Abstract
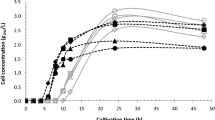
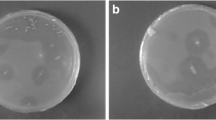
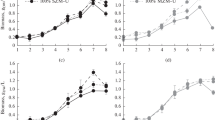
When studying the biosynthesis of mucidin under production (glucose as the main carbon source) and non-production (glucitol as the main carbon source) conditions it could be shown that the producer,Oudemansiella mucida, utilizes glucitol both for growth and for mucidin biosynthesis. However, the production of mucidin is 10 times ower than on glucose. When the culture was preincubated on glucose and transferred to non-production conditions the negative effect of glucitol could not be demonstrated. Biosynthesis of mucidin is influenced by the used carbon source already at an early stage of the cultivation
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Musílek V., Černá J., Šašek V., Semerdžieva M., Vondráček M.: Antifungal antibiotic of the basidiomyceteOudemansiella mucida. I. Isolation and cultivation of a producing strain.Folia Microbiol. 14, 377 (1969).
Nerud F., Musílek V.: Biosynthesis of fatty acids and sterols in relation to the antibiotic formation inOudemansiella mucida.Folia Microbiol. 23, 385 (1978).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Part VI of the series Antifungal antibiotic of the basidiomyceteOudemansiella mucida Part V:Folia Microbiol. 26, 8 (1981).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zouchová, Z., Nerud, F. & Musílek, V. Effect of glucitol on the production of mucidin inOudemansiella mucida . Folia Microbiol 27, 35–37 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02883835
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02883835