staskawicz, B. J., Mudgett, M. B., Dangl, J. L. et al., Common and contrasting themes of plant and animal diseases, Science, 2001, 292: 2285–2290.
Song, W. Y., Wang, G. L., Chen, L. L. et al., A receptor kinase-like protein encoded by the rice disease resistance gene,Xa21, Science, 1995, 279: 1804–1806.
Yoshimura, S., Yamanouchi, U., Katayose, Y. et al., Expression ofXa1, a bacterial blight-resistance gene in rice, is induced by bacterial inoculation, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 1998, 95: 1663–1668.
Wang, W. M., Zhai, W. X., Luo, M. Z. et al., Chromosome landing at the bacterial blight resistance geneXa4 locus using a deep coverage rice BAC library, Molecular General Genetics, 2001, 265: 118–125.
Sun, X., Yang, Z., Wang, S. et al., Identification of a 47-kb DNA fragment containingXa4, a locus for bacterial blight resistance in rice, Theor. Appl. Genet., 2003, 106(4): 683–687.
Huang, N., Augetes, E. R., Domingo, J. et al., Pyramiding of bacterial blight resistance genes in rice: Marker-assisted selection using RFLP and PCR, Theor. Appl. Genet., 1997, 95: 313–320.
Li, Z. K., Sanchez, A., Angeles, E. et al., Are the dominant and recessive plant disease resistance genes similar? A case stude of rice R genesand Xanthomonas oryzaepv. Oryzae races, Genetics, 2001, 159: 757–765.
McCouch, S. R., Abenes, M. L., Angeles, R. et al., Molecular tagging of a recessive gene,xa5, for resistance to bacterial blight of rice, Rice Genet. Newsl., 1992, 8: 143–145.
Blair, M. W., McCouch, S. R., Micresatellite and sequence tagged site markers diagnostic for the rice bacterial leaf blight resistance genexa5, Theor. Appl. Genet., 1997, 95: 174–184.
Yang, D., Sanchez, A., Khush, G. S. et al., Construction of a BAC contig containingthe Xa5 locus in rice, Theor. Aappl. Genet., 1998, 97: 1120–1124.
Blair, M. W., Garris, A. J., Iyer, I. S. et al., High resolution genetic mapping and candidate gene identification at the xa5 locus for bacterial blight resistance in rice (Oryza sativa L.), Theor. Appl. Genet., 2003, 107: 62–73.
McCouch, S. R., Kotcket, G. Yu, Z. H. et al., Molecular mapping of rice chromosome, Theror. Appl. Genet., 1988, 76: 815–829.
Sambrook, J., Fritsch, E. F., Maniatis, T., Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual, 2nd ed., New York: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, 1989.
Harushima, Y., Yano, M., Shomura, A. et al., A high-density rice genetic linkage map with 2275 markers using a single F2 poulation, Genetics, 1998, 148: 479–494.
Markus, K., Laetitia, P. B., Annie, F. et al., The plant multidrug resistance ABC transporter AtMRP5 is involved in guard cell hormonal signaling and water use, The Plant Journal, 2003, 33: 119–129.
Li, Y. F., Le, G. J., Torki, M. et al., Characterization and functional analysis ofArabidopsis TFIIA reveal that the evolutionarily unconserved region of the large subunit has a transcription activation domain, Plant Mol. Biol., 1999, 39(3): 515–525.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Persons providing the equal contribution to this work
About this article
Cite this article
Zhong, Y., Jiang, G., Chen, X. et al. Identification and gene prediction of a 24 kb region containingxa5, a recessive bacterial blight resistance gene in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Chin. Sci. Bull. 48, 2725–2729 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02901764
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02901764