Abstract
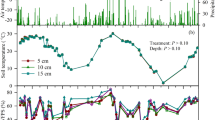
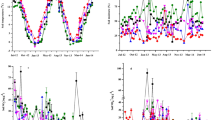
Soil samples were taken from depth of 0–12 cm in the virgin broad-leaved/Korean pine mixed forest in Changbai Mountain in April, 2000. 20 μL·L−1 and 200 μL·L−1 CH4 and N2O concentration were supplied for analysis. Laboratory study on CH4 oxidation and N2O emission in forest soil showed that fresh soil sample could oxidize atmospheric methane and product N2O. Air-dried soil sample could not oxidize atmospheric methane, but could product N2O. However, it could oxidize the supplied methane quickly when its concentration was higher than 20 μL·L−1. The oxidation rate of methane was increased with its initial concentration. An addition of water to dry soil caused large pulse of N2O emissions within 2 hours. There were curvilinear correlations between N2O emission and temperature (r2=0.706, p<0.05), and between N2O emission and water content (r2=0.2968, p <0.05). These suggested temperature and water content were important factors controlling N2O emission. The correlation between CH4 oxidization and temperature was also found while CH4 was supplied 200 μL·L−1 (r2=0.3573, p<0.05). Temperature was an important factor controlling CH4 oxidation. However, when 20 μL·L−1 CH4 was supplied, there was no correlation among CH4 oxidization, N2O emission, temperature and water content.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bender, M., Conrad, R. 1995. Effect of CH4 concentrations and soil conditions on the induction of CH4 oxidation activity [J]. Soil Biol. Biochem,27(12): 1517–1527.
Castro, M.S.,et al. 1995. Factors controlling atmospheric methane consumption by temperature forest soils [J]. Global Biogeochemical Cycles,9(1): 1–10.
Christensen, S., Simkns, S., Tiedje, J.M. 1990. Temporal patterns of soil denitrification: their stability and causes [J]. Soil Science Society of America Journal,54: 1614–1618.
Bouwman, A.A.F. 1990. Soil and the Greenhouse Effect. [M]. John Wiley & Sons LTD.
IPCC report. 1992. Estimated sources and sinks of nitrous oxide [R].
Knowles, R. 1982. Denitrification [J]. Microbiological Reviews,46: 43–70.
Rickard, C.W.H. 1988. Climate of the Handford site [C]. In Shrub-Steppe Balance and Change in a Semi-Arid Terestrial Ecosystem (W.H. Rickard, L/E. Rogers B.E/ Vaughan and S.F. Liebetrau, Eds). New York: Elsevier, 13–21.
Smith, J.L., McNeal, B.L., Cheng, H.H. 1985. Estimation of soil microbial biomass an analysis of the respiratory response of soils [J]. Soil Biology & Biochemistry,17: 11–16.
Yuan Yanxiao, Cong Caizhu. 1997. Methane oxidation in paddy soil [J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology,12(6): 589–594.
Whalen, S.C., Reeburgh, W.S., Sandbeck, K.A., 1990. Rapidly methane oxidation in a landfill cover soil [J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology.56: 3405–3411.
Xu Hui. 1999. Factors controlling N2O and CH4 fluxes in mixed broad-leaved/Korean pine forest of Changbai Mountain [J]. Journal of Forestry Research,10(4): 214–217.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Foundation item: This paper was supported by Chinese Academy of Sciences.
Biography: ZHANG Xiu-jun (1960-), female, Ph. Doctor, lecture in Laboratory of Ecological Process of Trace Substance in Terrestrial Ecosystem, Institute of Applied Ecology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shenyang 110015, P.R. China.
Responsible editor: Song Funan
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xiu-jun, Z., Hui, X. & Guan-xiong, C. Effects of soil moisture and temperature on CH4 oxidation and N2O emission of forest soil. Journal of Forestry Research 11, 203–206 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02855525
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02855525