Summary
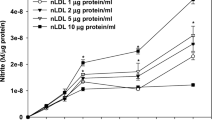
Serum low-density lipoprotein (LDL) and high-density lipoprotein (HDL) were prepared by gradient ultracentrifugation. Cholesterol and lipid peroxide of the two lipoproteins wers determined. Human umbilical vein endothelial cells were cultured in lipoprotein-deficient serum media with LDL or HDL added. The release of 6-keto-PGF1α in the media was measured by radioimmunoassay. The morphological changes were observed under phase-contrast and electron microscope. Endothelial cells injured by LDL (100–600 cholesterol ug/ml) showed contraction (reversible), rounding-up, lysis and detachment from the surface of culture bottle (irreversible) respectively. The cellular ultrastructure was also damaged. The severity of cell injury was correlated with the concentration of LDL-cholesterol and the time of action. The synthesis of prostacyclin (PGI2) was stimulated by HDL, and inhibited by LDL, in culture (P< 0.01). A close relationship between morphological injury and decrease in PGI2 synthesis induced by LDL was demonstrated. The injury of endothelial cells induced by LDL was supposed to be due to the increase in lipid peroxide. The results of this study showed that the noxious effect of LDL on morphology and PGI2 synthesis may play an important role in thrombogenesis and atherosclerosis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Michael A, et al. Vascular endothelium and atherosclerosis. In: Sean Moore eds. Vascular injury and atherosclerosis. Marcel Dekker Inc., New Ycrk, Easel 1981; 25–52.
Mason RG, et al. The endothelium: roles in thrombosis and hemostasis. Arch Pathol Lab Med 1977;101:61–4.
Wissler RW, et al. Abnormalities of the arterial wall and its metabolism in atherogenesis. Prog Cardiovasc Dis 1976;18:341–69.
Miller GJ, Miller NE. Plasma-high-density-lipoprotein concentration and development of ischaemic heart-disease. Lancet 1975;1:16–9.
Nordϕy A, et al. Liporroteins and the inhibitory effect of human endothelial cells on platelet function. Cir Res 1978;43:527–34.
Fleisher LN, et al. Stimulation of arterial endothelial cell prostacyclin synthesis by high density lipoprotein. J Eiol Chem 1982;257:6653–5.
Jaffe EA, et al. Culture of human endothelial cells derived from umbilical veins. Identification by morphologic and immunologic criteria. J Clin Invest 1973; 52:2745–56.
Chung EH, et al. Preparative and quantitative isolation of plasma Jipoproteins: rapid, single discontinuous density gradient ultracentrifugation in a vertival rotor. J Lipid Res 1980;21:284–91.
1981;29:221.
1984;4(2):93–5.
Henriksen T, et al. Injury to human endothelial cells in culture induced by low density lipoproteins. Scand J Clin Lab Invest 1979;39:361–8.
Hessler JR, et al. LDL-induced cytotoxicity and its inhibition by HDL in human vascular smooth muscle and endothelial cells in culture. Atherosclerosis 1979;32:213–29.
Tauber JP, et al. Effect of high and low density lipoproteins on proliferation of cultured bovine vascular endothelial cells. J Clin Invest 1980;66:696–708.
Neri-Serneri GG, et al. Prostacyclin, thromboxane, and ischemic heart disease. Atherosclerosis Reviews, New York, Raven Press, 1981;8:139–57.
Masotti G, et al. Early changes of the endothelial antithrombotic properties in cholesterol fed rabbits:I. Decreased PGI2 production by aortic wall. Thrombos Haemostas 1979;42:423.
Beitz J, Förster W. Influence of human low density and high density lipoprotein cholesterol on the in vitro prostaglandin I2 synthetase activity. Biochim Biophys Acta 1980;620:352–5.
Evensen SA, et al. LDL-induced cytotoxicity and its inhibition by anti-oxidant treatment in cultured human endothelial cells and fibroblasts. Atherosclerosis 1983;49:23–30.
Nordϕy A, et al. The effect of lipoproteins on the synthesis of prostacyclin, von Willebrand factor and apolipoproteins A-I and A-I in cultured human endothelial cells. Atherosclerosis 1984;50:307–23.
Szczeklik A, et al. Serum lipoproteins lipid peroxides and prostacyclin biosynthesis in patients with coronary heart disease, Prostaglandins 1981;22:795–807.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shao-ming, W., Wen-hua, R. & Zhen-yi, W. Effects of LDL and HDL on morphology of and prostacyclin synthesis in cultured vascular endothelial cells. Journal of Tongji Medical University 7, 123–129 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02888174
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02888174