Abstract
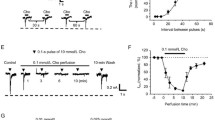
Using nystatin-perforated whole-cell recording configuration, the modulatory effect of N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) on γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA)-activated whole-cell currents was investigated in neurons freshly dissociated from the rat sacral dorsal commissural nucleus (SDCN). The results showed that: (i) NMDA suppressed GABA-and muscimol (Mus)-activated currents (Igaba and IMus), respectively in the Mg2+-free external solution containing 1 μmol/L glycine at a holding potential (V H ) of −40 mV in SDCN neurons. The selective NMDA receptor antagonist, D-2-amino-5-phosphonovaleric acid (APV, 100 γmol/L), inhibited the NMDA-evoked currents and blocked the NMDA-induced suppression of Igaba; (ii) when the neurons were incubated in a Ca2+-free bath or pre-loaded with a membrane-permeable Ca2+ chelator, BAPTA AM (10 μmol/L), the inhibitory effect of NMDA on IGAba disappeared. Cd2+ (10 μmol/L) or La3+ (30 μmol/L), the non-selective blockers of voltage-dependent calcium channels, did not affect the suppression of Igaba by NMDA application; (iii) the suppression of IGAba by NMDA was inhibited by KN-62, a calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II (CaMKII) inhibitor. These results indicated that the inhibition of GABA response by NMDA is Ca2+-dependent and CaMKII is involved in the process of the Ca2+-dependent inhibition.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Liang, Q. C., Xu, T. L., Molecular structure and functional characteristics of AMPA and KA receptors, Prog. Physiol. Sci. (in Chinese), 1997, 28:352.
Wang, W., Xu, T. L., Structure and function of the NMDA receptor channels, Prog. Biochem. Biophys. (in Chinese), 1997, 24: 321.
Pang, Z. P., Xu, T. L., Li, J. S., Intracellular modulation and its mechanisms of GABAA receptors, Chin. Pharmacol. Bull, (in Chinese), 1998, 14(review): 60.
Llano, I., Leresche, N., Marty, A., Calcium entry increases the sensitivity of cerebellar Purkinje cells to applied GABA and decreases inhibitory synaptic currents, Neuron, 1991, 6: 565.
Aguayo, L. G., Espinoza, F., Kunos, G. et al., Effects of intracellular calcium on GABAA receptors in mouse cortical neurons, Pflügers Arch., 1998, 435: 382.
Martina, M., Kilic, G., Cherubini, E., The effects of intracellular Ca2+ on GABA-activated currents in cerebellar granule cells in culture, J. Membr. Biol., 1994, 142: 209.
Mouginot, D., Feltz, P., Schlighter, R., Modulation of GABA-gated chloride currents by intracellular Ca2+ in cultured porcine melanotrophs, J. Physiol. (Lond.), 1991, 437: 109.
Xu, T. L., γ-Aminobutyric acid-induced responses in acutely dissociated neurons from the rat sacral dorsal commissural nucleus, J. Autonomic Nerv. Syst., 1999, 75: 156.
Xu, T. L., Li, J. S., Akaike, N., Functional properties of the ionotropic glutamate receptor channels in the rat sacral dorsal commissural neurons, Neuropharmacology, 1999, 38: 659.
Xu, T. L., Akaike, N., Suppression of NMDA response in rat sacral dorsal commissural neurons by AMPA receptor activation: a study by the nystatin-perforated patch technique, Chin. J. Neuroanat. (in Chinese), 1996, 12: 349.
Xu, T. L., Li, J. S., Jin, Y. H. et al., Modulation of the glycine response by Ca2+-permeable AMPA receptors in rat spinal neurons, J. Physiol. (Lond.), 1999, 514: 701.
Xu, T. L., Molecular mechanisms of neuronal calcium signaling, Chin. J. Neuroanat. (in Chinese), 1998, 14: 195.
Wu, L. G., Westenbroek, R. E., Borst, J. G. G. et al., Calcium channel types with distinct presynaptic localization couple differentially to transmitter release in single calyx-type synapses, J. Neurosci., 1999, 19: 726.
Xu, T. L., Pang, Z. P., Li, J. S. et al., 5-HT potentiation of the GABAA response in the rat sacral dorsal commissural neurons, Br. J. Pharmacol., 1998, 124: 779.
Xu, T. L., Imanishi, T., Akaike, N., Modulation of the GABAA response in rat ventromedial hypothalamic neurons by pregnanolone, Comp. Biochem. Physiol., 1997, 117A: 219.
Chen, Q. X., Wong, R. K. S., Suppression of GABAA receptor responses by NMDA application in hippocampal neurones acutely isolated from the adult guinea-pig, J. Physiol. (Lond.), 1995, 482: 353.
Obrietan, K., van den Pol, A. N., GABA neurotransmission in the hypothalamus: developmental reversal from Ca2+ elevating to depressing, J. Neurosci., 1995, 15: 5065.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, D., Lü, H. & Xu, T. Mediation by calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II of suppression of GABAA receptors by NMDA. Sci. China Ser. C.-Life Sci. 43, 655–662 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02882287
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02882287