Abstract
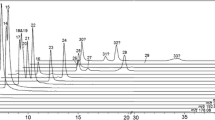
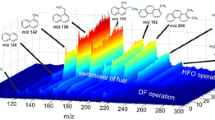
Organic pollution has been gaining more and more attention. Yet, at present the determination of virtually all of them, including polycyclic aromatic carbons (PAHs), the largest single class of chemical carcinogens known today, is made via pre-purification and pre-concentration, The major problems are complexity and time-consuming, thus, no ideal real-time on-line monitoring can be done. Laser mass spectrometry combines UV spectroscopy and time-of-flight mass spectrometry (TOF-MS) through resonance-enhanced multiphoton ionization (REMPI). It is characteristic of high sensitivity, high selectivity and rapidity. In this paper, after its principles, a small mobile laser mass spectrometer, in which a mini-excimer (KrF, 248 nm) laser was used, is introduced. Real-time analysis of vehicle exhaust gas was made using this instrument, and the results showed some advantages over traditional methods: multicomponent detection, including benzene, toluene, xylene, C3-benzene, naphthalene, and methyl-naphthalene; high sensitivity (100 ppb); high time-resolution (0.1 s); and no need for prepurification or pre-concentration of samples.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bjorseth, A., ed., Handbook of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons, New York: Marcel Dekker Inc., 1983.
Otsen, R., Leach, J. M., Chung, L. T. K., Sampling of airbone polycyclie aromatic hydrocarbons, Anal. Chem., 1987, 59: 1701–1705.
Zimmermann, R., Heger, H. J., Kettrup, A. et al., A mobile resonance-enhanced multiphoton ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry device for on-line analysis of aromatic pollutants in waste incinerator flue gases: first results, Rap. Commu. in Mass Spectro., 1997, 11: 1095–1102.
Weickhardt. C., Boesl, U., Schlag, E. W., Laser mass spectrometry for time-resolved multicomponent analysis of exhaust gas, Anal. Chem., 1994, 66(7): 1062–1069.
Heger, H. J., Zimmermann, R., Dorfner, R. et al., On-line emission analysis of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons down to pptv concentration levels in the flue gas of an incineration pilot plant with a mobile resonance-enhanced multiphoton ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometer, Anal. Chem., 1999, 71: 46–57.
Boesl, U., Laser mass spectrometry for environmental and industrial chemical trace analysis, J. Mass Spectrum., 2000, 35: 289–304.
Castaldi, M. J., Senkan, S. M., Real time, ultrasensitive monitoring of air toxics by laser photoionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry, J. Air & Waste Management Assoc., 1998, 48: 77–81.
Loepfe, M., Burtscher, H., Siegmann, H. C., Analysis of combustion products using time-of-flight mass spectrometry, Water, Air and Soil Pollution, 1993, 68: 177–184.
Franzen, J., Frey, R., Nagel, H., Fast monitoring of motor exhaust components by resonant multiphoton ionization and time-of-flight mass spectrometry, J. of Molecular Structure, 1995, 347: 143–151.
Zhang Liandi, Wei Jie, Zheng Haiyang et al., Laser mass spectrometry for high sensitive andmulti-component analysis of exhaust gas from vehicles, Chinese Science Bulletin, 2001, 46(1): 86–88.
Jaffee, H., Orchin, M., Theory and Applications of Ultraviolet Spectroscopy, New York: John Wiley and Sons, 1962. 12. Robin, M. B., Higher Excited States of Polyatomic Molecules, Volume II, New York: Academic Press, 1975, 209–268.
Henberg, Z., Molecular Spectra and Molecular Structure: III. Electronic Spectra and Electronic Structure of Polyatomic Molecules, Princeton: D Van Nostrand Company, Inc., 1966, 555–561.
Boesl, U., Neusser, H. J., Schlag, E. W., Multiphoton ionization in the mass spectrometry of polyatomic molecules: cross section, Chem. Phys., 1981, 55: 193–204.
Wei, J., Zhang, B., Fang, L. et al., REMPl time-of-flight mass spectra of C2 H7N isomers, Opt. Commu., 1998, 156: 331–336.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wei, J., Zhang, B., Zheng, H. et al. Rapid analysis of trace pollutants using laser mass spectrometry. Sci. China Ser. A-Math. 44, 940–946 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02880144
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02880144