Abstract
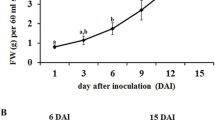
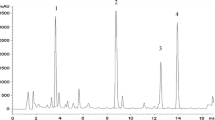
Strong anti-inflammatory saponinsPhytolacca americana (Phytolaccaceae) were obtained from callus mass derived from the stems and also from that derived from the roots of cultivatedPhytolacca americana (which were designated as PAS and PAR, respectively). The callus were grown on Linsmair and Skoog's agar medium supplemented with 1ppm of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid. Phytolaccoside B and D were obtained from PAS and phytolaccoside A and B from PAR. The thin layer chromatograms of the crude saponins from PAS and PAR were similar to those of original plants. PAS contained phytolaccoside B as a major component while phytolaccoside E was a major saponin in original plants.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature Cited
W.S. Woo, K.H. Shin and S.S. Kang:Kor. J. Pharmacog. 7(1), 47 (1976).
W.S. Woo, S.S. Kang,et al.:Planta Medica. 34, 87 (1978).
W.S. Woo and S.S. Kang:J. Pharm. Soc. Korea,21, 159 (1977).
W.S. Woo, Hyung Joon Chi and S.S. Kang:Kor. J. Pharmacog. 7(1), 51 (1976).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chi, H.J., Kim, H.S. Saponins from the callus mass ofPhytolacca americana . Arch. Pharm. Res. 8, 15–20 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02897561
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02897561