Abstract
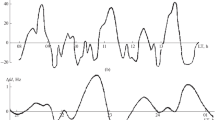
Using the techniques of second derivatives, digital filtering and power spectral analysis, the fine structure of the quasi-biennial oscillation (qbo) in the equatorial geomagnetic field in the Indian zone is studied. The salient results are: (i) in the quiet day field,qbo is weak and the signal strength has no local time dependence; (ii) in the disturbance field the signal is strongest in the afternoon and evening hours and (iii) larger magnitudes are manifested closer to the dip equator. The difference in dawn and dusk amplitudes of the signal and the absence of significant strength close to noon in the electrojet region rules outeuv flux as the responsible agent.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Angell J K and Korshover J 1964J. Atmos. Sci. 21 479
Behannon K W and Ness N F 1966 NASA Tech. Note TH D-3341
Bhargava B N 1972Planet. Space Sci. 20 423
Bhargava B N and Rangarajan G K 1975J. Geomag. Geoelec. 27 257
Eckhardt D, Larner K and Madden T 1963J. Geophys. Res. 68 6279
Gosling J T, Asbridge J R and Bame S J 1977J. Geophys. Res. 82 3311
Pittock A B 1978Rev. Geophys. Space Phys. 16 400
Raja Rao K S and Joseph K T 1971.J. Atmos. Terr. Phys. 33 797
Rangarajan G K and Bhargava B N 1974.Proc. Indian Acad. Sci. A80 249
Rangarajan G K and Bhattacharyya A 1983Proc. Indian Acad. Sci. (Earth Planet. Sci.) 92 5
Shapiro R and Ward F 1962J. Atmos. Sci. 19 506
Stacey F D and Westcott P 1962Nature (London) 198 730
Sugiura M 1976Geophys. Res. Lett. 3 643
Sugiura M and Poros D J 1977.J. Geophys. Res. 82 5621
Yacob A and Bhargava B N 1968J. Atmos. Terr. Phys. 30 1907
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rangarajan, G.K. Quasi-biennial oscillation in geomagnetic disturbance field. Proc. Indian Acad. Sci. (Earth Planet Sci.) 94, 29–34 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02863406
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02863406