Abstract
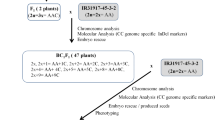
A rice mutant,G069, characteristic of few tiller numbers, was found in anther culture progeny from theF 1 hybrid between anindica-japonica cross, Gui630×02428. The mutant has another two major features: delayed tillering development and yellowing apex and margin on the mature leaves. As a donor parent,G069 was further backcrossed with the recurrent parent,02428, for two turns to develop aBC 2F2 population. Genetic analysis in theBC 2F2 population showed that the traits of few-tillering and yellowing apex and margin on the mature leaves were controlled by one recessive gene. A pool of equally mixed genomic DNA, from few-tillering individual plants inBC 2F2, was constructed to screen polymorphism with simple sequence repeat (SSR) markers in comparison with the02428 genome. One SSR marker and three restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP) markers were found possibly linked with the recessive gene. By using these markers, the gene of few-tillering was mapped on chromosome 2 between RFLP marker C424 and S13984 with a genetic distance of 2.4 cM and 0.6 cM, respectively. The gene is designatedft1.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Xu, Y. B., Shen, Z. T., Diallel analysis of tiller number at different growth stages in rice (Oryza sativa L.), Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 1991, 83(2): 243–249.
Wu, W. R., Li, W. M., Tang, D. Z. et al., Time-related mapping of quantitative trait loci underlying tiller number in rice, Genetics, 1999, (151): 297–303.
Wu, P., Zhang, G., Huang, N., Identification of QTLs controlling quantitative characters in rice using RFLP markers, Euphytica, 1996, 89(3): 349–354.
Khush, G. S., Breaking the yield frontier of rice, GeoJournal, 1995, 35(3): 329–332.
Chen, X., Themnykh, S., Xu, Y. et al., Development of microsatellite framework providing genome-wide coverage in rice (Oryzae sativa L.), Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 1997, 95(4): 553–567.
Panaud, O., Chen, X., McCouch, S. R. et al., Development of microsatellite markers and characterization of simple sequence length polymorphisms (SSLPs) in rice (Oryzae sativa L.), Molecular and General Genetics, 1996, (252): 597–607.
McCouth, S. R., Kochert, G., Yu, Z. H. et al., Molecular mapping of rice chromosomes, Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 1988, 76: 815–829.
Harushima, Y., Yano, M., Shomura, A. et al., A high-density rice genetic linkage map with 2275 markers using a single F2 population, Genetics, 1998, 148: 479–494.
Lander, E. S. et al., Mapmaker: An interactive computer for construction primary genetics linkage maps of experimental and natural populations, Genomics, 1987, (1): 174–182.
Kinoshita, T., Report of committee on gene symbolization, nomenclature and linkage groups, Rice Genetic Newsletter, 1995, (12): 9–153.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tang, J., Zeng, W., Wang, W. et al. Genetic analysis and gene mapping of a rice few-tillering mutant in early backcross populations (Oryza sativa L.). Sci. China Ser. C.-Life Sci. 44, 570–575 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02879350
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02879350