Summary
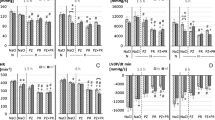
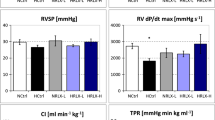
In this, study, we observed the effect of endotoxemia on hypoxic pulmonary vasoconstriction (HPV) in dogs and explored roles played by prostaglandins and leukotrienes in this process. 5 μg/kg BW of E. coli endotoxin induced transient rise in pulmonary arterial pressure and pulmonary vascular resistance (PVR). 30 min after injection of endotoxin when PVR tended to decline, pulmonary vasoconstriction response to alveolar hypoxia was lest, and the ratio of TXB2 to 6-keto-PGF1 α decreased significantly. HPV was enhanced at 60–100 min and then returned to the control level at 2 h after injection of endotoxin. At these periods the ratio of TXB2 to 6-keto-PGF1 α was the same as before use of endotoxin, whereas plasma concentration of leukotrienes was markedly increased. Indomethacin could prevent the early loss of HPV, but no effect on the late increment of HPV was found. Diethylcarbamazine, which blocked the production of leukotrienes after use of endotoxin, could inhibit late increment of HPV. We concluded that the early loss of HPV was related to the vasodilator prostacyclin, and the late increment of HPV was mainly brought about by leukotrienes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brigham KL, et al. Endotoxin and lung injury. Am Rev Respir Dis 1986:135(5): 913
Olson NC, et al. Dimethylthiourea attenuates endotoxin-induced acute respiratory failure in pigs. J Appl Physiol 1987;63(6):2426
Orange RP, Austen KF. The biological assay of slow reacting substances-SRS-A, bradykinin and prostaglandins. In: Williams VCA, Chase MW eds. Methods in Immunology and Immunochemistry. New York: Academic Press Inc., 1976: 1
Augstein J, et al. Selective inhibitor of slow reacting substance of anaphylaxis. Nature (New Biol) 1973:245
Olson NC, et al. Dexamethasone and indomethacin modify endotoxin-induced respiratory failure in pigs. J Appl Physiol 1985;58(1):274
Kubo K, et al. Effects of OKY-046, a selective thromboxane synthetase inhibitor, on endotoxin-induced lung injury in unanesthetized sheep. Am Rev Respir Dis 1985;132(3):494
Hales CA, et al. Role of thromboxane and prostacyclin in pulmonary vasomotor changes after endotoxin in dogs. J Clin Invest 1981;68(2):497
Ogletree ML, et al. Evidence for pulmonary release of 5-hydroxyeicosa-tetraenoic acid (5-HETE)during endotoxemia in unanesthetized sheep. Prostaglandins 1982:23 (4):459
Morganroth ML, et al. Leukotriene synthesis and receptor blockers block hypoxic pulmonary vasoconstriction. J Appl Physiol 1984:56(5):1340
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ming, F., Zhen-han, Z. & Di-xun, W. Effect of endotoxin on hypoxic pulmonary vasoconstriction — The role of prostaglandins and leukotrienes. Journal of Tongji Medical University 12, 11–16 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02887752
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02887752