Abstract
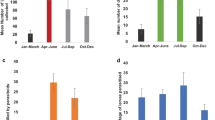
In the Shennongjia National Nature Reserve of Central China, the vegetative growth behavior of henon bamboo (Phyllostachys nigra var.henonis (Mitford) Stapf. ex Rendle) was studied from shoot recruitment to culm establishment. In May, bamboo shoots emerging from the ground achieved an average density of 2.7 shoots m−2 during the sprouting phase of 16 days. However, about 32% of the new shoots died back before maturity. Insect damage, withering death and rodent predation were responsible for 57%, 29% and 14% of the total shoot mortality, respectively. From May to June, the shoots attained 400±23 cm during the height growth phase of 34 days, with a daily rate varying from 1 to 56 cm. All branches and leaves unfolded during the branch spreading phase from June to August. Shoot production was positively related to the density of standing culms, but negatively to both coverage and height of herb layers.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ban Jide., Qi Gensheng, Li Bo, Liu Lide, Li Zhaohua. 1995. Studies on the vegetation in West Hubei [M]. Wuhan: Press of Central China University of Science and Technology (in Chinese).
Barnes, J. A., Gounder, R. K., Johnston T. J. 1999. Bamboo development for the Asian stir fry export markets [C]. Kingston RIRDC Publication (No. 99/136).
Cao, C. S. 1989. A guide to bamboo grown in Britain. Kew: Royal Botanical Gardens. 1–48.
Diver, S. 2001. Bamboo: A multipurpose agroforestry crop [C]. Fayetteville: Appropriate Technology Transfer for Rural Areas (ATTRA).
Dransfield, S., Widiaja, E. A. 1995. Plant resources of South-East Asia (No. 7) —Bamboos [M]. Leiden: Backhuys Publishers.
Fu Maoyi. 1989. Nutrient cycling in bamboo stands (I): Leaf litter and its decomposition in purePhyllostachys pubescens stands [J]. Forest Research.2: 207–213. (in Chinese)
Fu M. Y. 1994. Management of monopodial bamboo stands: Past and present research and future research directions [C]. In: Stinson P. (ed.). Constraints to production of bamboo and rattan—with special reference to planting materials and management of natural stands. New Delhi: INBAR (International Network of Bamboo and Rattan). 166–174.
Fu, M. Y., Banik, R. L. 1995. Bamboo production systems and their management [C]. In: Rao I V R, Sastry C B. (eds.). People and environment: Proceedings of the Vth international bamboo workshop and the IVth international bamboo congress, Ubud, Bali, Indonisia, 19–22 June 1995 (Vol. 1). Beijing: INBAR. 18–30.
Gao, R. L., Lin, Z. P., Wang, J. L. 2000. Growth dynamics of bamboo shoot and young bamboo ofDendrocalamopsis oldhami [J]. Subtropical Plant Research Communication,29: 27–30.
Geng Beijie, Wang Zengping. 1996. Flora republicae popularis Sinicae, Tomus 9(1). Beijing: Science China Press. (in Chinese)
Gielis, J., Everaert, I., Goetghebeur, P., De Loose, M. 1997. Bamboo and molecular markers [C]. In: Rao I V R, Sastry C B (eds) Bamboo, people and the environment (Vol. 2)—biodiversity and genetic conservation. Beijing: INBAR. 45–67.
Gielis, J., Oprins, J. 1998. The strategic role of biotechnology in mass scale production woody bamboos[C]. In: El Bassam N., Behl R K, Prochnow B. (eds.). Sustainable agriculture for food, energy and industry. London: Science Publishers Ltd., 167–171.
Gielis, J. 1999. Micropropagation andin vitro flowering of temperate and tropical bamboos [C]. In: Raychaudhuri S P, Maramorosch K. (eds.). Biotechnology and plant protection in forestry sciences, Enfield: Science Publishers. 13–18.
He Mei. 1993. Reasonable age structure and growth regulation of Moso bamboo (Phyllostachys pubescens) grove [J]. Journal of Bamboo Research,12(3): 52–55. (in Chinese)
Huang Keqing, Ma Bingyang, 1994. Study on the growth regulation of young shoots fromPhyllostachys makinoi [J]. Journal of Fujian College of Forestry,14: 291–294. (in Chinese)
Isagi, I., Kawahara, T., Kamo, K., Ito, H. 1997. Net production and carbon cycling in a bambooPhyllostachys pubescens stand [J]. Plant Ecology,130: 41–52.
Jin Aaiwu, Shao Xiaogen, Qiu Shuihua, Zhang Fagen. 1999. Biological characteristics ofPhyllostachys heteroclada [J]. Journal of Zhejiang Forestry College,16: 238–241 (in Chinese)
Lee, A.W.C., Addis, S.C. 2001. Growth characteristics of Moso bamboo in South Carolina. Forest Product Journal [J].52: 88–89.
Lei, J.F. 2001. A development strategy for bamboo resource and industry in China [C]. In: Zhu Z-H (ed.). Sustainable development of the bamboo and rattan sectors in tropical China. Beijing: China Forestry Publishing House. 1–18.
Lewis, D.B. 1998. Thin your grove to increase productivity [J]. Pacific Northwest Sustainable Agriculture10 (4): 6–8.
Li, Z., 2003. Diversity and ecology of mountain bamboos in the Shennongjia National Nature Reserve of Central China: Implications for resource management and biodiversity conservation [M]. Göttingen: Cuvillier Verlag.
Liese, W. 1985. Bamboos-biology, silvics properties, utilization [M]. Eschborn: GTZ. 20–132.
Liese, W. 1991. Progress in bamboo research [J]. Journal of the American Bamboo Society,8: 151–167.
Liese, W. 2001. Advances in bamboo research [J] Journal of Nanjing Forestry University,25(4): 1–6.
Linvill, D., Linton, F., Hotchkiss, M. 2001. Growing bamboo in Georgia [C]. Athens: Cooperative Extension Service (The University of Georgia).
Lu, F. 2001. China's bamboo product trade: performance and prospects [M]. Beijing: INBAR.
McClure, F.A. 1993: The Bamboos [M]. Washington: Smithsonian Institution Press. 1–368.
Midmore, D.J. 1997. Bamboo [C]. In: Hyde K. (ed.). RIRDC compendium of new and emerging industries. Canberra: R IRDC. 188–195.
Miles, C.A., Chen, C.H., Flores, T. 2000. On-farm bamboo production in the Pacific Northwest [C]. Pullman: Cooperative Extension Agricultural System (Washington State University).
Qin Zisheng, Taylor, A., Huang, J.Y. 1993. Research intoFargesia robusta biological characteristics [J]. Journal of Bamboo Research,12(1), 16–17, (in Chinese)
Qiu, G.X., Shen, K.S., Li, D.Y., Wang, Z.W., Huang, Q.M., Yang, D.D., Gao, A.X. 1992. Bamboo in subtropical eastern China [C]. In: Long S P. (ed.). Primary production of grass ecosystems of the tropics and subtropics. London: Chapman and Hall. 159–188.
Quintans, K.N. 1998. Ancient grass, future national resource [M]. Beijing: INBAR.
Shoch, D., Stoney, C. 2001 Preliminary analysis of the potential economic and conservation outcomes of bamboo production in the Southeastern United States [C]. Arlington: Winrock International.
Shor, G. 2002. Bamboo species list (No. 22) [C]. Albany: American Bamboo Society.
Tewari, D.N. 1993. A monograph on bamboo [M]. Dehra Dun: International Book Distributors.
Wang, J.X., Ma, Z.G., Liu, C.X., Gan, L.M. 1991. Preliminary study on the growth and development rules ofFargesia denudata bamboo [J]. Journal of Bamboo Research,10(3): 38–48.
Watanabe, M. 1994. On the management of bamboo stands, with special reference of Japanese research [C]. In: Stinson P. (ed.) Constraints to production of bamboo and rattan-with special reference to planting materials and management of natural stands, New Delhi: INBAR, 175–191.
Yi Tongpei. 1997. Compendium of bamboos in Sichuan [M]. Beijing: China Forestry Publishing House. (in Chinese)
Zhang Xi, Zhang Xinming, Wang Jianping, An Qqianning, Hu Xxiaoqong. 1995. Study on shooting and setting regularity ofPhyllostachys nidilaria [J]. Journal of Bamboo Research,14(4): 54–64. (in Chinese)
Zhang Zengxiang, He Xicheng, Hu Caozong, Zheng Fangdong Wang Peng. Jin Haiyang. 1997. Study on biological properties ofPhyllostachys nigra [J]. Journal of Bamboo Research,16(1): 6–12. (in Chinese)
Zheng, Yushang, Hong Wei, Zhang Weigen. 1998a. Study on age structure of high-yield both bamboo shoot and timber stand [J]. Scientia Silvae Sinicae,34(sppl.): 46–51. (in Chinese)
Zheng Yushang, Hong Wei, Qiu Erfa. 1998b: Study on the regulation of shoot emergence and degradation ofPhyllostachys heterocycla cvpubescens shoot [J]. Scientia Silvae Sinicae,34((sppl.): 73–77. (in Chinese)
Zhong, M.G., Xie, C. Zheng, W., Fu, M.Y., Xie, J.H. 1998. Bamboo in Anji: A case study of an intensive production-to-consumption systems [M]. Beijing: INBAR.
Zhou Benzhi. 1999. Rule of shooting and height-growth ofDendrocalamus latiflorus [J]. Forest Research,12: 461–466. (in Chinese)
Zhu Shiling, Ma Naixun, Fu Maoyi. 1994. Compendium of Chinese bamboo species [M]. Beijing: China Forestry Publishing House. (in Chinese)
Zhu Zhaoquan, Song Zhongshu. 1999. Scientific survey of the Shennongjia Nature Reserve [M]. Beijing: China Forestry Publishing House. (in Chinese)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item: This research was financed by the Center for Development Research (ZEF) of the University of Bonn, Germany (P. 52015), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 30470284) and the Scientific Research Foundation for the Returned Overseas Chinese Scholars (No. 2004-527).
Biography: Li Zhao-hua (1964-), male, Doctoral of Natural Science (Bonn University), Professor of Ecology (Hubei University, Wuhan 430062, P. R. China).
Responsible editor: Chai Ruihai
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao-hua, L., Denich, M. & Borsch, T. Growth behavior ofPhyllostachys nigra var.henonis (Bambusoideae) in Central China. Journal of Forestry Research 16, 163–168 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02856808
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02856808