Abstract
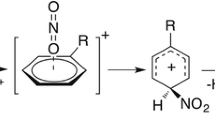
A simple model for computing the electron transfer rate constant of a cross-reaction has been proposed in the framework of semiclassical theory and employed to investigate the electron transfer system NO +2 /NO. The encounter complex of electron transfer NO +2 +NO→N02+NO+ has been optimized at the level of UHF/6-31G. In the construction of diabatic potential energy surfaces the linear coordinate was used and the kinetic quantities, such as the activation energies and the electron transfer matrix elements, have been obtained. For comparison, the related selfexchange reactlon systems NO +2 /NO2 and NO+/NO were kinetically investigated. The calculated activation energies for the electron transfer reactions of systems NO +2 /NO, NO +2 /NO2, and NO+/NO are 81.4, 128.8, and 39.8 kJ.mol-1, respectively. With the solvent effect taken into account, the contribution of solvent reorganization to the activation energy has been estimated according to the geometric parameters of the transition states. The obtained rate constants show that the activity of NO +2 as an oxidizing reagent in the aromatic nitration will be greatly decreased due to a high activation barrier contributed mainly from the change of bond angle ONO.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Eberson, L., Radner, F., Electron transfer reactions in organic chemistry (VI): Possible role of electron transfer in aromatic nitration by nitrosonium and nitroniurn ion,Acta Chem. Scand., 1984, B38: 861.
Feng, J.-K., Zheng, X.-H., Zerner, M. C., Theoretical study ofipso attack in aromatic nitration,J. Org. Chem., 1986, 51: 4531.
Sandall, J. P. B., The mechanism of aromatic nitration in solution: Marcus theory and semiempirical molecular orbital calculations on NO +2 and NO+ as one-electron oxidants,Chem. Soc. Perkin. Trans. 2, 1992: 1689.
Eberson, L., Radner, F., Electron transfer mechanisms in electrophilic aromatic nitration,Acc. Chem. Res., 1987, 20: 53.
Newton, M. D., Quantum chemical probes of electron-transfer kinetics: the nature of donor-acceptor interactions.Chem. Rev., 1991, 91: 767.
Mikkelsen, K. V., Ratner, M. A., Electron tunneling in solid-state electron-transfer reactions,Chem. Rev., 1987, 87: 113.
Li, X.-Y., Tian, A.-M., He, F.-C.et al., Field-dependent rate constant for intramolecular electron transfer reactions,Chinese Sci. Bull., 1995, 40: 20.
Zener, C., Non-adiabatic crossing of energy levels,Proc. Roy. Soc. Ser., 1932, A137: 696.
Newton, M. D., Sutin, N., Electron transfer reactions in condensed phases,Ann. Rev. Phys. Chem., 1984, 35: 437.
Li, X.-Y., Tian, A.-M., He, F.-C.etal., Electric field dependence of the diabatic potential energy surface for gas-phase electron transfer O2O −2 →O −2 O2,Chem. Phys. Lett., 1995, 233: 227.
Takagi, H. D., Swaddle, T. W., Estimation of the outer-sphere contribution to the activation volume for electron exchange reactions using the mean spherical approximation,Chem. Phys. Lett., 1996, 248: 207.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, X., He, F. Electron transfer NO +2 +NO→N02+NO+ in aromatic nitration. Sc. China Ser. B-Chem. 40, 523–528 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02875422
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02875422