Abstract
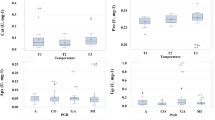
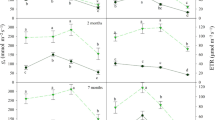
Eco-physiological responses of seedlings of eight species,Pinus koraiensis, Picea koraiensis, Larix olgensis, Populus ussuriensis, Betula platyphylla, Tilia amurensis, Traxinus mandshurica andAcer mono from broadleaved/Korean pine forest, to elevated CO2 were studied by using open-top chambers under natural sunlight in Changbai Mountain, China in two growing seasons (1998–1999). Two concentrations of CO2 were designed: elevated CO2 (700 μmol·mol−1) and ambient CO2 (400 μmol·mol−1). The study results showed that the height growth of the tree seedlings grown at elevated CO2 increased by about 10%–40% compared to those grown at ambient CO2. And the water using efficiency of seedlings also followed the same tendency. However, the responses of seedlings in transpiration and chlorophyll content to elevated CO2 varied with tree species. The broad-leaf tree species were more sensitive to the elevated CO2 than conifer tree species. All seedlings showed a photosynthetic acclimation to long-term elevated CO2.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bai Kezi, Zhong Zhipu. 1996. Response of physiology to atmospheric CO2 enrichment [J]. Chinese Science Bulletin,41(2): 164–166 (in Chinese).
Ceulemans, R. & Mousseau, M. 1994. Effects of elevated atmospheric CO2 on woody plant [J]. New phytol,127: 425–446.
Delucia, E.H., Callaway, R.M., Thomas, E.M., Schlesinger, W.H. 1997. Mechanisms of phosphorus acquisition of ponderosa pine seedling under high CO2 and temperature [J]. Ann Bot79: 111–120.
Delucia, E.H., Sasek, T.W., Strain, B.R. 1985. Photosynthetic inhibition after long-term exposure to elevated levels of atmospheric carbon dioxide [J]. Photosynth Res,7: 175–184.
Garbutt, K., Williams, W.E., Bazzaz, F.A. 1990. Analysis of annuals to elevated CO2 during growth [J]. Ecology,71(3): 1185–11943.
Genthon, C., Barnola, J.M., Raynaud, D.,et al. 1987. Vostok ice core: climatic response to CO2 and orbital forcing changes over the last climatic cycle [J]. Nature,329: 414–418.
Gunderson, C.A., Wullschleger, S.D. 1994. Photosynthetic acclimation in trees rising atmospheric CO2: A broader perspective [J]. Photosynthesis Res,39: 369–388.
Han Shijie, Zhou Yuemei, Wang Chenrui, Zhang Junhui, Zou Chunjing. 2000. Ecophysiological responses and carbon distribution ofPinus koralesis seedlings to elevated carbon dioxide [J]. Journal of Forestry Research11(3): 149–155.
Houghton, J.T., Meira, Filho, L.G., Callander, B.A. (eds.) 1996. Climate Change 1995: The Science of Climate Change [M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Jiang Gaoming, Han xingguo, Lin guanghui 1997. Responses of plant growth to elevated CO2: A review on the chief methods and basic conclusions based on experiments in the external countries in past decade [J]. Acta Phytoecologica Sinica,21(6): 489–502. (in Chinese)
Jiang Gaoming, Lin Guanghui, Bruno D., Marino, V. 1999. The response on dark respirations of some tropical rain forest and coastal desert plant species to the elevation of CO2 concentration [J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica,19(4): 519–522. (in Chinese).
Lecain, D.L., Morgan, J.A. 1998. Growth, gas exchange, leaf nitrogen and carbohydrate concentrations in NAD-ME and NADP-ME C4 grasses grown in elevated CO2 [J]. Physiol Plant102: 297–306.
Liang Chun, Lin Zhifang, Kong Guohui. 1997. Photosynthesis—light responses characteristics of subtropical tree species seedlings under different irradiants [J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology,8(1): 7–11. (in Chinese)
Lin Fengping, Chen Zhanghe, Chen Zhaoping, Zhang Deming. 1999. Photosiological and biochemical responses of the seedlings of four Legume tree species to high CO2 concentration [J]. Acta Phytoecologica Sinica,23(3): 220–227 (in Chinese)
Lin weihong. 1998. Response of photosynthesis to elevated atmospheric CO2 [J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica,18(5): 529–538. (in Chinese)
Peng Changlin, Lin Zhifang, Sun Zijian, Lin Guizhu, Chen Yizhu-Z. 1998. Response of rice photosynthesis to CO2 enrichment [J]. Acta Phytophysiologica Sinica,24(30): 272–278. (in Chinese)
Sanders, G.E., Clark, A.G., Collsm, J.J. 1991. The influence of open-top chambers on the development of field bean [J]. New Phytol., (1): 439–447.
Van ooslen, J.J. 1992. Long-term effects of a CO2 enriched atmosphere on enzymes of the primary carbon metabolism of spruce trees. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry,30: 389–399.
Wei Caimiao, Kong Guohui, Lin Zhifang. 1997. Effect of elevated CO2 concentration on leaf water regime of subtropical tree seedlings [J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology,8(1): 12–16. (in Chinese).
Xu Daquan. 1994. Response of photosynthesis and related processes to long-term high CO2 concentration [J]. Plant Physiology Communication,30(2): 81–87. (in Chinese)
Xu Guangshan, Ding Guifanget al. 1980 A primary study on soil humus and its characteristics in the main forest types on northern slope of Changbai Mountain [C] (1). in: Research of Forest Ecosystem Vol. 1 (eds: Changbai Mountain Research Station of Forest Ecosystem). p215-200. (in Chinese)
Xue Yinglong. 1985. The experimental handbook of plant physiology [M]. Shanghai. Science and Technology Publishers (in Chinese)
Yelle, S., Beeson, R.C., Trudel, M.J. 1989. Acclimation of two tomato species to high atmospheric CO2 [J]. Physiol Plant.90: 1465–1472.
Ziska, L.H., Bunce, J.A. 1997. The role of temperature in determining the stimulation of CO2 assimilation at elevated carbon dioxide concentration in soybean seedlings [J]. Physiol Plant.100: 126–132.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Foundation item: The project was supported by National Key Basic Development of China (G1999043400) and the grant KZCX 406-4, KZCX1 SW-01 of the Chinese Academy of Sciences
Biography: WANG Miao (1964-), maie, associate professor in Institute of applied Ecology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shenyang 110016, P. R. China.
Responsible editor: Song Funan
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Miao, W., Qiu-rong, L., Li-min, D. et al. Response of seedlings of different tree species to elevated CO2 in Changbai Mountain. Journal of Forestry Research 14, 112–116 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02856775
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02856775