Abstract
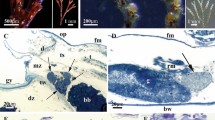
By means of ultrathin section, negative staining and sucrose gradient ultra-centrifugation, a new baculovims has been discovered and purified in lymphoid organs and such tissues as muscles of the shrimps which have been spontaneously attacked by diseases and artificially infected. With a diameter of 96–112 nm, this is the thickest baculovirus of shrimps ever known. In the center is the highrdensity nucleus. Between the capsid and the envelope is a broad space, which is not found in any of the baculoviruses of the prawns ever reported. On the surface of the purified nucleocapsid, there is a subunit of the spiral arrangement, which is also characteristic of this virus. It has not been observed and found in the epithelial cells of the livers, intestines and cheeks, which is quite different from the fact that prawn baculoviruses infect a certain epithepilial cell of the above-mentioned ones without exception. The viruses only multiplicate inside the core of target cells, which will not form occluded bodies or inclusion bodies. It is a new virus which has never been reported. It is called lymphoid cell nuclear baculovirus (LNBV).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen Xifa, Wu Dinghu. Huang Huai.et al., The ultrastructural cytopathological changes of a new virus disease in shrimps and their diagnostics,J. Xiamen University (in Chinese), 1996, 35(4): 612.
Couch, J. A., An enzootic nuclear polyhedrosis virus of pink shrimp: ultrastructure, prevalence, and enhancement,J. Invert. Pathol., 1974, 24:311.
Chen Xifa, Wu Dinghu, Huang Huaiet al., ultrastructire ofPenaeus monodon baculovirus,J. Fish of China (in Chinese), 1995, 19(3): 203.
Lightner, D.V., Redman, R. M., A baculovirus-caused disease of penaeid shrimp,Penaeus monodon, J. Invert. Pathol., 1981. 38: 299.
Sano, T., Nishimura, T., Oguma, K.et al., Baculovirus infection of cultured Kuruma shrimpP. japonicus in Japan,Fish Pathol. 1981, 15:185.
Owens, L., Disruption of the first haemocytic rod-shaped virus from a penaeid prawn,Dis. Aquat.Org., 1993, 16:217.
Lester, R. J. G., Doubrovsky, J. L., Paynter, S.K.et al., Light and electron microscope evidence of baculovirus infection in the prawn P.plebejus, Dis. Aquat. Org., 1987, 3: 217.
Boonyaratpalin, S. K., Supamattaya, J., Kasornchandra, S.et al., Non-occluded baculo-like virus, the causative agent of yellow head disease in the black tiger shrimp (P. monodon),Fish Pathol., 1993, 28: 103.
Kiyoshi Inouye, Satoshi Miwa, Norihisa Osekoet al., Mass mortalities of cultured Kuruma shrimp P.japonicus in Japan in 1993: Electron microscopic evidence of the causative virus,Fish. Pathology, 1994, 29(2): 149.
Zhang Hongwei, Wang Jinsheng, Yu Shiguang, The agent of infections disease of prawns in Shandong, China,Oceanographic Science (in Chinese), 1995, (1):5.
Chen Xifa, Wu Dinghu, Huang Huaiet al., Massive sign and its pathological changes of virus affected shrimp,China Fisheries (in Chinese), 1993, 213(8–9): 32.
Chen Xifa, Wu Dinghu, Huang Huaiet al., Ultrastructural features of a virus in the mariculture shrimp,J. China Electron Microscopy Society (in Chinese), 1994, 13(5): 357.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, X., Chen, P., Wu, D. et al. A new baculovirus of cultured shrimps. Sci. China Ser. C.-Life Sci. 40, 630–635 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02882693
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02882693