Summary
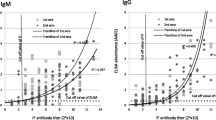
Purified phase I rickettsial suspension was obtained from the spleen of mouse infected with Henzerling strain Q fever by differential centrifugation, trypsin digestion and ether treatment. ELISA coating antigen of Q fever was then prepared by further disruption with ultrasonic wave and high speed centrifugation. The antibody of the infected guinea pig was detected by indirect method of ELISA by antigen coated microtitreplates with protein concentration of 7.89 μg/ml. The positive rate accounted for 40% 4–5 days, 68.7% 6–7 days and 100% 8 days after infection. By agglutination test, however, the same sera were all negative within 7 days after infection, 20% 8–9 days and all positive 18 days after inoculation. ELISA reached the peak titre (1:64–1:1024) on the 24th day after infection whereas agglutination test in the same period only gave a titre of 1:8–1:32, and reached its peak titre (1:128–1:256) 1 month after infection. Since the Q fever antibody of the guinea pig could be detected 66.7% as positive 1–2 days after fever onset by the ELISA indirect method, the ELISA appears to be a more ideal method for early diagnosis of Q fever than other serological methods.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kathke N. Q-Fieber Infektionen in einer Großstadt. Öff Gesundhwesen 40(5):286, 1978
Morbid Mortal Wkly Rep: In Abstr on Hyg, 52(6): 707, 1977
Бацина З В и др: Лихо радка Ку в Мордовской АССР, ЖМЭИ 5:91, 1979
Engvall E, et al: Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. J Immunol 109:129, 1972
Voller A, et al: Enzyme immunoassay in diagnostic medicine: Theory and practice. Bull WHO 53(1): 55, 1976
Herrmann JE, et al: Enzyme immunoassay and radioimmunoprecipitation tests for the detection of antibodies to Rochalimaea (Rickettsia) quintana. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med 154: 285, 1977
Halle S, et al: Sensitive enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for detection of antibodies against typhus rickettsiae. Rickettsia prowazekii and Rickettsia typhi. J Clin Microbiol 6(2): 101, 1977
Dasch G A, et al: Sensitive microplate enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for detection of antibodies against the scrubtyphus rickettsia, Rickettsia tsutsugamushi. Excerpta Medica Section 4, 37(3): 152, 1980
4–5, 1979
140–158, 1979
Hollingdale MR, et al: Enzyme immunoassay of antibody to Rochalimaea quintana. diagnosis of trench fever and serologic crossreactions among other rickettsiae. J Infect Dis 137(5): 578, 1978
Токаревич Н К и др: С очетанное приме-ние с ерологических тесто в с целью диагностики и изучения ку-риккетс ио-за, Qzмэи 12:90, 1979
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pukang, Y., Ruilin, D. & Gongzhi, L. Experimental study of enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) for detection of Q fever antibody. Acta Academiae Medicinae Wuhan 3, 137–142 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02856646
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02856646