Abstract
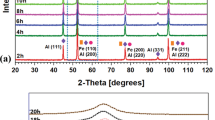
The nanostructures of the ball milled FeCo particles were characterized as functions of the ball milling time (t) using quantitative X-ray diffraction (XRD), high resolution transmission electron microscopy (HRTEM) analysis techniques. The results show that the nanocrystalline bcc FeCo particles are available using carbonyl iron and cobalt powders as the start materials during the high-energy ball milling. At the early stage of ball milling, Co powders are easily mashed into nanocrystalllites, by which the surface of the larger Fe particles of about 80–150 nm is coated. With t increasing, the refinement of grain size and the incorporation of defects including dislocations, disclinations and grain boundaries happen, and then FeCo alloy with a certain layered structure is formed, finally the layered structure disappears with the formation of isotropic grains having a steadystate grain size in the nanometer regime after a certain period of t.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M W Chen, E Ma, K J Hemker,et al. Deformation Twin-ning in Nanocrystalline Aluminum.Science, 2003, 300: 1275
H Gleiter. Progress in Nanostructured Materials.Prog. Mater. Sci., 1989, 33: 233
J P Wilcoxon, P P Provencio. Use of Surfactant Micelles to Control the Sturctural Phase of Nanosize Iron Clusters.J. Phys. Chem. B, 1999, 103: 9 809
E E Carpenter, J A Sims, J A Wienmann,et al. Magnetic Properties of Iron and Iron Platinum Alloys Synthesized via Microemulsion Techniques.J. Appl. Phys., 2000, 87: 5615
A Martino, M Stoker, M Hicks,et al. The Synthesis and Characterization of Iron Colloid Catalysts in Inverse Micelle Solutions.Appl. Catalysis A: General, 1997, 161: 235
X M Lin, C M Sorensen, K J Klabunde,et al. Control of Cobalt Nanoparticle Size by the Germ Growth Methos in Inve-rse Micelle System: Size Dependent Magnetic Properties.J. Mater. Res., 1999, 14: 1542
D C Douglass, A J Cox, J P Bucher,et al. Magnetic Proper-ties of Free Cobalt and Gadolinium Clusters.Phys. Rev., 1993, B47: 12874
C C Koch. The Synthesis and Structure of Nanocrystalline Ma-terials Produced by Mechanical Attrition: A Review.Nano-struct. Mater., 1993, 2: 109
C C Koch. Synthesis of Nanostructured Materials by Mechani-cal Milling: Problems and Opportunities.Nanostruct. Mater., 1997, 9: 13
H J Fecht. Nanostructure Formation by Mechanical Attrition.Nanostruct. Mater., 1995, 6: 33
M Murayama, J M Howe, H Hidaka,et al. Atomic-Level Ob-servation of Disclination Dipoles in Mechanically Milled Nano-crystalline Fe.Science, 2002, 259: 2 433
M Murayama, J M Howe, H Hidaka,et al. High-resolution TEM Analysis of Defect Structures in Mechanically Milled Nanocrystalline Fe.IS1J International, 2003, 43: 755
Joint Committee on Powder Diffraction Standards.Powder Diffraction File. Swarthmore, PA, 1990, No. 60696
H P Klug, L E Alexander.X-ray Diffraction Procedures for Polycrystalline and Amorphous Materials, 2nd ed. John Wiley and Sons, New York, 1974, Chapter 9
V G Harris, M Liou, B N Das,et al. Pappas. Structure and Magnetism of Multi-Phase Sm0.080 Co0.645 Fe0.276 Powders.J. Appl. Phys., 1997, 81: 5 121
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Funded by the 863 High Technology Research Project (No. 2001AA339020 and 2002AA305302) from the Ministry of Science and Technology of China, and by the Excellent Young Teachers Program of MOE(2002[350])
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qi, W., Wei, W., Jianguo, G. et al. XRD and HRTEM analyses of the ball milled nanocrystalline FeCo alloy. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol.-Mat. Sci. Edit. 21, 68–71 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02861474
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02861474