Abstract
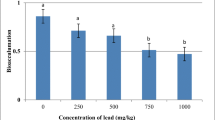
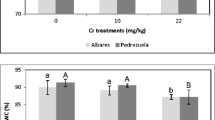
The responses of barley and wheat seedlings to lead and cadmium ions in relation to the concentration and duration of treatment were studied. Both metals inhibited seed germination and growth of roots and shoots, but the toxic effect of cadmium was observed at lower concentrations. Inhibition of seedling growth was already recorded already within a day after the beginning of the treatment, and then increased further. The sensitivity of the processes studied to both the metals decreased in the order: root growth, shoot growth and seed germination. The resistance of barley and wheat to lead was similar, whereas the resistance to cadmium was higher in barley
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Burzynski, M.: The influence of lead and cadmium on the absorption and distribution of potassium, calcium, magnesium and iron in cucumber seedlings. - Acta Physiol. Plant.9: 229–238, 1987.
Foy, C.D., Chaney, R.L., White, M.C.: The physiology of metal toxicity in plants. - Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol.29:511–566, 1978.
Il’in, V.B., Garmash, G.A., Garmash, N.Yu.: [Effect of heavy metals on growth, development and productivity of agricultural crops.] - Agrokhimiya6: 90–100, 1985. [In Russ.]
Ivanov, V.B., Bystrova, E.I., Yakovlev, K.I., Rozhkova, N.D., Stetsenko, A.I., Adamov, O.M.: [Growth inhibiting and cytostatic activities of triamine platinum II complexes with heterocyclic amines] - Izv. Ros. Akad. Nauk Ser. biol.6: 898–907, 1992. [In Russ.]
Kobbia, T.E., Ibrahim, A.: Tolerance of different plant species to cadmium. - Egypt. J. Soil Sci.28: 9–22, 1988.
Malone, C., Koeppe, D.E., Miller, R.J.: Localization of lead accumulated by corn plants. - Plant Physiol.53:388–394, 1974.
Mewly, P., Rauser, W.D.: Alteration on thiol pools in roots and shoots of maize seedlings exposed to cadmium. - Plant Physiol.99: 8–15, 1992.
Nishizono, H., Kubota, K., Suzuki, S., Ishii, F.: Accumulation of heavy metals in cell walls ofPolygonum cuspidatum roots from metalliferous habitats. - Plant Cell Physiol.30: 595–598, 1989.
Poschenrieder, G., Gunse, B., Barcelo, J.: Early effects of cadmium on water relations in bean plants. -Physiol. Plant.79 (2, Part 2): A170, 1990.
Rauser, W.E.: Phytochelatins. - Annu. Rev. Biochem.59: 61–86, 1990.
Steffens, J.C.: The heavy metal-binding peptides of plants. - Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. Plant mol. Biol.41: 553–575, 1990.
Stiborová, M., Doubravová, M., Brezinová, A., Friedrich, A.: Effect of heavy metal ions on growth and biochemical characteristics of photosynthesis of barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). - Photosynthetica20: 418–425, 1986.
Wilkins, D.A.: A technique for the measurement of lead tolerance in plants. - Nature180: 37–38, 1957.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Acknowledgements: This work was partly supported by the Russian Fundamental Research Foundation (Grant N 94-04-12981)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Titov, A.F., Talanova, V.V. & Boeva, N.P. Growth responses of barley and wheat seedlings to lead and cadmium. Biol Plant 38, 431–436 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02896675
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02896675