Summary
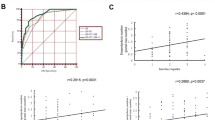
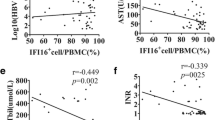
To explore the expression of Fas/Fas-L in liver tissue of hepatitis gravis patients and its implication in hepatocyte apoptosis, Fas/Fas-L expression and cell apoptosis was detected by the means of inmmunohistochemistry and terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase mediated dUTP nick end labeling (TUNED. It was found that in the 20 patients with clinical hepatitis gravis, Fas in hepatocytes showed strong expression and Fas-L also showed intensive expression in infiltrating lymphocytes and scattering hepatocytes. The apoptosis existed in all the samples, scattering in the area of inflammatory, necrotic area and hepatic lobule. It was suggested that the overexpression of Fas/Fas-L could cause the death of hepatocytes and thus the occurrence of hepatitis gravis. The apoptosis caused by Fas might be one of the important pathogeneses of hepatitis gravis. Among the detected samples, apoptosis and necrosis coexisted, indicating that both two types of cellular death were closely associated with the pathogenesis of hepatitis gravis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ryo K, Kamogawa Y, Lkeda Iet al. Fas and Fas ligand strongly expressed in liver of fulminant hepatitis patients. Hepatology, 1995, 22(4 pt 2):230A
Kondo T, Suda T, Fukuyama Het al. Essential role of the Fas-ligand in the development of hepatitis. Nat Med, 1997, 3:409
Ganter F, Leist M, Lchse A W. Concanavalin A-induced T-cell mediated hepatic injury in mice: the role of tumor necrosis factor. Hepatology, 1995, 21:190
Kagi D, Vignaur F, Ledermann Bet al. Fas perforin pathways are major mechanisms of T cell mediated cytotoxicity. Science, 1994, 265:528
Ryo K, Kamogawa Y, Yamauchi Ket al. Involvement of Fas and Fas ligand in case of human fulminant hepatitis. Nippon Rinsho, 1996, 54(7):1965
Galle P R, Krammer P H. CD95-induced apoptosis in human liver disease. Semin Liver Dis, 1998, 18(2): 141
Nagata S, Golstein P. The Fas death factor. Science, 1995, 267(5203):1449
Ando K, Hiroishi K, Kaneko Tet al. Perforin, Fas/Fas ligand, and TNF-altha pathways as specific and bystander killing mechanisms of hepatitis C virus-specific human CTL. J Immunol, 1997, 158(11):5283
Dayan C M, Elsegood K A, Maile Ret al. FasL expression on epithelial cells; the Bottazza Feldman hypothesis revisited. Immunol Today, 1997, 18:203
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qin, X., Shuxian, S. Study on FAS/FAS-L expression in liver tissue and hepatocyte apoptosis in patients with hepatitis gravis. Current Medical Science 21, 112–114 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02888071
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02888071