Abstract
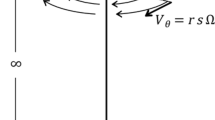
The steady, axisymmetric laminar flow of a homogeneous incompressible fluid with suspended particles occupying the half-infinite space over a differentially rotating rigid plane boundary is analyzed in this paper. The effect of suspended particles is described by two parametersf and τ. The mass concentration parameterf is a measure of the concentration of suspended dust particles. The interaction parameter τ is a measure of the rate at which the velocity of dust particles adjusts to changes in the fluid velocity and depends upon the size of the individual particles. Due to Ekman suction, the particle density remains no longer a constant in the boundary layer but varies with the axial coordinate ξ. Flow characteristics and density variations are studied as functions off, τ and ξ. Possible limiting cases for τ≪1 and τ≫1 which correspond to the case of fine dust and coarse dust respectively are derived and discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Datta N and Mishra S K, Boundary layer flow of a dusty fluid over a semi-infinite flat plate,Acta Mech. 42 (1982) 71–83
Greenspan H P,The theory of rotating fluids (Cambridge: University Press) (1980) 30–31, 1st ed.
Gupta A S, Effect of suspended particles on the Ekman boundary layer,Bull. Soc. Math. Sci. Romania XXVI (1977) 45–52
Marble F E, Dynamics of dusty gases,Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 2 (1970) 397–446
Michael D H and Miller D A, Plane parallel flow of a dusty gas,Mathematika Vol. 13 (1966) 97–109
Pedlosky J,Geophysical fluid dynamics (Springer-Verlag) (1979) p.182, 1st ed.
Saffman P G, On the stability of laminar flow of a dusty gas,J. Fluid Mech. 13 (1962) 120–128
Zung L B, Flow induced in fluid-particle suspension by an infinite rotating disk,Phys. Fluids 12 (1969) 18–23
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rao, C.N.B., Murty, V.V. & Somaraju, V. Linear flow induced in fluid particle suspension by an infinite differentially rotating disk. Proc. Indian Acad. Sci. (Math. Sci.) 101, 25–36 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02872007
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02872007