Summary
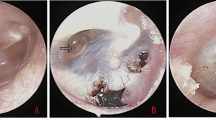
To investigate the etiology and pathogenesis of cholesteatoma otitis media accompanied by cholesterol granuloma and the relationship between cholesteatoma and cholesterol granuloma, 63 cases of middle ear cholesterol granuloma treated in our hospital during the period from March 1988 to May 2000 were retrospectively reviewed. All cases were surgically and pathologically verified. 15 cases of cholesteatoma coexisting with cholesterol granuloma were found among the 63 patients. All 15 cases had a long-term history of otitis media, such as otorrhea (sanguine purulent otorrhea and bloody otorrhea in 8 cases) and perforation of the eardrum (perforation of pars flaccida in 8 cases). Temporal bone CT scans showed cholesteatoma in 11 cases. All patients were treated surgically, and cholesteatoma and cholesterol granuloma were found coexisting alternately, the latter lying mainly in the tympanic antrum, attic and mastoid air cells. Chocolate-colored mucus was accumulated in well-developed mastoid air cells, and glistening dotty cholesterol crystals were also found. In most cases, enlarged aditus, destruction of lateral attic wall, erosion of ossicular chain, exposure of horizontal segment of facial nerve and tegmen of attic were observed. Occlusion of Eustachian tube was noted in 6 cases, and occulusion of tympanic isthmus was revealed in all cases. A post-operative dry ear was achieved in all patients, and hearing improvement was achieved in all 12 cases following tympanoplasty. Cholesteatoma and cholesterol granuloma in middle ear may share a common pathophysiological etiology: occlusion of ventilation and disturbance of drainage. The diagnosis should be considered when patients presented with chronic otitis media with bloody otorrhea. CT and magnetic resonance imaging are useful for the diagnosis before operation. The surgical approach depends on the location, extension and severity of the lesion, The purpose of surgery is to remove the lesion and create an adequate drainage.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gherini S, Brackmann D, William W Met al. Cholesterol granuloma of the petrous apex. Laryngoscope, 1985, 95: 659
Farrior B, Kampsen E, Tampa F Let al. The positive pressure of cholesterol granuloma idiopathic blue eardrum differential diagnosis. Laryngoscope, 1981, 91: 1286
Hiraide F, Nouye T, Miyakogawa N. Experimental cholesterol granuloma histopathological and histochemical study. J Laryngol Otol, 1982, 96: 491
Ferlito A, Devaney K O, Rinaldo Aet al. Clinicopathological consulation ear cholesteatoma versus cholesterol granuloma. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol, 1997, 106: 79
Brodkey J A, Robertson J H, Shea III J Jet al. Cholesterol granuloma of the petrous apex: combined neurosurgical and otological management. J Neurosurg, 1996, 85: 625
Friedmann I, Graham M G. The ultrastructure of cholesterol granuloma of the middle ear. J Laryngol Otol, 1979, 93: 433
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
LUO Linghui, female, born in 1977, Postgraduate
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Linghui, L., Shusheng, G., Guangping, B. et al. A retrospective study on cholesteatoma otitis media coexisting with cholesterol granuloma. Current Medical Science 22, 168–170 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02857685
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02857685