Abstract
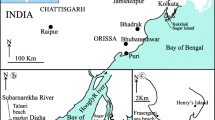
Grain size statistical parameters of the surface sediment samples collected from the innershelf off Gopalpur were calculated using graphic and moment methods. Fine-grained sand present up to 15m water depth shows symmetrical skewness and good sorting. These are leptokurtic. The coarse-grained sand beyond 15 m water depth has positive or negative skewness and moderate sorting. These are platy kurtic. Bivariate plot of mean vs skewness indicates two types of sample spread, keeping approximately 2.3ϕ mean as the demarcating boundary suggesting the presence of dune and beach types of sands. The study of log-probability sub-populations further supports these two types of sand as dune with single dominant saltation and beach with two distinct saltation populations. CM patterns suggest the role of rolling and graded suspension. The irregularity observed in bathymetry coincides with difference in the nature of sands within and beyond 15 m water depth. The behaviour of the grain size parameters and the associated bathymetrie features suggest the presence of relict environments of dune and beach.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bagnold B A 1963 Mechanics of Marine Sedimentation; inThe Sea, ideas and observations on progress in the studies of the sea (eds) M H Hill, B D Goldberg, C O D Iselin and W H Munk (New York: John Wiley & Sons)3 507–528
Bloom A L 1979 Atlas of sea level curves (Cornell University).
Curray J R (1964) Transgression and regression in Marine Geology (ed.) R L Miller (New York: Macmillan Publishing Co. Inc.) pp. 531
Dietz R S 1963 Wave base, Marine profile of equilibrium and wave built terraces: A critical appraisal;Bull. Geol. Soc. Am. 74 971–990
Fisher J J 1968 Transactions National Symposium on Ocean Sciences and Engineering of the Atlantic Shelf (eds) A E Margolis and R C Steere (Washington DC: Marine Technological Society) pp. 143–149
Fisher A G 1961 Stratigraphic record of transgressing seas in light of Sedimentation on Atlantic coast of New Jersey;Bull. Am. Assoc. Petrol. Geol. 45 1656–1666
Folk R L 1974 Petrology of Sedimentary Rocks (Hamphill, Austin, Texas) p. 182
Folk R S and Ward W C 1957 Brazos river bar: a study in the significance of grain size parameters;J. Sediment. Petrol. 27 3–27
Friedman G M 1961 Distinction between dune, beach and river sands from their textural characteristics;J. Sediment. Petrol. 31 151–163
Hayes M O 1964 Gulf Coast Assoc. Geol. Societies Field Trip guide book, Depositional Environments, South Central Texas Coast pp. 121–126
Ingle J C Jr 1966 The movement of beach sand (Amsterdam: Elsevier Publishing Co.) p. 221
Miller R L and Zeigler J M 1964 Marine Geology, Shepard Commemorative Volume (ed.) R L Miller (New York: Macmillan & Co.) p. 133
Moiola R J and Weiser D J 1968 Textural parameters: An evaluation;J. Sediment. Petrol. 38 45–53
Passaga R 1957 Texture as characteristic of elastic deposition;Bull. Am. Assoc. Petrol. Geol. 41 1952–1984
Passega R 1964 Grain size representation by CM patterns as a tool;J. Sediment. Petrol. 34 830–847
Passega R and Byramjee R 1969 Grain size image of elastic deposits;Sedimentology 13 233–251
Rajamanickam G V and Gujar A R 1984 Sediment depositional environment in some bays in the Central West Coast of India;Indian J. Mar. Sci. 13 53–59
Rajamanickam G V and Gujar A R 1985 Indications given by median distribution and CM patterns on elastic sedimentation in Kalbadevi, Mirya and Ratnagiri bays, Maharashtra, India;Cioroale di Geologie 47 237–254
Rajamanickam G V and Gujar A R 1988 Depositional environment of the sediments in Konkan bays: Inferred from multi-group discrimination analysis using grain size distribution statistics;Indian J. Earth Sci. 15 234–247
Schlee J and Webster J 1967 A computer programme for grain size data;Sedimentology 8 45–53
Shrivastava R L and Rao B R 1976 A note on the relict sand (?) and movement of sediments of Gopalpur, Orissa Coast, India;J. Geol. Soc. India 17 401–404
Swift D J P, Sanford R B, Dill C E Jr and Avingnon N E 1971 Textural differentiation on the shore face during erosional retreat of an unconsolidated coast, Cape Henry to Cape Hatteras, Western North Atlantic Shelf;Sedimentology 16 221–245
Subba Rao M 1964 Some aspects of continental shelf sediments off the east coast of India;Mar. Geol. 1 59–87
Visher G S 1969 Grain size distribution and depositional processes;J. Sediment. Petrol. 39 1074–1106
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rao, K.M., Rajamanickam, G.V. & Rao, T.C.S. Holocene marine transgression as interpreted from bathymetry and sand grain size parameters off Gopalpur. Proc. Indian Acad. Sci. (Earth Planet Sci.) 98, 173–181 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02863242
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02863242