Abstract
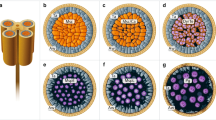
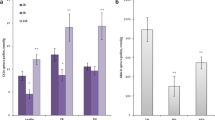
The temporal and spatial expression patterns of calmodulin mRNA in the developing tobacco anthers were investigated byin situ RNA hybridization, using digoxigening-labeled anti-RNA probe. Calmodulin mRNA was distributed in various developmental stages of tobacco anthers, but the expression level had temporal and spatial differences distinctly. During early stage of anther development, the expression level of calmodulin mRNA was significantly high, mainly distributed in epidermis, tapetum and transfusion parenchyma cells and so on. Especially, more mRNA was accumulated in the nuclei and chromosomes of microspore mother cells prior to and during meiosis. With the development of anther, mRNA was decreased gradually in the anther wall and pollen. By mature pollen stage, only a stronger positive reaction still existed in the epidermis of anther wall and transfusion parenchyma cells. The results suggest that the temporal and spatial expression of calmodulin mRNA is closely correlated with cell division, pollen development and substance transport.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Roberts, D. M., Lukas, T. J., Watterson, D. M., Structure, function, and mechanism of action of calmodulin,Crit. Rev. Plant Sci., 1986, 4: 311.
Roberts, D. M., Harmon, A. C., Calcium-modulated proteins: targets of intraceilular calcium signals in higher plants,Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. Plant Mol. Biol., 1992, 43: 375.
Jena, P. K., Redd, A. S. A., Poovaiah, B. W., Molecular cloning and sequencing of a cDNA for plant CaM: signal-induced change in the expression of CaM,Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 1989, 86:3644.
Breton, C., Chabound, A., Rochon, E. M.et al., PCR-generated cDNA library of transition-stage maize embryos: cloning and expression of calmodulin genes during early embryogenesis,Plant Mol. Biol., 1995, 27: 105.
Davies, S. P., Singh, M. B., Knox, R. B., Identification andin situ location of pollen-specific genes,Int. Rev. Cytol., 1992, 140: 19.
Sasaki, T., Song, J., Koga-ban, Y.et al., Toward cataloguing all rice gene: large-scale sequencing of randomly chosen rice cDNAs from acallus cDNA library,Plant J., 1994, 6: 615.
Sarmbrook, J., Fritsch, E. F., Maniatis, T.,Molecular Cloning: a Laboratory Manual, 2nd ed., New York: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, 1989, 16.
Chen, S. R., Bi, X. Z., Lu, Y. T.et al., An optimizedin situ RNA hybridization technique in plant tissues,Hereditas (in Chinese), 1998, 3: 27.
Poovaiah, B. W., Reddy, A. S. N., Calcium and signal transduction in plant,Crit. Rev. Plant Sci., 1993, 12(3): 185.
Means, A. R., Tash, T. S., Chafouleas, T. G., Physiological implications of the presence, distribution, and regulation of calmodulin in eukaryotic cells,Physiol. Rev., 1982, 62(1): 1.
Goddard, R. H., Wick, S. W., Silflow, C. D.et al., Microtubule components of the plant cell cytoskeleton,Plant Physiol., 1994, 104: 1.
Fisher, D. D., Gilroy, S., Cyr, R. J., Evidence for opposing effects of calmodulin on cortical microtubules,Plant Physiol., 1996, 112: 1079.
Knight, M. R., Smith, S. M., Trewavas A., J., Wind-induced plant motion immediately increases cytosolic calcium,Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 1992, 89: 4967.
Oh, S. A., Kwark, J. M., Kwun, I. C.et al., Rapid and transient induction of calmodulin-encoding gene(s) ofBrassica napus by a touch stimulus.Plant Cell Rep., 1996, 15: 586.
Dauwalder, M., Roux, S. J., Hardison, L., Distribution of calmodulin in pea seedlings: immunocytochemical localization in plumules and root apices,Planta, 1986, 168: 461.
Lin, C. T., Sun, D., Song, G. X.et al., Calmodulin: localization in plant tissue,J. Histochem. Cytochem., 1986, 34: 561.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, S., Lu, Y. & Yang, H. In situ localization of calmodulin mRNA in the developing tobacco anthers. Chin. Sci. Bull. 44, 142–146 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02884738
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02884738