Abstract
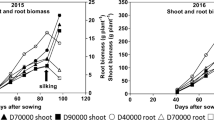
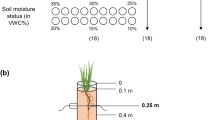
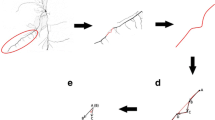
Fractal geometry was applied and box dimension was used as an indicator to analyze the effects of doubled CO2 concentration on the root growth of plant seedlings. Results showed that doubled CO2 concentration displayed different effects on root branching characteristics of C3 and C4 plants. There was an obvious increase of root branches in spring wheat while there were no significant effects on roots of sweet sorghum. In different soil layers, root branching of spring wheat was stimulated and this promotion was most significant in the second layer (10–20 cm), which denoted that elevated CO2 altered the root branching pattern. That means higher CO2 concentration influences not only root growth but also its differentiation and development.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yang, P. L., Luo, Y. P., Fractal characteristics of root morphology in winter wheat,Chinese Science Bulletin, 1994(20): 1911.
Yang, D. A., Ecological information system,Science of Life (in Chinese), 1992, 4(4): 4.
Castillo, D. D., Acock, B., Reddy, V. R.et al., Elongation and branching of roots on soybean plants in a carbon dioxide-enriched environment.Agron. J., 1989, 81: 692.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Y., Zhang, H., Yang, D. et al. Fractal analysis for root growth of plant seedlings under doubled CO2 concentration. Chin. Sci. Bull. 43, 1891–1893 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02883466
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02883466