Summary
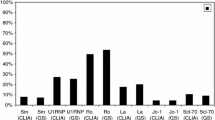
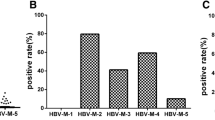
The solid phase C1q-binding assay has been adapted to an enzymatic micromethod in which alkaline phosphatase labeled solubleStaphylococcus aureus protein A is used in place of the second antibody. The assay, which is run in microtiter plates, provides a rapid, sensitive (0.030 mg/ml of human heat-aggregated IgG detected) and reproducible method for the measurement of soluble immune complexes in a large number of samples. Soluble immune complexes preparedin vitro with bovine serum albumin (BSA) and anti-BSA antibodies on a wide range of antigen to antibody ratios were all detected with this method. When applied to the screening of unselected patient sera, soluble immune complexes were frequently found in systemic lupus erythematosus (52%) and chronic active hepatitis (57%) and in lower percentages in patients with malignant melanoma (28%), rheumatoid arthritis (30%) and essential mixed cryoglobulinemia (17%).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cochrane C. G., Koffler D.: Immune complex disease in experimental animals and man. In:Dixon F. J., Kunkel H. G. (Eds): Advances in immunology. Academic Press, New York, 1973; p. 186.
Engvall E., Perlmann P.: Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, ELISA. III. Quantitation of specific antibody enzyme-labeled-anti-immunoglobulin antigen-coated tubes — J. Immunol.109, 129, 1972.
Hay F. C., Nineham L. J., Roitt I. M.: Routine assay for detection of immune complexes of known immunoglobulin class using solid phase C1q — Clin. exp. Immunol.28, 40, 1976.
Hunt J. S., Kennedy M. P., Barber K. E., McGiven A. R.: A microplate adaptation of the solid phase C1q immune complex assay — J. immunol. Meth.33, 267, 1980.
Lambert P. H., Dixon F. J., Zubler R. H., Agnello V., Cambiaso C., Casali P., Clarck J., Cowdery J. S., McDuffie F. C., Hay F. C., MacLennan I. C. M., Masson P. L., Müller-Eberhard H. J., Penttinen K., Smith M., Tappeneiner G., Theofilopoulos A. N., Verroust P.: A WHO collaborative study for the evaluation of eighteen methods for detecting immune complexes in serum — J. clin. lab. Immunol.1, 1, 1978.
Lawley T. J., Gorevic P. D., Hamburger M. I., Franklin E. C., Frank M. M.: Multiple types of immune complexes in patients with mixed cryoglobulinemia — J. invest. Derm.75, 297, 1980.
Natali P. G., Cordiali Fei P.: Metodi per la determinazione di immunocomplessi solubili. (Il test di legame di125I-C1q) — La Ricerca Clin. Lab.7 (Suppl. 2), 1, 1977.
Nydegger U. E., Lambert P. H., Gerber H., Miescher P. A.: Circulating immune complexes in the serum of SLE and in carriers of hepatitis B antigen — J. clin. Invest.54, 297, 1974.
Stanworth D. R., Turner M. W.: Immunochemical analysis of immunoglobulins and their subunits. In:Weir D. M. (Ed.): Handbook of experimental immunology. Blackwell Sci. Publ., Oxford, 1979; vol. 1, chapt. 6.1.
Svehag S. E.: A solid phase radioimmunoassay for C1q binding immune complexes — Scand. J. Immunol.4, 687, 1978.
Theofilopoulos A. N., Andrews B. S., Urist M. M., Morton D. L., Dixon F. J.: The nature of immune complexes in cancer sera — J. Immunol.119, 657, 1977.
Theofilopoulos A. N., Dixon F. J.: The biology and detection of immune complexes. In:Dixon F. J., Kunkel H. G. (Eds): Advances in immunology. Academic Press, New York, 1979; p. 89.
Theofilopoulos A. N., Wilson C. B., Dixon F. J.: The Raji cell radioimmunoassay for detecting immune complexes in human sera — J. clin. Invest.57, 169, 1976.
Wilson C. B., Dixon F. J.: Quantitation of acute and chronic serum sickness — J. exp. Med.134, 7s, 1971.
Yonemasu K., Stroud R. M.: C1q rapid purification method for preparation of monospecific antisera and for biochemical studies — J. Immunol.106, 304, 1971.
Zubler R. H., Lambert P. H.: Detection of immune complexes in human diseases — Progr. Allergy24, 89, 1979.
Zubler R. H., Lange G., Lambert P. H., Miescher P. A.: Effect of heating on the binding of C1q by immune complexes and application of the test to systemic lupus erythematosus — J. Immunol.116, 232, 1976.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This study was supported in part byConsiglio Nazionale delle Ricerche (CNR), Roma, Italy, ‘Progetto Finalizzato Controllo della Crescita Neoplastica’, grant no. 80.01599.96.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fei, P.C., Natali, P.G. A C1q solid phase microenzymatic assay for the detection of soluble immune complexes. La Ricerca Clin. Lab. 11, 207–214 (1981). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02890526
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02890526