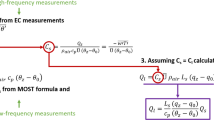
Abstract
Based on the drop size distribution models built from the observational data of microphysical properties of water clouds, the relationships between the optical properties and microphysical characteristics of water clouds have been investigated, and some different parameterization schemes of cloud optical properties have been analyzed. It is found that with the parameterization scheme, in addition to the equivalent radius, also including the mean radius of cloud droplet size distribution, the role of small cloud drops might be able to be considered more properly and better accuracies of parameterization calculation of cloud optical properties can be obtained, compared with that of using only the equivalent radius as parameter.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cess, R. D., Potter, G. L., Blanchet, J. P.et al., Intercomparison and interpretation of climate feedback processes in 19 atmospheric general circulation models,J. Geophys. Res., 1990, 95: 16601.
Slingo, A., Schrecker, H. M., On the shortwave radiative properties of stratiform water clouds,Quart J. R. Met. Soc., 1982, 108: 407.
Slingo, A., A GCM parameterization for the shortwave radiative properties of water clouds,J. Atmos. Sci., 1989, 46: 1419.
Hu, Y. X., Stamnes, K., An accurate parameterization of the radiative properties of water clouds suitable for use in climate models,J. Climate, 1993, 6: 728.
Asano, S., Shiobara, M., Nakanishi, Y.et al., Western North-Pacific Cloud-Radiation Experiment,Progress Report of WCRP in Japan, 3.Clouds and Radiation, Nagoya Univ. Sept. 1992, 19–49.
Stephens, G. L., Radiation profiles in extended water clouds, I. Theory,J. Atmos. Sci., 1978, 35: 2111.
Welch, R. M., Cox, S. K., Davis, J. M., Solar radiation and clouds,Meteorological Monograph 17, American Meteorological Society, 1980, 3–42.
Chylek, P., Damiano, P., Polynomial approximation of the optical properties of water clouds in 8–12 μm spectral region,J. Appl. Meteor., 1992, 31: 1210.
Hunt, G. E., Radiative properties of terrestiral clouds at visible and infrared thermal window wavelengths,Quart, J. Roy. Met. Soc., 1973, 99: 346.
Perez, C. A., Martinez, D., Petrov, V. V., Microstructure, mixing and turbulence in cumulus clouds over Cuba and the Caribbean Sea, inProceedings of WMO Workshop on Cloud Microphysics and Applications to Global Change, WMP Report No. 19, 10–14 Aug. Toronto, Canada, 1992, 245–256.
Leaitch, W. R., Johnson, D. W., Korolev, A. V., Panel report on data summaries, inProceedings of WMO Workshop on Cloud Mimphysics and Applications to Global Change, WMP Report No. 19, 10–14 Aug. Toronto, Canada, 1992, 301–307.
Gu Fuyin, Ma Peiming, You Laiguanget al., Research on low clouds in Junggar Basin, inProceedings of National Cloud Physics and Weather Modification Conference (in Chinese), Beijing: Meteorological Press, 1989, 18–23.
Wu Dui, The microphysical characteristics of precipitus stratiform clouds in summer in Ningxia, inProceedings of National Cloud Physics and Weather Modification Conference (in Chinese), Beijing: Meteorological Press, 1989, 24–34.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, H., Zhao, G. Parameterization for narrow band shortwave optical properties of water clouds. Chin.Sci.Bull. 44, 277–280 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02896293
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02896293