Summary
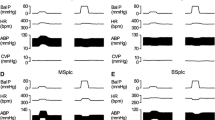
The rabbits anaesthetized with urethane were made hyperthermic under heat stress. Effect of naloxone injected intracerebroventricularly on arterial baroreflex sensitivity (ABS) was investigated. The experimental animals were divided into two groups: the control and the naloxone-treated group. ABS decreased stepwisely in the control group when rectal temperature rose to over 40 °C. Mean arterial pressure (MAP) dropped markedly beyond 42°C. However, in the naloxone-treated group, ABS showed no significant change temperature reached 42°C. but it decreased dramatically at 43°C. Then, MAP was still maintained at about 90 mmHg. The results suggested that the marked reduction of ABS during hyperthermia might be related to endogenous opioid release.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gribbin B, et al. Effect of age and high blood pressure on baroreflex sensitivity in man. Circ Res 1971;29:424–30.
Conway J, et al. Involvement of the baroreceptor reflexes in the changes in blood pressure with sleep and mental arousal. Hypertension 1983;5:746–8.
Faris IB, et al. Effect of exercise on gain of the carotid-sinus reflex in rabbits. Clin Sci 1983;63:115–9.
Mc Ritchie RJ, et al. Role of arterial baroreceptors in mediating cardiovascular response to exercise. Am J Physiol 1976;230:85–9.
Nunomura T, et al. Effect of restraint on baroreflex sensitivity in altering heart rate and heat production in rats. Jpn J Physiol 1983;33:667–70.
Carretta T, et al. Baroreflex function after therapy withdrawal in patients with essential hypertension. Clin Sci 1983; 64:259–63.
Corman AJ, et al. Influence of heat stress on arterial baroreflex control of heart rate in the baboon. Circ Res 1982; 51:73–81.
Fraioli F, et al. Physical exercise stimulates marked concomitantly release of beta-endorphin and adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) in peripheral blood in man. Experientia 1980;36:987–95.
Roger Guillemin, et al. β-endorphin and adrenocorticotropin are secreted concomitantly by the pituitary gland. Science 1977;197:1367–9.
1985;1(3):191–6.
Yang K, et al. Effect of hyperthermia induced by environmental heat stress on vascular interoceptor reflexes. Acta Acad Med Wuhan 1985;5:86–91.
Newman PP, et al. Cardiovascular and respiratory responses to heating the carotid blood. J Physiol (London) 1960; 152:87–92.
Holmes RL, et al. A heat-sensitive region in the medulla. J Phyriol (London) 1960;152:93–8.
Petty MA, Reid JL. The effect of opiates on arterial baroreceptor reflex function in the rabbit. Naunyn Schmiedeberg’s Arch Pharmacol 1982;319:206–11.
Holaday JW, Faden AI. Naloxone reversal of endotoxin hypotension suggests role of endorphins in shock. Nature 1978;275:450–1.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kun, Y., Wen-xiang, L., Jia-min, Z. et al. Effect of naloxone injected into the lateral cerebral ventricle on the arterial baroreflex sensitivity during heat stress-induced hyperthermia in rabbits. Journal of Tongji Medical University 7, 84–88 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02888167
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02888167