Abstract
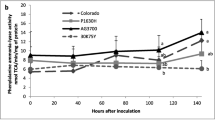
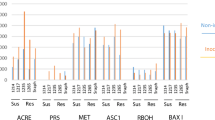
Bipolaris maydis race C strain 523 (C523) induces severer leaf blight on cytoplasmic male sterility (CMS)-C maize than on normal (N) maize. Previously, a pathotoxin isolated from C523 (C-toxin) was shown to be responsible for the disease. To understand the basis of the differential responses between CMS-C and N maizes to this fungus, protein synthesisin vitro by mitochondria from N and CMS-C cytoplasms was monitored after their incubation in a solution containing the toxin (0.3%). Similar protein products were detected between the two alloplasmic lines, indicating that the toxin does not directly act on the mitochondrial membrane, nor inhibits the expression of mitochondrial genes. To further locate the action site of the toxin, intact leaves from both N and several subtypes of CMS-C lines were treated by 0.3% toxin. Analysis of electrolyte leakage of leaf cells showed that the leakage rates were similar to one another among the alloplasmic maize lines. In contrast, at a lower concentration of the toxin (0.05%), the leaf cells from CMS-C line were more susceptible to the toxin than those of the other lines. All these results indicate that the target of the toxin action appears to be the cellular-membrane rather than mitochondria, suggesting that the variable susceptibilities toB. maydis between the alloplasmic maize lines might be related to a difference in their cellular-membranes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Liu, K. M., Su, H., Cui, Y. et al., The responses of the different subgroups in CMS-C maize to the infection ofBipolaris maydis race C, China Agri. Sci. (in Chinese), 1991, 24(40): 58.
Cui, Y., Ma, C. H., Wei, J. K. et al., Study on the biological activity of the purified toxin fromBipolaris maydis race C in maize, Chinese J. Plant Path. (in Chinese), 1992, 22 (2): 175.
Xie, Y. J., Storey, K., Gengenbach, B., Study on thein vitro protein synthesis of mitochondria of maize, Hereditas (in Chinese), 1986, 8(1): 14.
Leaver, C. J., Forde, B. G., Mitochondria1 genome expression in higher plants, in Genome Organization and Expression in Plants (ed. Leaver, C. J.), New York: Plenum Press, 1980, 411–423.
Siedow, J. N., Rhoads, D. M., Ward, G. C. et al., The relationship between the mictochondrial geneT-urf13 and fungal pathotoxin sensitivity in maize, Biochi. Biophy. Acta, 1995, 1271: 235.
Goudet, C., Very, A. A., Milat, M. L. et al., Magnesium ions promote assembly of channel-like stmctures from beticolin O, a non-peptide fungal toxin purifed fromCercospora beticola, Plant J., 1998, 14: 359.
Cui, Y., Wei, J. K., Shen, Z. W. et al., Chemical and spectral characterization of toxin produced by helminthosporium maydis (Bipolaris maydis) race C, Acta Biophy. Sin. (in Chinese), 1997, 13(4): 551.
Hohn, T. M., Pmvtor, R. H., Desjardins, A. E., Biosynthesis of sesquiterpenoid toxins by fungal pathogens, in Molecular Biology of Filamentous Fungi (eds. Stahl, U. & Tudzynski, P.), Weinheim: VCH, 1992, 99–109.
Voluevich, E. A., Bulocichik, A. A., Nucleocytoplasmic interaction in the resistance of wheat to fungal pathogens (IV)-Quantitative resistance to powdery mildew in seedlings of alloplasmic lines of the varietyChinese Spring, Genetika Moskia, 1992, 28: 104.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, Z., Xue, Y. & Dai, J. The pathogenic site of the C-toxin derived fromBipolaris maydis race C in maize (Zea mays). Chin.Sci.Bull. 45, 1787–1791 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02886268
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02886268