Abstract
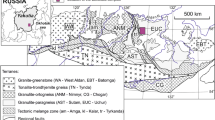
Dated isotopic ages for 15 alkaline intrusives in the Yanliao-Yinshan area, ranging from 268 to 190 Ma, ten of which are from 250 to 208 Ma, indicate that most of them were formed in the Triassic Epoch. All the ENd(t) ratios from - 17.19 to -3.21 averaging -7.09, the ESr(t) ratios fmm 11.7 to71.5 averaging 36.63, and the Isr(t) ratios from 0.705 0 to 0.709 3 averaging 0.706 8, show their characteristics of enrichment. On the ENd (t) virus ESr(t) correlation diagram, the samples from these intmsives were plotted within the enriched mantle trend lines and just outside, demonstrating their close connection to materials from the enriched mantle reservoir, taking into account the same Pb isotopic composition as that of the mantle.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mu Baolei, Yan Guohan, Some Triassic alkaline and sub-alkaline complexes in Yanliao area: their geochemistry and implications,Acta Geologica (in Chinese), 1992, 66(2): 108.
Han Baofu, Wang Shiguang, Hong Dawei, Forming age of Guangtoushan alkaline granite at Plngquan in Hebei Province,Goological Sciences (in Chinese), 1993, 28(2): 183.
Li Zhitong, Yu Changtao, Cheng Delin et al., Geological characteristics of Hekanai alkaline complex at Lingyuan in Liaoning Province, Bulletin of the Shenyang Institute of Geology and Mineral Resources, Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences (in Chinese), 1986, (14): 43.
Zhou Lingdi, Ulao Zhenhua, Zhou Guofu, Studies on isotopic chronology of some alkaline rock bodies in China.Geochemistry (in Chinese), 1996, 25(2): 164.
Peng Yujing, Wang Zhanfu, Determination of A-type granite belt in central Jilin Rovince and its tectonic implications,Jilin Geologica (in Chinese), 1995, 14(3): 31.
Zhao Zhenhua, Intrusives rich in alkaline materials: a window through which to investigate the composition of the mantle, inNew Progress in Mineralogy, Petrology, Geochemistry in China (in Chinese), ((ed. Quyang Ziyuan), Lanzhou: Lanzhou University Press, 1994, 113–114.
Zhang Ligang, Liu Jingxiu, Wang Kefa et al.,Plate Geology of Asia Lithosphere:Isotopic Geochemistry and Its Drivihg Force on Upper Mantle, Base and Granite (in Chinese), Beijing: Science Press, 1995, 226–231.
Wei Juying, Wang Guanyu,Isotope Geochtry (in Chinese), Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1998, 81–84.
Zartman, R. E., Doe, B. R., Plume tectionics—The model,Tectomphysics, 1981, 75: 135.
Li Changnian,Igneous Petrology of Trace Elements (in Chinese), Wuhan: China University of Geological Sciences Press, 1992, 147–154.
Wu Fuyuan, Jiang Boming, Liu Qiang, Studies on isotopic characteristics and cmst growth implications of post-orogenic granite in orogenic belts in North China,Science Newsletter (in Chinese), 1997, 42(20): 2188.
Xu Baoliang, Wang Shiguang, Han Baofu et al., Studies on depleted and enriched A-type granites: Rocks from Yanshan area in North China and from Wulungu River in Xinjiang as examples,Acta Peking University (Natural Sciences Edition) (in Chinese), 1998, 34(2–3): 352.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yan, G., Mu, B., Xu, B. et al. Triassic alkaline intrusives in the Yanliao-Yinshan area: their chronology, Sr, Nd and Pb isotopic characteristics and their implication. Sci. China Ser. D-Earth Sci. 42, 582–587 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02877785
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02877785