Abstract
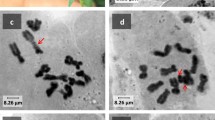
Chromosome aberrations were observed in the tapetum and pollen-mother-cells, generally in form of chromosome bridges, fragments and elimination of univalent chromosomes and fragments. Chromatid bridge formation varied from 13.1 to 10.25% in the first and second anaphases respectively.
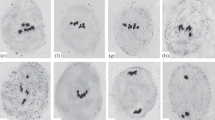
Endoreduplication with a high degree of ploidy was observed in tapetal cells. Chromosomal reduplication was so marked that the normal diploid chromosome number 24 reached 96.
The association of chromosomes in three, four, five and six occurred in 49.4% of the cases observed. The occurrence of high frequency of polyvalents in a diploid seemed to indicate the presence of translocation interchanges inS. venturii.
The frequency of univalents varied from 1.3 to 18.7%. Structural changes and gene mutation are probably responsible for failure of pairing among pairable chromosomes. The behaviour of univalents varied, they either pass to poles or lag and divide. The division and elimination of univalents causes unequal distribution of chromosomes on second metaphase plates. Univalents and fragments which failed to be included in the daughter nuclei formed micronuclei. The chromosome irregularities and abortion of pollen grains (45.4%) are presumably due to gene mutation which may have been enhanced in aged seeds.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature Cited
Avanzi, M. G. 1950. Endomitosis and mitosis with diplochromosomes in the development of tapetal cells ofS. tuberosum. Caryologia 2: 205–222.
Beadle, C. W. 1932. A gene for sticky chromosome inZea mays. Z. ind. Abst. Vererb. 63: 195–217.
Cartledge, J. L. and Blakeslee, A. F. 1934. Mutation rate increased by aging seeds as shown by pollen abortion. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. 20: 103–110.
Choudhuri, H. C. 1943. Cytological studies in the genusSolanum I. Wild and native cultivated ‘diploid’ potatoes. Trans. Roy. Soc. Edin. Lxi. 113–135.
Darlington, C. D. 1929. Chromosome behaviour and structural hybridity inTradescantiae. J. Genet. 21: 207–286.
Gairdner, A. E. and Darlington, C. D. 1931. Ring-formation in diploid and polyploidCampanula persicifolia. Genetica 12: 113–150.
Giles, N. 1940. Spontaneous chromosome aberrations inTradescantia. Genetica 25: 69–87.
Kato, Y. 1960. Mitotic abnormalities in root meristems and ovular tissue ofClivia miniata Regel. and other seasonal variation of their occurrences. Cytologia. 25: 313–321.
Lamm, R. 1945. Cytogenetic studies inSolanum Sect.Tuberarium. Hereditas 31: 1–218.
Magoon, M. L., Cooper, D. C. and Hougas, H. W. 1958. Cytogenetic studies in some diploidSolanum Sect.Tuberarium. Amer. J. Bot. 45: 207–222.
Navashin, M. 1933. Origin of spontaneous mutations. Nature 131: 436–438.
Smith, S. C. 1935. Chromosome fragmentation produced by crossing over inTrillium erectum L. J. Genet. 30: 227–232.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Choudhuri, H.C. Spontaneous chromosome aberrations in diploid solanum. American Potato Journal 48, 187–194 (1971). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02862993
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02862993