Abstract
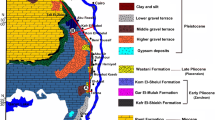
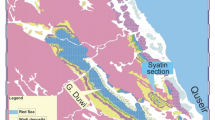
The late Quaternary paleosols in the Yangtze Delta area developed in the period of 25 000–12 000 aBP. Phytolith ratios (value A) of contents of fan, square and rectangle types indicating the warm and humid climate to those of bar, hat and point types indicating cold and dry climates decrease upwards overall on profiles of the paleosols, suggesting that the climates turned from warm and humid to cold and dry. So, the paleosols developed mainly during the regression before the last glacial maximum. Changes of value A indicate no trend of warming, suggesting that the transgression was rapid after the last glacial maximum. The development of the paleosols exhibited obvious stages, which were controlled remarkably by transgression and regression: I. Period of alternation of deposition and pedogenesis, which was from the occurrence of regresson before the last glacial maximum to the time when sea levels fell close to the lowest; II. Exposure period with continual pedogenesis, which was terminated when the paleosols were drown in the post-glacial transgression; III. Period of being drown and buried, the paleosols were buried by marine sediments, and reworked by early diagenesis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen Qingqiang, Li Gngxian, Preliminary studies on the late Ouatemaly paleosols and paleoenvironments in the Yangtze Delta area,Acta Sedimentologica Srnicu (in Chinese with English abstract), 1995, 13(Suppl.): 79.
Min Qiubao, Wang Pinxian, Quaternary transgressions in Shanghai region,Jounud of Tongji University (in Chinese with English abstract), 1979(2): 109.
Li Congxian, Min Qiubao, Sun Hepinget al., Holocene strata and transgressions at the southem flank of the Yangtze Delta,Chinese Science Bulletin (in Chinese), 1986, 31(21): 1650.
Sun Shuncai, Wu Yifan, Formation and evolution of Ihihu Lake and modem sedimentation,Science in China, Ser. B, (in Chinese), 1987(2): 1329.
Zheng Xiangmin. Yan Qinshang, Eolian loess deposition during the last glaciation in the northern part of Jiangsu Province and the land extending area in the East China Sea, QuaternaryResearch (in Chinese with English abshact), 1995(3): 258.
Wang Yongji, Lu Houyuen,Studies on Phytoliths and Their Applications (in Chineae), Beijing: Ocean Press, 1993, 2–4; 43–44; 50–110.
Wang Kaifa, Zhang Yulan, Jiang Huiet al., The Quaternary sporopollen assemblages and their significance of strata and paleogeography at the Yangtze Delta,Acta Oceanologica Sinica (in Chinese), 1984, 6(4): 485.
Wang Kaifa, Zhang Yulan, Jiang Hui, The late Pleistocene assemblages of spropollen and algae and paleoenvironmental evolution in the East China Sea,Science in China, Ser. B, (in Chineqe), 1987(8): 874.
Shackleton, N. J., Opdyke, N. D., Oxygen isotope and paleomagnetic evidence for Northern Hemisphere glaciation,Nature, 1977, 270: 216.
Xiong Yi, Li Qingkui,Soils in China (2nd ed.) (in Chinese), Beijing: Science Prese, 1990, 374–388.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Q., Li, C. Stage characteristics for the development of late Quaternary paleosols in the Yangtze Delta area. Chin. Sci. Bull. 44, 857–860 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02885037
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02885037