Abstract
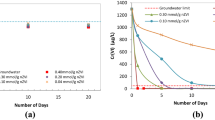
Groundwater remediation by nanoparticles has received increasing interest in recent years. This report presents a thorough evaluation of hexavalent chromium removal in aqueous solutions using iron (Feo) nanoparticles. Cr(VI) is a major pollutant of groundwater. Zero-valent iron, an important natural reductant of Cr(VI), is an option in the remediation of contaminated sites, transforming Cr(VI) to essentially nontoxic Cr(III). At a dose of 0.4 g/L, 100% off Cr(VI) (20 mg/L) was degraded. The Cr(VI) removal efficiency decreased significantly with increasing initial pH. Different Feo type was compared in the same conditions. The reactivity was in the order starch-stabilized Feo nanoparticles>Feo nanoparticles>Feo powder>Feo filings. Electrochemical analysis of the reaction process led to the conclusion that Cr(OH)3 should be the final product of Cr(VI). Iron nanoparticles are good choice for the remediation of heavy metals in groundwater.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alowitz, M.J., Scherer, M.M., 2002. Kinetics of nitrate, nitrite, and Cr(IV) reduction by iron metal.Environ. Sci. Technol.,36:299–306.
Bowman, R.S., 2003. Applications of surfactant-modified zeolites to environmental remediation.Microporous and Mesoporous Materials,61:43–56.
Buerge, I.J., Hug, S.J., 1999. Influence of mineral surfaces on chromium(VI) reduction by iron(II).Environ. Sci. Technol.,33:4285–4291.
Chen, J.M., Hao, O.J., 1998. Microbial chromium(IV) reduction.Critical Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol.,28:219–251.
He, F., Zhao, D., 2005. Preparation and characterization of a new class of starch-stabilized bimetallic nanoparticles for degradation of chlorinated hydrocarbons in water.Environ. Sci. Technol.,39:3314–3320.
Hideaki, Y., Toshiiyuki, Y., Takashi, T., 2002. Adsorption of chromate and arsenate by amino-functionalized MCM-41 and SBA-1.Chem. Mater.,14:4603–4610.
Hua, B., Deng, B., 2003. Influences of water vapor on Cr(VI) reduction by gaseous hydrogen sulfide.Environ. Sci. Technol.,37:4771–4777.
Lee, T., Lim, H., Lee, Y., Park, J., 2003. Use of waste iron metal for removal of Cr(VI) from water.Chemosphere,53:479–485.
Ponder, S.M., Darab, J.G., Mallouk, T.E., 2000. Remediation of Cr(VI) and Pb(II) aqueous solutions using supported, nanoscale zero-valent iron.Environ. Sci. Technol.,34:2564–2569.
Powell, R.M., Puls, R.W., Hightower, S.K., Sabantini, D.A., 1995. Coupled iron corrosion and chromate reduction: mechanisms for subsurface remediation.Environ. Sci. Technol.,29:1913–1922.
Pratt, A.R., Blowes, D.W., Ptacek, C.J., 1997. Products of chromate reduction on proposed subsurface remediation material.Environ. Sci. Technol.,31:2492–2498.
Raveendran, P., Fu, J., Wallen, S.L., 2003. Complete “green” synthesis and stabilization of metal nanoparticles.J. Am. Chem. Soc.,125:13940–13941.
Ruiz, N., Seal, S., Reinhart, D., 1995. Surface chemical reactivity in selected zero-valent iron samples used in groundwater remediation.Journal of Hazardous Materials,B80:107–117.
Wei, J.J., Xu, X.H., Liu, Y., 2004. Kinetics and mechanism of dechlorination ofo-chlorophenol by nanoscale Pd/Fe.Chem. Res. Chinese U.,20:73–76.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Project (No. 20407015) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shao-feng, N., Yong, L., Xin-hua, X. et al. Removal of hexavalent chromium from aqueous solution by iron nanoparticles. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 6, 1022–1027 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02888495
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02888495