Summary
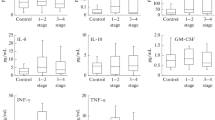
To study the changes of cytokines in peritoneal fluids of patients with endometriosis and their effects on reproductive activity, levels of tumor necrosis factor (TNF) and interleukin 6 (IL-6) in peritoneal fluids and peritoneal macrophages’ culture supernatant were studied by using enzyme linked immunoassay (ELISA) in 14 infertile patients with endometriosis (EMT group) and 11 infertile women with normal pelvis (control group). The effects of peritoneal fluids in patients with endometriosisin vitro on sperm motility and development of 2-cell mouse embryos were also studied. The results showed that the levels of TNF and IL-6 in peritoneal fluids and peritoneal macrophages’ supernatant in EMT group were elevated significantly as compared with those in the control group (P <0. 01). The percent of sperm straight line movement and total sperm motility were decreased significantly in EMT group (P<0.01). The percent of 2-cell mouse embryos developing to 16-cells was 32.5% in EMT group, while 47.6% in control group after 48 h co-culture with peritoneal fluid (P <0.01). It is likely that the elevation of peritoneal fluid cytokines in patients with endometriosis may play a role in infertility associated with endometriosis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
American Fertility Society. Revised American Fertility classification of endometriosis 1985. Fertil Steril, 1985, 43:351
Koama N, Matsura K, Okamura H. Cytokines in the peritoneal fluid of patients with endometriosis. Int J Gynecol Obstet, 1993, 43:45
Boutten A, Dehoux F, Proserpio Pet al. IL-6 and acute phase protein in the peritoneal fluid of women with endometriosis/ Clin Chem Acta, 1992, 40:187
Vercellini P, De-Baenedetti F, Rossi E. Tumor necrosis factor in plasma and peritoneal fluid of women with or without endometriosis. Gynecol Obste Invest, 1993, 36: 39
Buyalos R P, Funari V A, Azziz Ret al. Elevated interleukin 6 levels in peritoneal fluid of patients with pelvi pathology. Fertil Steril, 1992, 58:302
Curtis P, Lindsay A E, Jackson Fet al. Adverse effects on sperm movement characteristic in women with minimal and mild endometriosis. Br J Obstet Gynecol, 1993, 100:165
Leach R E, Ameson B W, David Ball Get al. Absence of antisperm antibodies and factors influencing sperm motility in the cul-de-sac fluid of women with endometriosis. Fertil Steril, 1990, 53:351
Taketani Y, Kuo T M, Miauno M. Comparison of cytokine levels and embryo toxicity in peritoneal fluid in infertile women with untreated or treated endometriosis. Am J Obstet Gynecol, 1992, 167:265
Eisermann J, Register K B, Strickler R Cet al. The effect of tumor necrosis factor on human sperm motility in vitro. J Androl, 1989, 10:270
Taketani Y, Kuo T M, Mizuno M. Tumor necrosis factor inhibits the development of mouse embryos cocultured with oviducts: possible relevance to infertility with endometriosis. J Mamm OV Res, 1991, 8:175
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yi, L., Lilan, L. & Haibo, Z. Changes of cytokines levels in peritoneal fluids of patients with endometriosis and its effect on reproductive activity. Current Medical Science 20, 163–165 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02887062
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02887062