Abstract
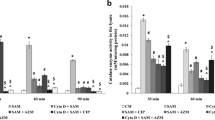
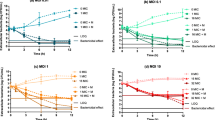
The activity of a calmodulin antagonist, trifluoperazine (TFP), was testedin vitro againstMycobacterium avium (ATCC 25291). The minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC) and minimal bactericidal concentration (MBC) of this compound forM. avium were 20 and 30 μg/ml, respectively. TFP was also found to completely inhibit the growth of 10 isolates ofM. avium (5 patient isolates and 5 environmental isolates) at 30 μg/ml. At near neutral pH (6.8), the MIC of TFP was found to be 20 μg/ml. However, at pH 5.5 (intracellular pH of macrophages), there was a decrease in the inhibitory activity of the compound against this organism. Interestingly, 99.6% ofM. avium within human monocyte-derived macrophages were killed at a drug concentration of 30 μg/ml, which correlates well with the MBC of TFP againstM. avium in vitro. Although the MIC for TFP appears to be higher than that forMycobacterium tuberculosis H37Rv, our studies suggest that calmodulin antagonists might be useful as drugs against infection due toM. avium. It is suggested that administration of TFP in combination with other known drugs may enhance the overall bactericidal effect.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hawkins, C.C., Gold, J.W.M., Whimbey, E., Kiehn, T.E., Brannon, P., Cammarata, R., Brown, A.E. and Armstrong, D. (1986)Mycobacterium avium complex infections in patients with the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Ann. Intern. Med. 105, 184–188.
Wallace, J.M. and Hannah, J.B. (1988)Mycobacterium avium complex infection in patients with the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome: A clinicopathologic study. Chest. 93, 926–932.
Horsburgh, C.R. (1991)Mycobacterium avium complex infection in the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. New Engl. J. Med. 324, 1332–1338.
Heifets, L.B. (1991) Dilemmas and realities in drug susceptibility testing ofM. avium—M. intracellulare and other slowly growing nontuberculous mycobacteria. In: Drug susceptibility in the Chemotherapy of Mycobacterial infections. Ed. Heifets, B. CRC Press, Inc., Florida, 123–146.
Lindholm-Levy, P.J. and Heifets, L.B. (1988) Clofazimine and other rimino compounds: Minimal inhibitory and minimal bactericidal concentrations at different pHs forM. avium complex. Tubercle, 69, 179–186.
Heifets, L. (1988) Minimum inhibitory concentration as a quantitative measurement of the susceptibility ofMycobacterium avium to seven antituberculosis drugs. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 32, 1131–1136.
Heifets, L.B. Iseman, M.D. and Lindholm-Levy, P.J. (1988) Combinations of rifampin or rifabutine plus ethambutol againstMycobacterium avium complex: Bactericidal synergistic and bacteriostatic additive of synergistic effects. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis., 137, 711–715.
Heifets, L.B., Lindholm-Levy, P.J. and Flory, M. (1990) Thiacetazone:in vitro activity againstM. avium andM. tuberculosis. Tubercle 71, 287–291.
Heifets, L.B., Lindholm-Levy, P.J. and Flory, M. (1990) Bactericidal activityin vitro of various rifamycins againstMycobacterium avium andMycobacterium tuberculosis. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 141, 626–630.
Gangadharam, P.R.J., Ashtekar, D. and O'Sullivan, J.F. (1992)In vitro, in vivo and intracellular chemotherapeutic activity of B 746, a clofazimine analogue againstMycobacterium avium complex. Tubercle Lung Dis. 192–199.
Falah, A.M.S., Bhatnagar, R., Bhatnagar, N., Singh, Y., Sidhu, G.S., Murthy, P.S. and Venkitasubramanian, T.A. (1988) On the presence of calmodulin like protein in mycobacteria. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 56, 89–93.
Burra, S.S., Hemalatha Reddy, P., Falah, S.M., Venkitasubramanian, T.A. and Suryanarayana Murthy, P. (1991) Calmodulin like protein and the phospholipids ofMycobacterium smegmatis. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 80, 189–194.
Hemalatha Reddy, P., Burra, S.S. and Suryanarayana Murthy, P. (1992) Correlation between calmodulin like protein, phospholipids and growth in glucose grownMycobacterium phlei. Canad. J. Microbiol. 38, 339–342.
Ratnakar, P. and Suryanarayana Murthy, P. (1992) Antitubercular activity of trifluoperazine, a calmodulin antagonist. FEMS. Microbiol. Lett. 97, 73–76.
Rao, S.P., Murthy, P.S. and Catanzaro, A. (1993a) In vitro activity of trifluoperazine againstMycobacterium avium-Mycobacterium intracellulare. Amer. Rev. Respir. Dis. (Suppl) 147, Abst. 917. (1993b) In vitro activity of trifluoperazine againstM. avium andM. bovis BCG. 33rd Interscience Conf. on Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy. (Amer. Soc. Microbiol.) Abst. 1345.
Ogata, K., Linzer, B.A., Zuberi, R.I., Ganz, T., Lehrer, R.L. and Catanzaro, A. (1992) Activity of defensins from human neutrophilic granulocytes againstMycobacterium avium Mycobacterium intracellulare. Infect. Immun. 60, 4720–4725.
Ashtekar, D.R., Femandez, F. and Kale, P.N. (1985) Rapid pyrazinamide susceptibility testing ofM. tuberculosis. IRCS Med. Sci. 13, 736–737.
Wright, S.D. and Silverstein, S.C. (1982) Tumorpromoting phorbol esters stimulate C3b and C3b' receptor-mediated phagocytosis in cultured human monocytes. J. Exp. Med. 156, 1149–1164.
Rao, S.P., Ogata, K. and Catanzaro, A. (1993)Mycobacterium avium—M. intracellulare binds to the integrin receptor αV β3 on human monocytes and monocyte derived macrophages. Infect. Immun. 663–670.
Young, L.S. (1988) AIDS Commentary:Mycobacterium avium complex infection. J. Infect. Dis. 157, 863–867.
Ohkuma, S. and Poole, B. (1978) Fluorescence probe measurements of the intralysosomal pH in living cells and the perturbation of pH by various agents. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. (USA) 75, 3327–3331.
Sibley, L.D., Weidner, E. and Krahenbuhl (1985) Phagosome acidification blocked by intracellularToxoplasma gondii. Nature (London) 315, 416–419.
Ratnakar, P. and Suryanarayana Murthy, P. (1993) Trofluoperazine inhibits the incorporation of labelled precursors into lipids, proteins and DNA ofMycobacterium tuberculosis H37Rv. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 110, 291–294.
Heifets, L.B., Lindholm-Levy, P.J. and Flory, M. (1991) Comparison of bacteriostatic and bactericidal activity of isoniazid and ethionamide againstMycobacterium avium andMycobacterium tuberculosis. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 143, 268–270.
Heifets, L.B., Lindholm-Levy, P.J. and Comstock, R.D. (1992) Clarithromycin minimal inhibibory and bactericidal concentrations againstMycobacterium avium. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 145, 856–858.
Baldessarini, R.J. (1990) Drugs and the treatment of psychiatric disorders. In: Goodman and Gilman's, The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. Eds. Gilman, A.G. et al. Maxwell Macmillan. New York, NY, 8th edn. vol. 1, 383–435.
Heifets, L.B. (1982) Synergistic effect of rifampin, streptomycin, ethionamide and ethambutol onMycobacterium intracellulare. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 125, 43–48.
Kuze, F., Kurasawa, T., Bando, K., Lee, Y. and Mackawa, N. (1981)In vitro andin vivo susceptibility of atypical mycobacteria to various drugs. Rev. Infect. Dis. 3, 885–897.
Zimmer, B.L., De Young, D.R. and Roberts, G.D. (1982)In vitro synergistic activity of ethambutol, isoniazid, kanamycin, rifampin and streptomycin againstMycobacterium avium-intracellulare complex. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 22, 148–150.
Ozenne, G., Morel, A., Menard, J.F., Thauvin, C., Samain, J.P. and Lemeland, J.F. (1988) Susceptibility ofMycobacterium avium complex to various two-drug combinations of antituberculosis agents. Amer. Rev. Respir. Dis. 138, 878–881.
Pascual, A., Tsukayama, D., Kovarik, J., Gekker, G. and Peterson, P. (1987) Uptake and activity of rifapentine in human peritoneal macrophages and polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. 6, 152–157.
Hand, L.W., King-Thompson, N.L. and Steinberg, T.H. (1983) Interactions of antibiotics and phagocytes. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 12 (Suppl. C), 1–11.
Ratnakar, P., Rao, S.P., Sriramarao, P. and Murthy, P.S. (1995). Structure-antitubercular activity relationship of phenothiazine-type calmodulin antagonists. International Clinical Psychopharmacol. 10, 39–43.
Ochiai, H., Kurakawa, M. and Niwayama, S. (1991) Influence of trifluoperazine on the late stage of influenza virus infection in MDCK cells. Antiviral Res. 15, 149–160.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rao, S.P., Ratnakar, P., Murthy, P.S. et al. Inhibitory and bactericidal activity of the calmodulin antagonist, trifluoperazine, againstMycobacterium avium in vitro and within human monocyte-derived macrophages. Indian J Clin Biochem 10, 77–84 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02871006
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02871006