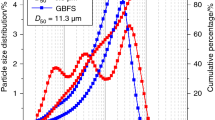
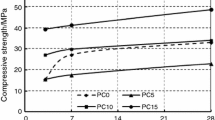
Abstract
The effect of the ground granulated blast-furnace slag (GGBFS) addition, the modulus n (mole ratio of SiO2 to Na2 O) and the concentration of sodium silicate solution on the compressive strength of the material, i e alkali-activated carbonatite cementitious material (AACCM for short) was investigated. In addition, it is found that barium chloride has a satisfactory retarding effect on the setting of AACCM in which more than 20% (by mass) ground carbonatite was replaced by GGBFS. As a result, a cementitious material, in which ground carbonatite rock served as dominative starting material, with 3-day and 28-day compressive strength greater than 30 MPa and 60 MPa and with continuous strength gain beyond 90 days was obtained.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Delia M Roy. Alkali-Activated Cements-Opportunities and Challenges.Cement and Concrete Research, 1999, 29(2): 249–254
Yin Suhong, Wen Ziyun, Wang Yuanguang. The Study on Alkali-activated-carbonatites Cementitious-grouting Material. in: Peimin Wang (Ed.),Proceedings of the 5thInternational Symposium on the Cement and Concrete, 2002: 917–924
Yin Suhong, Wen Ziyun, Yu Qijun. Study on Reaction Products of Alkali-activated Carbonatites Cementitious Material.Journal of the Chinese Ceramic Society, 2004, 32(3): 311–316
Zhao Sanyin, Yu Qijun, Qiao Fei,et al. Influence of Inorganic Mineral Powder on the Property of Alkali Activated-carbonatite Cementitious Material.Journal of Wuhan University of Technology, 2004, 26(7): 20–23
A R Brough, M Holloway, J Sykes, A Atkinson. Sodium Silicate-based Alkali-activated Slag Mortars Part II -The Retarding Effect of Additions of Sodium Chloride or Malic Acid.Cement and Concrete Research, 2000, 30(9): 1375–1379
J Deja. Immobilization of Cr6+, Cd2+, Zn2+ and Pb2+ in Alkali-activated Slag Binders.Cement and Concrete Research, 2002, 32(12): 1971–1979
Chong Yoon Rha, Seong Keun Kang, Chang Eun Kim. Investigation of the Stability of Hardened Slag Paste for the Stabilization/Solidification of Wastes Containing Heavy Metal Ions.Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2000, B73(3): 255–267
A R Brough, A Atkinson. Sodium Silicate-based Alkali-activated Slag Mortars Part I -Strength, Hydration and Microstructure.Cement and Concrete Research, 2002, 32(6): 865–879
E Douglas, J Brandstetr. A Preliminary Study of the Alkali Activation of Ground Granulated Blast Furnace Slag.Cement and Concrete Research, 1990, 20(5): 746–756
E Douglas, A Bilodeau, J Brandstetr, V M Malhotra. Alkali Activated Ground Granulated Blastfurnace Slag Concrete: Preliminary Investigation.Cement and Concrete Research, 1991, 21(1): 101–108
S D Wang, K L Scrivener. Hydration Products of Alkali Activated Slag Cement.Cement and Concrete Research, 1995, 25 (3): 561–571
S D Wang, K L Scrivener, P L Pratt. Factors Affecting the Strength of Alkali Activated Slag.Cement and Concrete Research, 1994, 24(6): 1033–1043
S D Wang. Review of Recent Research on Alkali Activated Concrete in China.Mag. Concr. Res., 1991, 43: 29–35
S D Wang, X C Pu, K L Scrivener, P L Pratt. Alkali Activated Slag Cement and Concrete: A Review of Properties and Problems.Adv. Cem. Res., 1995, 7: 93–102
V S Ramachandran.Concrete Admixtures Handbook-Properties, Science, and Technology(second edition). Park Ridge, Noyes Publications: 1995
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the National “863” Research Project of China (No. 2002AA335050),the National Natural Science Foundation of China(No. 50409011) and the High-level University Construction Project of South China University of Technology (No. B09-224)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sanyin, Z., Qijun, Y., Fei, Q. et al. Setting and strength characteristics of alkali-activated carbonatite cementitious materials with ground slag replacement. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol.-Mat. Sci. Edit. 21, 125–128 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02861489
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02861489