Abstract
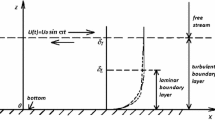
A theoretical expression for vertical profile of horizontal velocity in tenns of its depth-average is derived based on oscillatory boundary layer theory and estuarine flow characteristics. The derived theoretical profile is then incorporated into a vertical quasi-two-dimensional model, which is proved advantageous in more physical implications and less CPU time demand. To validate the proposed model, the calculated results are compared to the field data in the Yangtze River Estuary, exhibiting good agreement with observations. The proposed quasi-two-dimensional vertical model is used to study mixing process, especially dependence of salinity distribution and salt front strength on runoff and tides in estuaries.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mao, Z., A study on salt fronts in the Changjiang River Estuary,Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica (in Chinese), 1995, 26(5): 643.
Grubert, J. P., Interfacial mixing in stratified channel flows,J. Hydr. Div. ASCE, 1989, 115(7): 887.
Grubert, J. P., Interfacial mixing in estuaries and fjords,J. Hydr. Engrg., 1990, 116(2): 176.
Kurup, G. R., Hamilton, D. P., Patterson, J. C., Modeling the effect of seasonal flow variations on the position of salt wedge in a microtidal estuary,Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 1998, 47: 191.
Han, Z., Shao, Y., Lu, X. et a1., Numerical and experimental predictions of salt water intrusion in estuaries, inProceedings of 6th Conference on Computational Fluid Dynamics (in Chinese), Beijing: Science Press, 1992: 331.
Zhou, H., A study on characteristics of maximum turbidity zone in the Changjiang River Estuary and three-dimensinal numerical modeling of flow and sediment transport,Doctoral Thesis (in Chinese), Nanjing: Hohai University, 1992.
Kuang, C., A study on changes of mouth bar and suspended sediment settlement in the Chanejiang River Estuary and mathematical model for flow and transport of salinity and sediment,Doctoral Thesis (in Chinese), Nanjing: Nanjing Institute of Water Conservancy, 1993.
Bloss, S., Lehfeldt, R., Patterson, J. C., Modeling turbulent transport in stratified estuary,J. Hydr. Engin., ASCE, 1998, 114(9): 1115.
Jin, X., Krennhurg, C., Quasi-3D numerical modeling of shallow-water circulation,Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 1993, 119(4): 458.
Irene, K., Jan, S. R., Quasi-3D modeling of suspended sediment transport by currents and waves.Coastal Engineering. 1992, 18: 83.
Collins, M. B., Ke, X., Gao, S., Tidally- induced flow structure over intertidal flats,Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 1998, 46: 233.
Nielsen, P., Coastal bottom boundary layers and sediment transport,Advanced Series on Ocean Engineering, Vol. 4, Printed in Singapore by JBW Printers & Binders Pte. Ltd., 1992.
Wang, Y., Zhang, Z., Hydrochemical characteristics and clay minerals of suspended sediment in South Channel, Changjiang Estuary,Marine Science Bulletin (in Chinese), 1995, 14(3): 106.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Project supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 59879025), the National Climbing Project of the Ministry of Science and Technology of China and the Director Foundation of Institute of Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, J., Liu, Q. & Li, J. Mixing process in estuaries. Sci. China Ser. A-Math. 42, 1110–1120 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02889514
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02889514