Summary
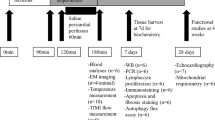
Whether conventional hypothermic CPB induces myocyte apoptosis in dog hearts and modulation of bcl-2, bcl-xl, bax, bad, and caspase-3 pathways in this setting was investigated. Ten healthy adult dogs were randomized into sham-operated and CPB groups. Samples of left ventricle were obtained before, during and 3 h after CPB. In situ TUNEL was used to detect apoptotic myocytes. Immunohistochemistry and flow cytometry were employed for detection of expressions of bcl-2, bcl-xl, bax and bad proteins. Z-DEVD-AMC substrate cleavage and TBARS methods were used to measure the activity of caspase-3 and the content of lipid peroxide in LV myocardium, respectively. After CPB, the number of apoptotic myocytes in CPB group was significantly increased. The results of immunohistichemistry demonstrated that bcl-2, bcl-xl, bax and bad proteins were constitutionally present on the sarcolemma of the LV myocytes. FACS results showed that, after CPB, expressions of bax and bad in CPB group were significantly upregulated, while the expressions of bcl-2 and bcl-xl were not significantly changed in both groups. The activity of caspase-3 and the content of lipid peroxide in LV myocardium in CPB group were also significantly increased after CPB. The present study shows that there exists myocardiocyte apoptosis in dog hearts undergoing conventional hypothermic CPB and the myocyte apoptosis is initiated by ischemia and performed during reperfusion. Moreover, the CPB-induced myocyte apoptosis was associated with upregulation of expressions of bax and bad proteins, activation of caspase-3 and increase of oxidative stress.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cheng W, Li B, Kajstura Jet al. Stretch-induced programmed myocyte cell death. J Clin Invest, 1995, 96: 2247
Struber M, Cremer J T, Gohrbandt Bet al. human cytokine responses to coronary artery bypass grafting with and without cardiopulmonary bypass. Ann Thorac Surg, 1999, 8: 1330
Gu Y J, de Vries A J, Boonstra P Wet al. Leukocyte depletion results in improved lung function and reduced inflammatory responses after cardiac sargery. Thorac Cardiovasc Surg, 1996, 112: 494
Slater A F G, Stefan C, Nobel Iet al. Signaling mechanism and oxidative stress in apoptosis. Toxiol Lett, 1995, 82–83: 149
Giardino I, Fard A K, Hatchell D Iet al. Aminoguanidine inhibits reactive oxygen species formation, lipid peroxidation, and oxidant-induced apoptosis. Diabetes, 1998, 47: 1114
Cook S A, Sugden P H, Clerk A. Regulation of bcl-2 family proteins during development and in response to oxidative stress in cardiac myocytes. Circ Res, 1999, 83: 940
Nakamura M, Wang N P, Zhao Z Qet al. Preconditioning decreases bax expresion, PMN accumulation and apoptosis in reperfused rat heart. Cardiovasc Res, 2000, 45: 661
Zhao Z Q, Nakaruma M, Wang N Pet al. Reperfusion induces myocardial apoptotic cell death. Cardiovasc Res, 2000, 45: 651
Chao D T, Korsmer S J. Bcl-2 family: regulator of cell death. Annu Rev Immunol, 1998, 16: 395
Gross A, Jokel J, Wei M Cet al. Enforced dimerization of Bax results in its translocation, mitochondrial dysfunction and apoptosis. EMBO J, 1998, 17: 3878
Yang E, Zhao J, Jockel Jet al. Bad, a heterodimer parterner for Bcl-xl and bcl-2, displaces Bax and promote cell death. Cell, 1995, 80: 285
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
SUN Zhongquan, male, born in 1944, Professor
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zongquan, S., Shunye, Z., Lixin, L. et al. Regulatory effect of Bcl-2 family proteins in CPB-induced cardiomyocyte apoptosis in dog hearts. Current Medical Science 22, 103–106 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02857665
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02857665